A Better Understanding of the Financial Burden
In the United States, roughly one in five people will struggle with some form of mental illness in any given year; yet, less than half of those people will obtain the appropriate care. The COVID-19 pandemic has further compounded the absence of effective mental health services, leaving millions of people with unmet treatment needs. Untreated mental illness has consequences that reach beyond the person who suffers from it. These consequences include a decrease in the individual’s quality of life, productivity, and overall health. They may even result in work difficulties or engagement with the legal system. Because of this, individuals, families, and society as a whole are forced to shoulder a tremendous amount of additional financial strain.
The Requirement for Detailed Information
Policymakers need comprehensive data on the financial consequences of untreated mental illness to address this issue effectively. Previous research has explored the financial impact of various mental diseases. However, no study has fully examined the costs of untreated disease. Health insurers, governments, and employers need this data. It helps them understand the total economic burden of untreated mental illness. It also shows the potential cost savings from improving access to and delivering mental health care.
A Case Study: Indiana
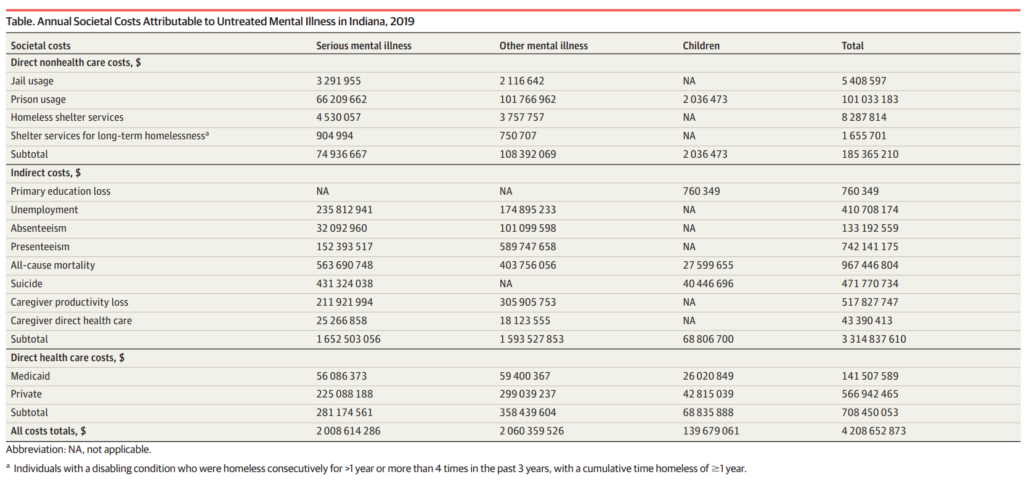
A recent study was conducted in Indiana with the purpose of estimating the economic impact of untreated mental illness in the state. The findings of this study will be used to inform legislation and programs that are designed to address this issue. The research presented a methodology at the societal level to evaluate both direct and indirect costs associated with untreated mental diseases. The research estimated the individual, family, workplace, and community expenses associated with untreated mental disorders. The findings were shocking: it was predicted that Indiana bears a total annual economic burden of $4.2 billion due to untreated mental illness.
Taking Steps to Address the Problem
The importance of early detection, counseling, and access to mental health services and therapies is driven home by these findings. Not only could these approaches increase the productivity of individuals and minimise their need for social services, but they also had the potential to drastically cut the expenses associated with incarceration and homelessness. It has been argued that telehealth might be used as a viable means to improve access to therapy, and recent regulatory changes in Indiana have made it possible for Medicaid to compensate providers for providing telehealth services.
The Duty That Falls on Policymakers
Policymakers have an important part to play in removing obstacles to seeking and getting treatment, such as providing care that is sensitive to cultural norms and addressing the stigma that is associated with seeking therapy. They are able to secure improved long-term outcomes and overall cost savings for health care systems as well as society as a whole when they embrace a comprehensive strategy to recognising and resolving the economic burden of untreated mental illness. This is possible because of the comprehensive nature of the approach.