
Introduction
The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) Biobank is transforming paediatric healthcare by collecting and analysing biospecimens and health data. This initiative of paediatric biobanks aim to uncover disease markers, develop new treatments, and improve diagnostic tools. The CHOP Biobank represents a significant step forward in understanding and treating childhood diseases.
The Importance of Paediatric Biobanks
Paediatric biobanks are essential for advancing child health research. Unlike adult-focused biobanks, paediatric biobanks collect and store biological samples from children. This includes blood, tissue, and health information. These samples are crucial for studying diseases that uniquely affect children. Childhood diseases are often more diverse and rare, with a stronger genetic component than adult diseases.
Healthy children’s samples are also vital. They serve as controls to understand normal growth and development. However, samples from children under five, a critical growth period, are nearly absent from most biobanks.
How the CHOP Biobank Operates
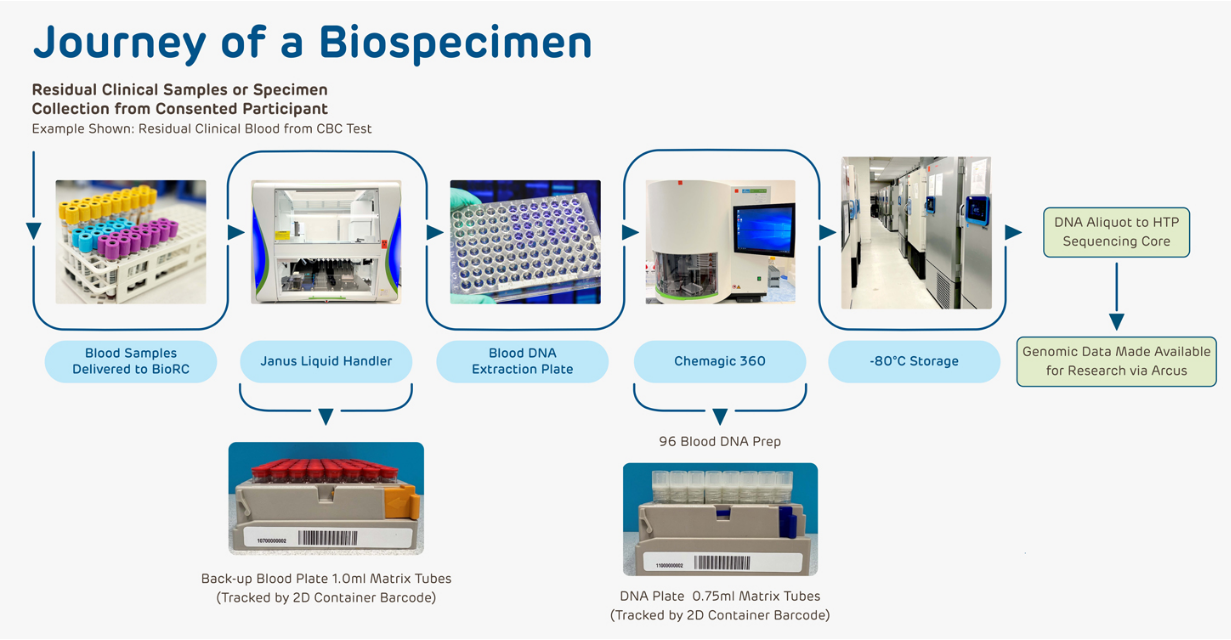
The CHOP Biobank collects biospecimens and health data from CHOP patients and their relatives. Participation is voluntary and open to all CHOP patients, including healthy children. The biobank uses various methods to obtain consent, including in-person meetings and digital platforms like the MyCHOP patient portal.
Once consent is obtained, the biobank collects samples such as residual blood from clinical tests. These samples are stored in a state-of-the-art facility, which includes temperature-controlled storage units. The Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS) tracks all specimens, ensuring effective management and de-identification.
Benefits for Researchers
The CHOP Biobank offers a robust infrastructure for researchers. It integrates with existing biobanking efforts at CHOP, such as the Birth Defects Biorepository and the Neuroscience Biorepository. This common infrastructure provides dashboards for researchers to visualise available samples and data across biobanks.
The biobank’s streamlined processes enable quicker study enrollment and data collection. Researchers can access de-identified data easily, and identifiable data with Institutional Review Board approval. This system reduces duplication of effort and maximises the use of donated samples.
Future Implications for Paediatric Healthcare
The CHOP Biobank aims to lead in developing new omics-based diagnostics and therapeutics for children. By combining genomic and phenotypic data, researchers can gain a comprehensive understanding of childhood diseases. This integrated approach will drive omics-based translational research, potentially transforming paediatric healthcare.
The biobank also supports the goal of providing predictive medicine in paediatrics. By understanding disease patterns and genetic contributions, researchers can develop more precise treatments and diagnostic tools. This will ultimately improve health outcomes for children.
Conclusion
The CHOP Biobank is a groundbreaking initiative that holds the potential to revolutionise paediatric healthcare. By collecting and analysing biospecimens and health data, the biobank provides invaluable resources for researchers. This effort will lead to new treatments, better diagnostic tools, and improved health outcomes for children.
