Introduction
The American Heart Association (AHA) has taken a significant step by releasing a comprehensive scientific statement. It sheds light on the current landscape of artificial intelligence (AI) applications in diagnosing and treating cardiovascular disease. This milestone underscores the growing interest within healthcare organisations to leverage AI’s stellar capabilities in elevating patient care. The report highlights the exciting potential of AI technologies and addresses critical aspects such as limitations, challenges, and the safe and effective deployment of AI in cardiovascular health. There was an emphasis on the inclusion of cutting-edge research on AI applications ranging from medical imaging and wearables to electrocardiography and genetics. This article will explore AI in cardiovascular disease diagnosis as per AHA’s statement.
Applications of AI in Cardiovascular Medicine
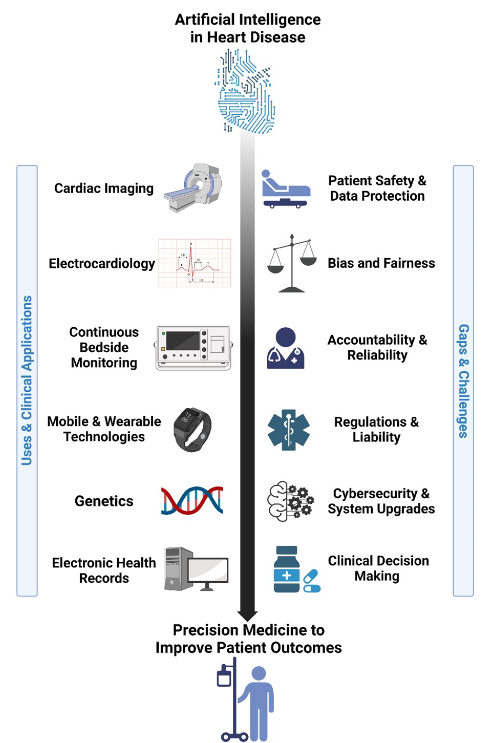
In cardiovascular medicine, the integration of AI can be applied across a variety of functions (Figure 1). This includes imaging, electrocardiography, and wearable technologies which present a promising frontier for improving diagnostic accuracy and patient care. AI’s ability has also stretched beyond initial parameters of detection and diagnostic services. The range includes analysis of complex imaging data, interpreting electrocardiograms with precision, and provision of continuous monitoring through wearable devices. These offer unprecedented opportunities to enhance early detection, personalised treatment, and remote patient management.
Challenges and Opportunities in AI Implementation
While AI and machine learning (ML) show promise in enhancing medical imaging for cardiovascular diagnosis, significant challenges persist. The AHA’s statement underscores the complexities of using AI for image interpretation, citing issues like the scarcity of diverse and high-quality datasets. There should be rigorous validation of these technologies across various clinical settings. This should be implemented and evaluated before widespread adoption, a crucial step towards ensuring their reliability and accuracy.
Conclusion
AI has the ability to analyse data from diverse sources such as implants, wearables, electrocardiograms, and genetic information. It also has the ability to interpret this wealth of data, which healthcare professionals can use to gain valuable insights. As the healthcare industry embraces AI-driven innovations, addressing challenges and maximising opportunities presented by AI will be key to advancing cardiovascular care.
