
Introduction
Every year, numerous children are born with severe genetic disorders, with a considerable number remaining undiagnosed due to the complexity of identifying causative genetic variants. The emergence of artificial intelligence (AI) in genetic diagnosis offers a promising avenue for addressing these challenges, pushing the boundaries of precision medicine.
Understanding the Diagnostic Challenge
Genetic disorders, often resulting from single-gene mutations, present a significant diagnostic challenge. Despite modern bioinformatics tools, the process of pinpointing the exact variant responsible for a disease remains a complex task, demanding both time and extensive knowledge. Despite the advent of sophisticated bioinformatics tools, the diagnostic rate for genetic disorders hovers between 30 and 40%. This complexity underscores the need for more efficient diagnostic methodologies.
The Power of AI in Genetic Analysis
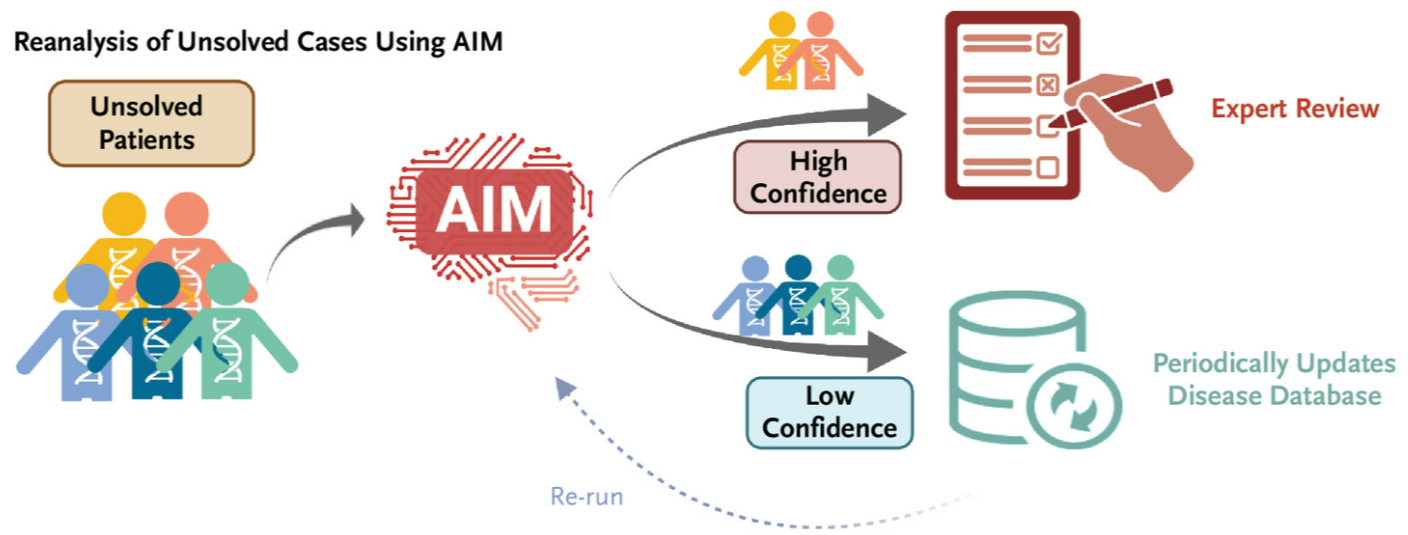
AI systems, such as AI-MARRVEL (AIM), have been developed to enhance the diagnostic process for Mendelian disorders. These systems leverage patient clinical features and sequencing profiles, offering a sophisticated approach to variant prioritisation. AIM, in particular, is trained on a more than 3.5 million variant data points and curated by certified experts, embodying a significant leap forward in genetic diagnostics.
Navigating the Limitations of Current Tools
While AI systems like AIM mark a significant advancement, they are not without limitations. The inability to analyse certain types of genetic variations and a focus on coding variants restrict their scope. However, these challenges present opportunities for further innovation and integration of more comprehensive analytical tools.
The Future of Genetic Diagnosis
AI in genetic diagnosis is not just a theoretical concept but a practical tool with a web interface for real-world application. It has the potential to truly enhance the periodic reanalysis of undiagnosed cases, making it a feasible and cost-effective option for many. As AI continues to evolve, its integration into clinical practice promises to enhance patient outcomes and set a new norm in genetic medicine.
