
Introduction
Cancer remains a significant global public health concern, with approximately 18.1 million new cases and 9.6 million deaths reported worldwide in 2018. Access to innovative oncology treatments is crucial in improving patient prognosis and quality of life. However, the high cost of these treatments often poses a barrier, particularly in lower-middle-income countries like Malaysia. This article explores the willingness of Malaysians to pay for these innovative treatments and how this information can be used to shape more sustainable funding solutions.
The Cost of Oncology Treatment
The financial burden of cancer treatment has seen a dramatic increase over the years. In many instances, the high cost of new oncology medicines that could potentially improve survival rates renders them unaffordable. Consequently, they are not listed in the Ministry of Health Malaysia Formulary. The financial strain often forces patients to pay out-of-pocket to access these new treatments, leading to potential economic hardships.
The Funding Challenge and Need for Innovative Solutions
In Malaysia, several foundations and non-governmental agencies occasionally provide funding assistance for cancer therapies. However, these funds are often insufficient, posing a barrier to early access to innovative oncology medicine. Therefore, there is a pressing need for innovative funding mechanisms involving multiple parties, such as healthcare providers, pharmaceutical companies, patients, non-government organisations, and other funding bodies.
Willingness to Pay for Innovative Oncology Treatments
A recent study sought to determine whether Malaysians are willing to pay for innovative oncology medicines and the amount they would be willing to pay for early access to treatment. The research was done in three hospitals in Malaysia, and also online from January 2021 to January 2022. Participants were given three hypothetical scenarios where they had to decide how much they would be willing to pay for a new diabetes medicine (IDM), a one-time payment for a new cancer medicine (IOMO), and an annual insurance premium for access to new cancer medicines (IOMI).
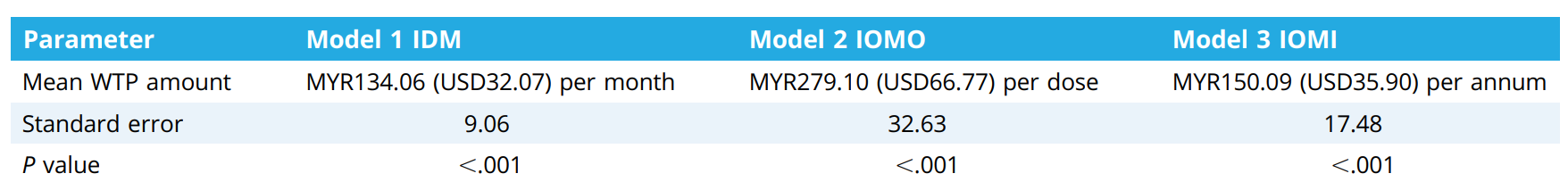
The results revealed that on average, for the first model (IDM), people were willing to pay around MYR134.06 per month. The study found that older individuals and those from Sabah/Sarawak were willing to pay a little more. Also, people with higher incomes (over MYR10,001) were willing to pay significantly more.
For the second model (IOMO), the average amount people were willing to pay was MYR279.10 per dose. Here, people with higher incomes again were willing to pay more, and married individuals also tended to pay more.
For the third model (IOMI), the average amount people were willing to pay was MYR150.09 per year. In this case, only those with higher incomes were willing to pay more.
Implications and Conclusion
The results from this study can help shape collaborative funding mechanisms for cancer care in Malaysia. It is essential to introduce appropriate financial screening in public hospitals to categorise patients based on their financial hardship and channel them to suitable financial assistance. Moreover, the results underscore the need for more education and marketing initiatives to highlight the benefits of medical and health insurance, especially for covering innovative cancer medicine.
