
Introduction
Diabetes, a prevalent global health concern, impacts millions worldwide, with projections indicating a significant rise in cases by 2045. The financial strain of diabetes has surged, prompting the need for advanced treatment approaches. Real-world data (RWD) has emerged as a valuable tool for predicting diabetes complications, offering insights into disease progression. Health technology assessment (HTA) methods based on RWD are evolving, presenting new opportunities and challenges for clinical research. Transferability of these methods across jurisdictions and disease areas remains a critical consideration. Leveraging artificial intelligence (AI), researchers aim to enhance diabetes prediction models and broaden their applicability. The transferability of AI methods for diabetes modelling in HTA is a critical topic. This study investigates how these methods can be applied across different countries, particularly between early and late adopters of emerging health technologies.
Understanding AI in Diabetes Modelling
AI has transformed diabetes care by predicting short- and long-term complications. The International Diabetes Federation reports that 537 million adults live with diabetes, a number expected to rise to 783 million by 2045. AI methods can enhance our understanding of diabetes, improve cost-effectiveness modelling, and refine patient stratification. These advancements can significantly impact clinical and reimbursement decisions across various jurisdictions.
Benefits of AI in Health Technology Assessment
AI methods offer several benefits for HTA. They enable the prediction of short- and long-term diabetes outcomes on both general and individual levels, aiding clinicians in making informed decisions for therapy maintenance. This can lead to better treatment recommendations and improved patient outcomes. For instance, the Clinical Practice Research Datalink (CPRD) in the UK covers over 11.3 million patients, providing valuable data for AI models. Similarly, the Type 1 Diabetes Exchange Registry in the US includes data from over 34,000 participants, offering a rich resource for research.
AI-based methods also allow HTA agencies to combine predictions with results from randomised clinical trials (RCTs) during the evaluation of new medicines, enhancing the overall assessment process. The systematic curation of RWD helps address issues with missing data and improves the quality of datasets. Furthermore, the advancement of AI methodologies is expected to enhance diagnosis and therapy, ultimately benefiting the healthcare system.
Challenges in Transferability
Despite the benefits, transferring AI methods between countries poses challenges. Differences in healthcare systems, patient demographics, and data quality can affect the applicability of AI models. Experts from Central and Eastern European (CEE) countries highlighted the need to clarify how RCT data can be integrated with RWD. This integration is crucial for making AI methods usable in a pragmatic HTA world.
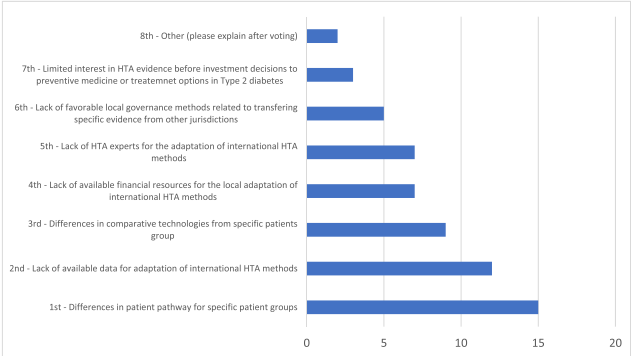
Recommendations for Successful Implementation
Several steps are necessary in order to successfully implement AI methods in HTA. Access to comprehensive databases, technical and programming expertise, and clear guidelines on RWD usage are essential aspects. Moreover, addressing the variability in patient demographics and co-treatments between countries can improve the transferability of AI models. Experts recommend developing a list of core transferable components and country-specific variables to enhance collaboration and transparency.
Conclusion
The transferability of AI methods for diabetes modelling holds great promise for improving healthcare outcomes. AI-driven methods leveraging RWD hold promise in enhancing diabetes care and facilitating HTA processes. Access to databases, technical proficiency, and clear guidelines are essential for their successful integration into healthcare practices. By addressing the challenges and leveraging the benefits, we can enhance the effectiveness of health technology assessments. This will ultimately lead to better decision-making processes and improved patient care.
