
Understanding the Growing Concern
Cardiovascular Implantable Electronic Devices (CIEDs) are life-saving marvels of modern medicine. However, with over 300,000 patients receiving a new CIED implantation annually in the US alone, there has been a simultaneous surge in device infections. These infections can lead to substantial morbidity, with infected patients facing over 3-fold higher mortality compared to those without infections. Moreover, the financial burden on the healthcare system is significant.
The Significance of Prompt Intervention
The efficacy of antibiotics as a standalone treatment for CIED infection is limited. These factors have the potential to result in increased rates of infection relapse and fatality. In patients diagnosed with a definite CIED infection, the recommended course of action is the comprehensive extraction of both the device and lead. Research findings indicate that conducting extractions promptly following diagnosis leads to notable reductions in 1-year mortality rates, shorter durations of hospitalisation, and a decreased frequency of physician or hospital visits.
CIED infections and early intervention
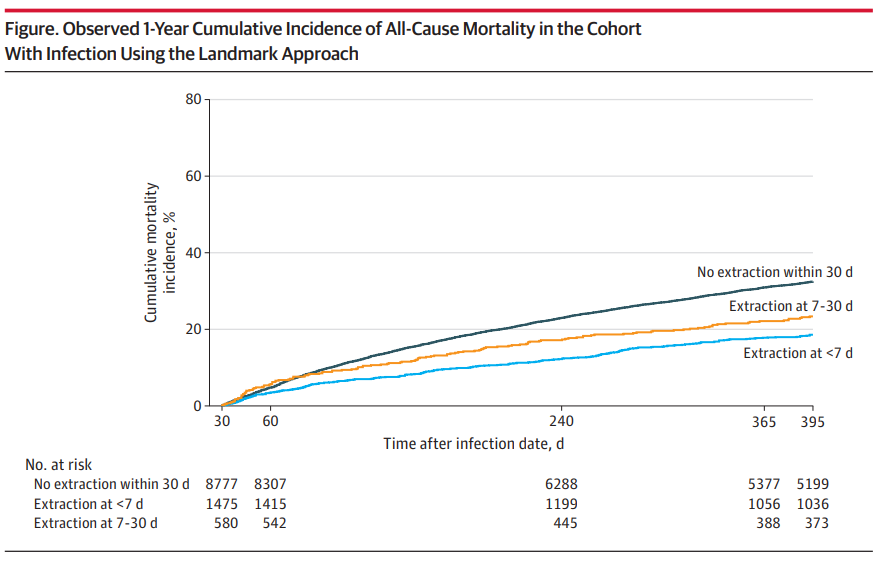
There are concerns about the lack of compliance with guidelines for removing hardware from patients with CIED infections. The goal of this analysis was to measure the number of Medicare beneficiaries with CIED-related infections. These patients had lead extraction procedures between 2007 and 2019. Additionally, the study attempted to analyse the resulting outcomes of these interventions. The researchers discovered that the process of lead extraction was linked to a decrease in mortality rates. Furthermore, they observed that conducting lead extraction at an earlier stage was correlated with even lower mortality rates compared to delaying the procedure.
This study identifies the need for comprehensive care in managing CIED infection. This includes identifying the infection, conducting a thorough examination, starting antibiotic treatment, making appropriate referrals, and deciding if extraction is needed. The study’s results highlight the urgent need to follow care guidelines more closely. They also stress the importance of improving quality within health systems.
