
Introduction
The rise of telehealth in the post-pandemic era has significantly impacted healthcare delivery, allowing patients to receive assessments and monitoring remotely. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services has taken steps to promote telehealth adoption, particularly automated remote health assessments, addressing challenges like limited clinic access and bias in traditional assessments. Artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and natural language processing (NLP) play essential roles in modern healthcare, enabling computer systems to analyse data and adapt without explicit programming. Recent advancements in digital technologies have facilitated the measurement of various human-centric signal modalities for remote patient assessment, offering insights into a wide range of health conditions, particularly in mental health and neurological disorders.
AI and NLP in Mental Health
AI and NLP have significantly improved the assessment of mental health conditions. By analysing text data from social media, interviews, and electronic health records, these technologies can identify early indicators of mental illness. For instance, linguistic features such as part-of-speech, sentiment scores, and topic modelling are used to detect signs of depression, anxiety, and other mental health issues. Recent studies have shown that NLP techniques can classify conversations of individuals with mental health disorders with high accuracy. This capability supports early detection and intervention, potentially improving patient outcomes.
Neurological Disorder Assessments
NLP and AI also play a crucial role in assessing neurological disorders. Conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD), traumatic brain injury (TBI), and autism can be evaluated through conversational analysis. Research has demonstrated that features like turn length, phonation time, and speech fluency are key indicators of these disorders. These findings demonstrate the potential of AI and NLP in providing objective and accurate assessments of neurological conditions.
Patient-Reported Outcome Measures (PROMs)
Traditional PROMs, such as the Parkinson’s Disease Questionnaire –39 and the ALS Functional Rating Scale – Revised for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), often lack the granularity needed to capture disease severity accurately. AI and NLP can address this issue by analysing patient-reported data in their own words. This approach allows for a more detailed understanding of how diseases affect daily functioning.
Multimodal Analytics for Disease Progression
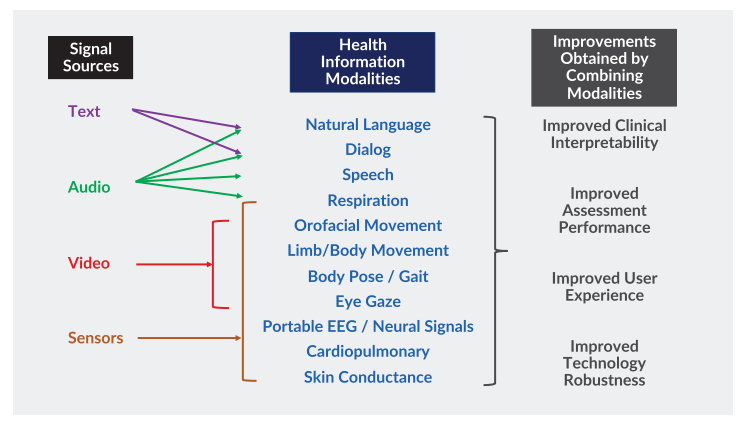
Combining multiple signal sources, such as audio, video, and text, offers a holistic view of patient health. Multimodal analytics can objectively monitor disease progression over time. For instance, studies have shown that frequent and remote speech analysis can detect early bulbar changes in ALS patients. This capability allows for timely interventions and better management of the disease. Similarly, video-based gait analysis can assess Parkinsonian gait in older adults, providing critical information for treatment planning.
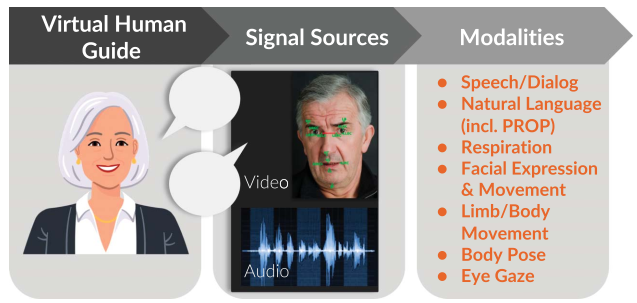
Case Study: The Modality Platform
The Modality platform exemplifies the benefits of multimodal technologies in remote health assessments. Utilising a cloud-based system and a virtual human guide, the platform conducts structured interactions with participants, capturing data from speech, text, orofacial movements, limb motor functions, and more. Furthermore, participants complete the Patient Report Of Problems (PROPs), a tool enabling them to detail their symptoms and severity in their own words. This comprehensive approach enhances clinical interpretability, performance, user experience, and technology robustness, making it a valuable tool for remote assessments across various health domains.
Conclusion
The integration of multimodal technologies in remote health assessments holds promise for early detection, accurate diagnosis, personalised precision health, digital clinical trials, and improved patient outcomes. While these technologies offer significant benefits, challenges such as signal diversity, atypical speech patterns, and privacy concerns must be addressed for widespread adoption. Collaborative efforts in overcoming these challenges will drive advancements in digital medicine and enhance healthcare practices. By leveraging multimodal analytics, healthcare providers can gain a comprehensive understanding of patient health. As AI and NLP continue to evolve, their impact on mental health and neurological assessments will offer new possibilities for patient care.
