
Introduction
The emergence of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in 2020 led to the onset of a health crisis marked by hyperinflammation symptoms. About a year later, manifestations like Kawasaki disease surfaced in children, termed multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C). This condition poses challenges, particularly severe cardiovascular complications necessitating intensive care. Therefore, understanding the cost and clinical impact of MIS-C is crucial for effective management and resource allocation in healthcare settings.
Diagnostic Evaluations and Treatment Outcomes
A retrospective cohort study involving 59 MIS-C patients revealed key insights. The mean age of patients ranged from 4 months to 16.5 years, with varying degrees of disease severity. The study highlighted the distribution of hospitalisation costs, with pharmacy and blood products constituting a significant portion. Notably, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) costs were substantial, underlining the financial burden of MIS-C treatment.
Patient Characteristics and Symptomatology
MIS-C is a severe condition linked to COVID-19, characterised by inflammation in multiple organ systems. Fever was a universal symptom, with a median duration of 5 days. Gastrointestinal symptoms were prevalent in 69.5% of cases, while mucocutaneous symptoms affected 62.7% of patients. Cardiovascular involvement was significant, with 18.8% experiencing systolic dysfunction and 3.4% showing coronary artery involvement. Laboratory findings indicated abnormalities in various parameters, emphasising the systemic impact of MIS-C.
Treatment Approaches and Healthcare Utilisation
The treatment of MIS-C involves various medical interventions, including immunoglobulin, steroids, and anticoagulants. In this study, 96.6% of patients received immunoglobulin, and 44.1% were treated with steroids. IVIG emerged as a primary treatment modality, often combined with corticosteroids. Additional interventions included low molecular weight heparin and respiratory support for deteriorating cases. The median hospital stay was 8 days, with 32.2% of patients requiring intensive care. The total cost of treatment was calculated using a combination of micro-costing techniques and hospital list data. Costs were initially recorded in Turkish lira and converted to US dollars, with an average exchange rate of 1$ = 7.7784 TL.
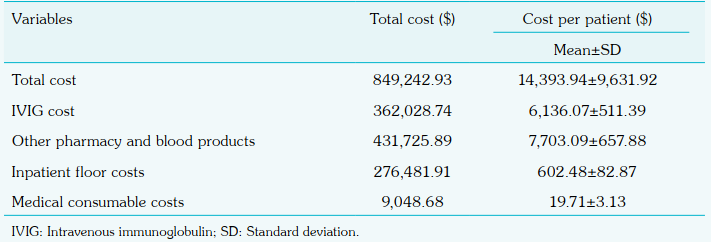
Cost and Clinical Impact of MIS-C
The total cost for treating 59 MIS-C patients was $849,242.93, with an average cost of $14,393.94 per patient. The direct medical costs include charges for inpatient care, laboratory tests, imaging, antimicrobial drugs, consultations, IVIG, and transfusions. Pharmacy and blood products accounted for 51.99% of the costs, while intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) made up 43.99%. The study applied equal discounting of costs and health effects. No significant cost differences were found between mild and moderate-severe cases or between patients with and without organ system involvement. The study emphasises the high cost of IVIG as a major factor and notes that using high-flow nasal cannula reduced the need for intensive care, thereby lowering overall costs. Organ system involvement did not significantly influence total costs, highlighting the uniformity in expenditure across different clinical presentations. Factors like IVIG treatment and respiratory support influenced healthcare costs, underscoring the need for efficient resource allocation.
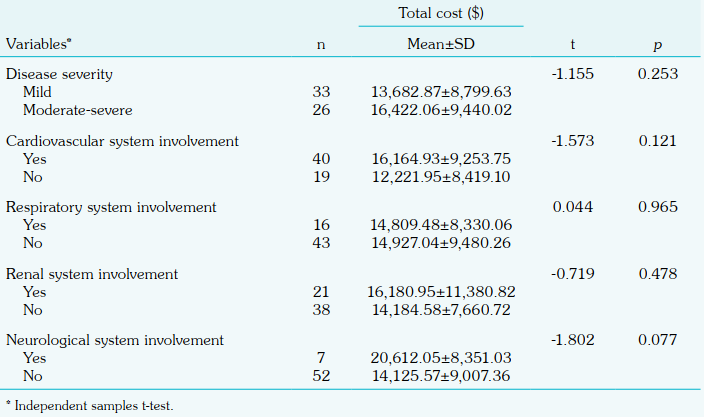
involvement with the total cost per person
Conclusion
This study sheds light on the economic ramifications of treating MIS-C, emphasising the costly nature of interventions required for severe myocardial dysfunction and multiorgan failure. The study underscores the importance of early diagnosis and appropriate treatment to mitigate the impact on children’s health and healthcare costs. Understanding the economic burden associated with MIS-C aids in healthcare resource planning and underscores the importance of cost-effective treatment strategies in managing this complex condition. Policymakers and healthcare providers must prioritise strategies to manage and prevent MIS-C effectively.
