
Introduction
The global demographic evolution involves significant shifts in population age structures. According to United Nations, the world’s population aged 65 and over is expected to double by 2050, while fertility rates are forecasted to decline. These changes carry extensive economic and societal implications, as seen in the correlation between population age structure and economic growth. Factors like human capital, health, and disability impact this dynamic. Health notably plays a crucial role in shaping work and consumption behaviours across the lifespan. Understanding how health influences the time older adults spend on non-market activities, such as housing, transport, nutrition, clothing, laundry services, childcare, adult care, and voluntary work can provide insights into the economic potential of healthy ageing.
The Economic Impact of Health at Older Ages
Investing in health at older ages presents a strategic economic opportunity. While economic growth has traditionally been associated with the working-age population, healthy ageing can prolong labour force participation, boost productivity, and cut healthcare costs. Furthermore, good health empowers older individuals to partake in non-market productive activities, significantly benefiting societal welfare. However, quantifying the economic gains linked to better health at older ages poses challenges.
Quantifying the Economic Value of Health
An innovative approach using time use surveys offers a fresh perspective on the economic value of healthy ageing. By examining how older individuals allocate their time based on health status, we can estimate the monetary value of health-related changes in time use. Findings indicate that good health correlates with increased engagement in non-market activities, leading to economic gains. This highlights the role of health in enabling active participation among older populations.
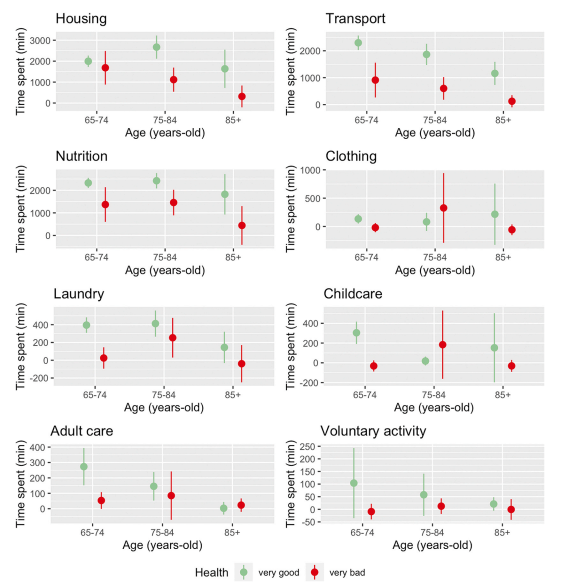
A recent study revealed significant differences in the time spent on non-market activities based on self-perceived health. For instance, individuals in very good health spent more time on nutrition-related activities compared to those in very bad health. Specifically, those in very bad health spent 958 fewer minutes per month on nutrition-related activities. Moreover, the study found that individuals in very good health were more likely to engage in part-time or full-time work. In contrast, less than 2% of those in fair or bad health were engaged in any paid work.
Economic Implications
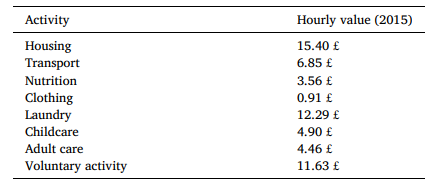
To estimate the economic impact of health improvements, researchers calculated a scenario where 10% of individuals in very bad health shifted to very good health. This shift could result in economic gains of up to £278 million (in 2015 GBP) through the production of non-market activities. This economic gain is mainly estimated by monetising the predicted value of minutes spent in non-market productive activities, based on the hourly values of each non-market activity as shown in Figure 2. For example, in the 65-74 age group, individuals in very good health engaged in non-market productive activities for about 7,831 minutes per month, compared to only 3,983 minutes for those in very bad health. This creates a monthly difference of £439 for an average person between being in very good versus being in very bad health.
Conclusion
Understanding the economic value of health at older ages is vital for crafting effective policies and interventions. By acknowledging the contributions of older individuals to society, a compelling case can be made for prioritising health investments in this demographic. Enhancing our comprehension of the intricate link between health, time use, and economic outcomes through refined approaches and objective health measures is crucial. Policymakers should consider these findings when designing health interventions aimed at older populations.
