
Introduction
Combination therapies (CTs) are increasingly used in oncology to enhance clinical outcomes by merging treatments with different mechanisms. However, assessing and pricing these therapies, especially when they involve on-patent drugs from different manufacturers, poses significant challenges. Primary value attribution frameworks are (VAFs) used to evaluate combination therapies and aim to determine the appropriate value shares for each component therapy within a combination.
Incremental Value (IV) Method
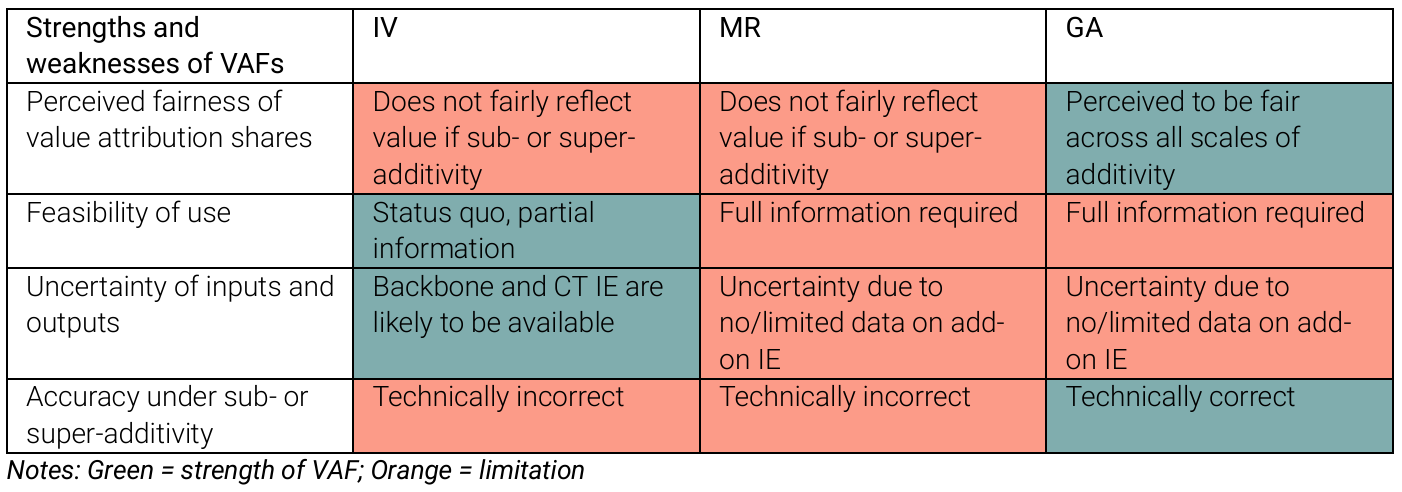
The Incremental Value (IV) method is the current standard for value attribution. It calculates the value of a combination therapy based on the additional benefit it provides over existing treatments. While IV is straightforward and feasible, it often fails to address cost-effectiveness issues, particularly in cases of sub- or super-additivity. This limitation can hinder patient access to effective combination therapies.
Monotherapy Ratio (MR) Approach
The Monotherapy Ratio (MR) approach, proposed by Briggs et al., 2021, aims to address some of the shortcomings of the IV method. MR requires extensive information about the individual components of the combination therapy. Although it can overcome the “not cost-effective at zero price” (NCZP) problem, its complexity and data requirements can be a barrier to implementation.
Generalised Approach (GA)
The Generalised Approach (GA), proposed by Towse et al., 2022, has gained the most support among industry stakeholders. Many view GA as a fair approach for attributing value across different scales of additivity. It addresses the NCZP problem and is a sensible, risk-mitigating strategy for portfolios that include both backbone and add-on therapies. However, the GA framework requires complete information, which can introduce uncertainty if data is incomplete.
Incentives and Competition Law
One of the main challenges in implementing VAFs is aligning incentives among manufacturers. Developers create an add-on treatment to combine with an existing backbone treatment. However, the price of the backbone therapy doesn’t change. This can make the combination therapy not cost-effective at a zero price, discouraging the development of add-on therapies.
Value Attribution and Implementation Problems
Fairly apportioning the value of a combination therapy among its components is crucial. The balance of market power among manufacturers can influence value attribution. The current IV method faces challenges in assessing cost-effectiveness and may not fairly attribute value except in cases of constant scale of additivity. The MR and GA frameworks, while addressing some of these issues, require extensive information and can be complex to implement.
Industry Perspectives on VAFs
The Office of Health Economics (OHE) developed an Excel tool to compare the value attribution shares under each VAF. This tool was piloted by the Association of the British Pharmaceutical Industry’s (ABPI’s) combination treatment project team. Feedback from the project team highlighted that while no single solution was ideal, the GA received the most support. It was considered the most appropriate for a range of products, including backbones and add-ons.
Future Directions and Recommendations
Based on the industry’s feedback, the GA framework is recommended as the starting point for value attribution in combination therapies. However, the selection of the GA depends on the availability of evidence and the ability to generate relevant data. Discussions between manufacturers, payers and health technology assessment (HTA) agencies should be supplemented by the shares generated using the IV and MR approaches.
Conclusion
Combination therapies present unique challenges in value attribution and pricing. While the GA framework offers a promising solution, its implementation requires comprehensive data and collaboration among stakeholders. By addressing these challenges, we can ensure that patients have access to effective combination therapies that improve clinical outcomes.
