
Introduction
Genome-wide sequencing (GWS) has emerged as a crucial diagnostic tool in the identification of rare diseases. This technique, which includes whole-exome sequencing (WES) and whole-genome sequencing (WGS), aims to reduce the diagnostic odyssey often experienced by patients. Rare diseases affect approximately 1 in 16 individuals globally. These diseases, often genetic, disproportionately impact children. Identifying the genetic causes is crucial for prognosis and clinical management. However, the journey to diagnosis, is often long and costly. It typically spans 4.8 to 7.4 years and involves multiple tests, costing healthcare systems over $5000 per patient in laboratory tests alone.
Understanding Genome-Wide Sequencing
GWS involves sequencing the entire set of genes or the entire genome, providing a comprehensive look at genetic variations. Traditional diagnostic methods for rare diseases include karyotyping, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), and chromosomal microarray analysis. However, these methods can be time-consuming and costly. GWS offers a more efficient alternative, potentially reducing the diagnostic timeline from years to months.
Clinical Impact of GWS
The clinical benefits of GWS are significant. By identifying the genetic basis of a disease, GWS can inform prognosis, guide clinical management, and enable targeted treatments. For instance, in children with neurodevelopmental disorders, GWS has shown a higher diagnostic yield compared to traditional methods. This can lead to more effective treatments and better management of symptoms.
Economic Implications of GWS
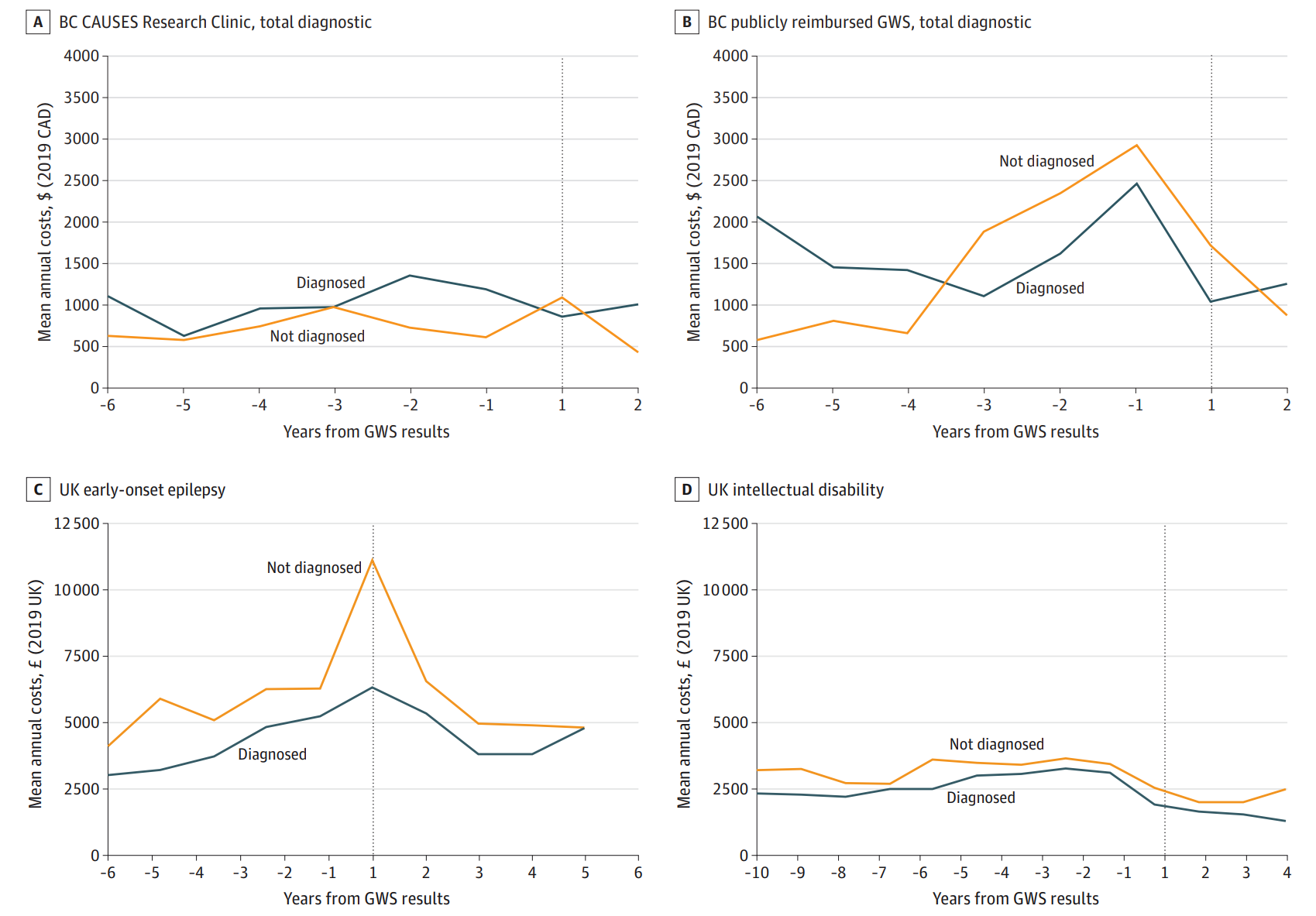
A study comparing healthcare costs in England and Canada found varying results. In Canada, GWS led to lower diagnostic testing costs, while in England, healthcare costs increased post-GWS. While the upfront costs of GWS can be high, it can save money in the long run by reducing the need for multiple, inconclusive tests. This study found varying rates of GWS diagnosis across cohorts. Interestingly, they did not find evidence that receiving a genetic diagnosis was associated with reduced costs, except in a British Columbia research setting. In this setting, patients accessed GWS early, avoiding exhaustive biochemical tests.
In the Canadian publicly reimbursed system, lower diagnostic testing costs were observed post-GWS. However, no changes were noted in a Canadian research setting. In England, increased inpatient and outpatient costs were observed post-GWS, varying by clinical condition. These findings suggest that while GWS may reduce diagnostic costs by ending the search for a diagnosis, it may also lead to increased healthcare use in other areas.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its benefits, GWS faces several challenges. The high initial cost and the need for specialised equipment and trained personnel can be barriers to widespread adoption. Furthermore, the interpretation of GWS results requires a high level of expertise. The economic impact of GWS is influenced by clinical and regional heterogeneity, and further research is needed to explore these dynamics. Future research should also focus on long-term cost-effectiveness and the broader impacts on healthcare systems.
Conclusion
Genome-wide sequencing is a powerful tool in diagnosing rare diseases, offering both clinical and economic benefits. However, its implementation should be guided by comprehensive evidence of its cost-effectiveness and patient benefits. As research continues, GWS has the potential to transform the diagnostic landscape for rare diseases, providing hope for patients and their families.
