The Institute for Clinical and Economic Review (ICER) has released an updated Evidence Report assessing the potential impact of two revolutionary gene therapies for sickle cell disease (SCD) – exagamglogene autotemcel (exa-cel) and lovotibeglogene autotemcel (lovo-cel).
Sickle cell disease is an inherited blood disorder caused by mutations in the gene HBB, affecting hundreds of thousands of people globally. The disease causes a range of severe health issues and is currently treated with supportive care, blood transfusions, and hydroxyurea. The only potentially curative treatment is hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), but it carries significant risks. Two new gene therapies, lovo-cel and exa-cel, are emerging as potential treatments for SCD. Both have shown promising results in clinical trials, reducing the number of vaso-occlusive events or crises in patients. However, they also carry risks of serious adverse events and uncertainties about their long-term effects. The FDA has accepted the Biologics License Application for both therapies, with regulatory decisions expected in December 2023. The cost-effectiveness of these therapies will depend on their actual prices.
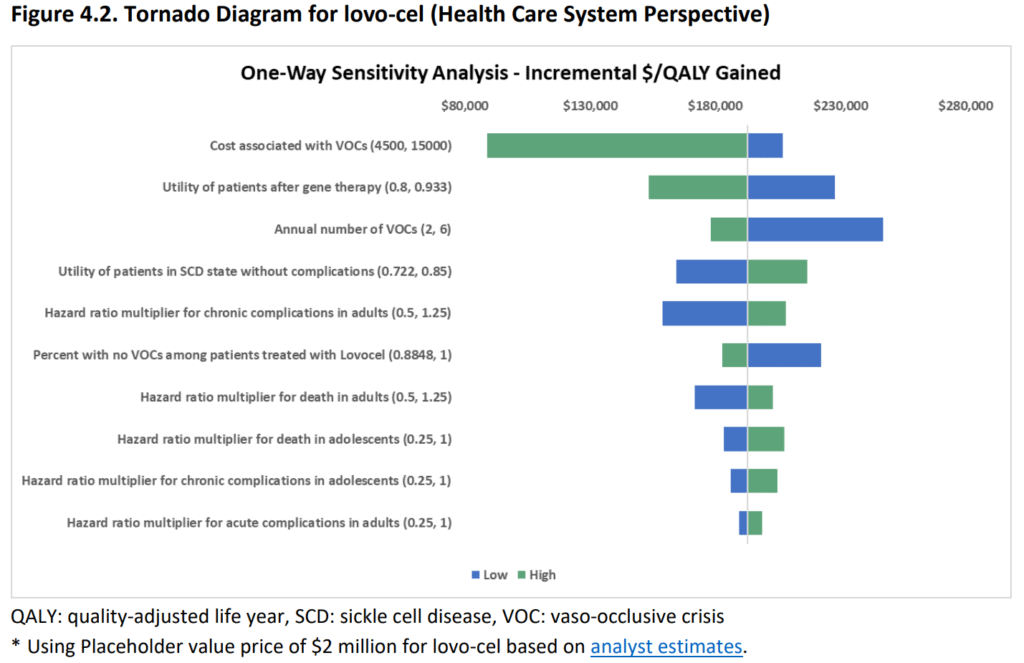
As the prices for lovo-cel and exa-cel are not available yet, and a placeholder value of $2 million was assumed based on analyst estimates. A sensitivity analysis was conducted to evaluate the effects of uncertainty on costs and health outcomes. The cost of VOCs, the utility of patients successfully treated with gene therapy, and the annual number of VOCs were found to be the major drivers of cost per QALY for both treatments. There was greater uncertainty around the treatment success rate of exa-cel due to a small sample size in the trial. The hazard ratios for death, acute, and chronic complications were estimated from published literature and varied based on the age of treatment.

The report indicates that lovo-cel may provide a substantial net health benefit for severe SCD patients, while exa-cel could offer comparable or possibly greater benefits.
Several studies have been conducted on SCD in recent years, focusing on complications, costs, utilities, and conceptual modeling. These studies have been crucial in the development of a cost-effectiveness model and addressing uncertainties in modeling SCD. However, there are still uncertainties regarding the impact of SCD gene therapy on quality of life and disease-related events. The cost-effectiveness of gene therapies also depends on the patient’s age, with younger patients associated with a lower cost-effectiveness ratio. Some people living with SCD may not opt for gene therapies due to their preferences and risk-benefit tradeoffs. The cost-effectiveness model assumes risk neutrality, which is a limitation. The potential cost savings and health gains contribute to the justification for the cost of gene therapies.
ICER’s Chief Medical Officer, David Rind, MD, highlighted the potential of these therapies to address the underlying genetics of SCD, bringing us closer to a cure. However, he also emphasised the need for caution due to potential risks associated with autologous bone marrow transplantation and the uncertainties surrounding CRISPR therapy.






