
Introduction
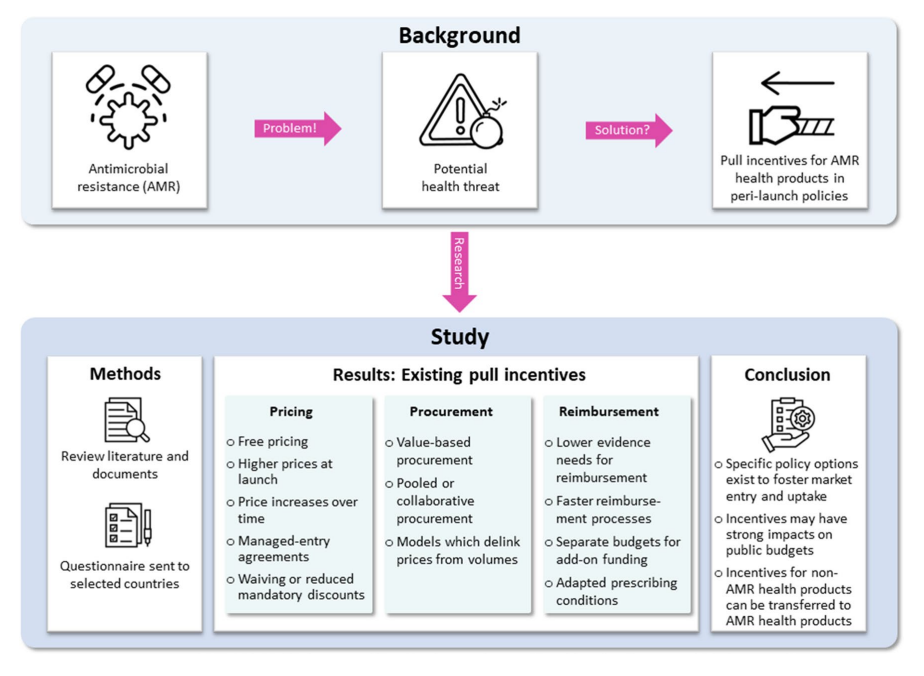
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a growing global health threat. According to recent estimates, AMR was responsible for 1.27 million deaths in 2019. This issue extends beyond human health, affecting animals, food, and the environment. The impact of AMR is also seen in the clinical and economic dimensions of global health. In order to manage AMR effectively, a comprehensive, multi-sectoral approach aligned with the One Health strategy is required. A recent study analysed the role of pull incentives in pricing, procurement, and reimbursement policies to encourage the development and market entry of novel antibiotics and AMR health products.
Understanding Pull Incentives
Pull incentives are financial rewards linked to research and development (R&D) results. Unlike push incentives, which provide direct funding and grants, pull incentives aim to stimulate market entry by making the market environment more attractive for suppliers. These incentives are crucial for AMR health products, given the high costs and uncertainties associated with developing novel antibiotics and diagnostics. In this study ten countries were selected for investigation: Australia, Brazil, France, Germany, Italy, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, South Korea, Spain, and Türkiye.
Current Policy Landscape
Some countries outside the selected countries have implemented innovative policies to address AMR. For instance, England introduced a “commercial model” in 2019, offering pharmaceutical companies a fixed annual fee of up to £10 million for novel antibiotics. For this a new cost-effectiveness evaluation methodology was developed by National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) to conduct health technology assessments (HTAs). Similarly, Sweden piloted a subscription-based model in 2020, granting companies a fixed annual revenue for specific low-volume antibiotics. These models aim to ensure the availability of essential antibiotics while encouraging their judicious use.
Transferability of Non-AMR Policies
Many non-AMR health products share characteristics with antibiotics, such as high prices, low volumes, and limited clinical evidence. These include examples such as oncology and orphan drugs. Policies successful in non-AMR contexts could be adapted for AMR health products. For example, orphan medicines often receive incentives to compensate for low volumes. Similar strategies could be applied to novel antibiotics, which may be produced in small quantities but have significant societal value.
Challenges and Future Directions
Implementing pull incentives comes with challenges. Financial incentives can strain public budgets and may require substantial policy modifications. Policymakers must balance the need to incentivise market entry with maintaining financial sustainability. Interestingly, they found more evidence for medicines than medical devices, suggesting a lower policy implementation level for medical devices. Future research needs to evaluate these policies’ effectiveness. We should also focus on developing indicators to measure their impact on health outcomes.
Conclusion
Addressing AMR requires a multi-faceted approach, including innovative pull incentives in pricing, procurement, and reimbursement policies. While these incentives can encourage the market entry of novel antibiotics, careful consideration of their financial and systemic impacts is essential. Policymakers must navigate these challenges to ensure sustainable and effective solutions for combating AMR.
