
Introduction: Understanding Health Technology Assessment
Health Technology Assessment (HTA) is a multidisciplinary process that summarises information about the medical, social, economic, and ethical issues related to the use of a health technology in a systematic, transparent, unbiased, and robust manner. It is an essential part in healthcare policies, affecting reimbursement and access to new medical interventions. A published report by the Office of Health Economics (OHE) dissects the dynamic nature of HTA and its profound impact on patient access to treatments.
The Significance of Geographical Variation
HTA policies vary significantly across regions and countries, influencing the availability of new treatments. The report analysed the methodological differences among 14 HTA agencies worldwide, focusing on discount rates, modifiers, patient involvement, real-world evidence (RWE), and surrogate endpoints. Findings reveal a landscape marked by diversity, reflecting the complex interplay of stakeholder interests, country-specific needs, and international collaborations.
The Role of Discount Rates
HTA often examines health outcomes and costs at various post-treatment phases. Therefore, predicted health outcomes and expenses are influenced by the need for immediate benefits. We use a discount rate to calculate the accrual of costs and benefits across the analytical time horizon. This report shows that most agencies favour a discount rate between 2.5% and 3.5%, with a trend towards lower rates. In fact, this shift signifies a growing emphasis on long-term benefits, which could have substantial implications for how treatments are valued and funded.
Modifiers in Decision-Making
Value of health gains depends on disease and patient variables. Modifiers can change innovative therapy cost-effectiveness standards. HTA agencies employ modifiers to address factors beyond cost-effectiveness, such as disease severity, innovation, and unmet needs. The analysis indicates an increasing trend towards flexibility in considering these modifiers, suggesting a move towards more equitable resource allocation.
Patient Involvement: A Growing Trend
Patient engagement in HTA is on the rise, and most agencies now offering explicit guidance on their involvement. This trend underscores a shift towards incorporating patient perspectives into healthcare decision-making, potentially leading to more patient-centric outcomes. Patient involvement can incorporate viewpoints and evidence not recorded in clinical or economic evaluations into decision-making.
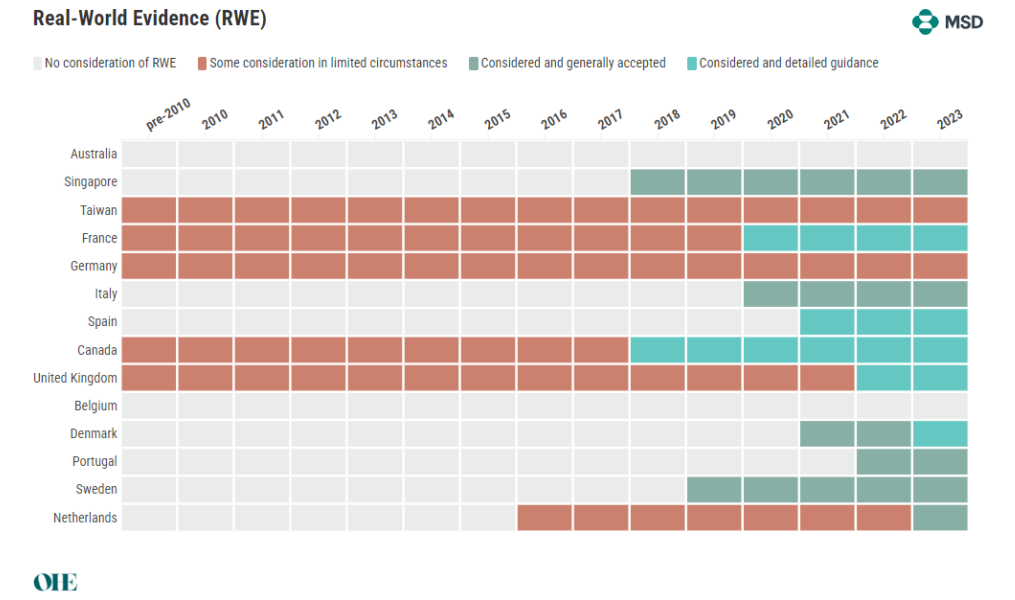
The Acceptance of Real-World Evidence
RWD is the collecting of clinical outcomes data for patients in regular healthcare delivery. Using RWD, long-term health consequences of interventions can be monitored and effectiveness measured in representative groups. The acceptance of RWE varies among HTA agencies, with a general trend towards greater consideration. However, clarity on the types of acceptable evidence remains elusive, indicating a need for more detailed guidelines.
Surrogate Endpoints: From Acceptance to Clarity
HTA agencies use surrogate endpoints (such as biomarkers) to accelerate up patient treatment, but they are somewhat controversial due to questions regarding the link between the endpoint and the clinically meaningful endpoint. Validating surrogate endpoints is vital, but HTA agencies use them differently. Surrogate endpoints are increasingly accepted under certain conditions, reflecting a move towards more pragmatic and adaptable evaluation frameworks. This new way of thinking could expedite patient access to new treatments by offering alternative evidence generation pathways.
Conclusion:
In brief, the growing field of HTA is continually evolving, driven by stakeholder engagement, cross-border collaboration, and methodological innovation. As HTA agencies adapt to these changes, the potential for improved patient outcomes grows. However, the quest for harmonisation and clarity in HTA practices remains a critical challenge that must be addressed to ensure equitable and timely access to healthcare innovations.
