
Introduction
The socioeconomic impact of cervical cancer in the UK is a significant concern and the fourth most common cancer type globally among women. This article, based on a report from the Office of Health Economics (OHE), quantifies that burden and the potential savings from reaching the World Health Organisation’s (WHO) elimination target set in 2020. Currently the disease burden in the UK is more than twice the WHO target of less than 4 cases per 100,000 women.
The Cost of Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer carries an estimated lifetime cost of £208,086 per case in the UK. This value includes direct healthcare expenses, individual patient costs, and broader societal costs (Figure 3) due to morbidity and mortality. The strain primarily falls on society and families, accounting for 85% of the total burden, with the healthcare system bearing just 8%. The primary factor influencing the overall cost throughout an individual person’s lifetime is the reduction in productivity (Figure 1), amounting to £130,984. This accounts for 63% of the individual burden and is mostly caused by the economic impact of mortality due to cervical cancer.
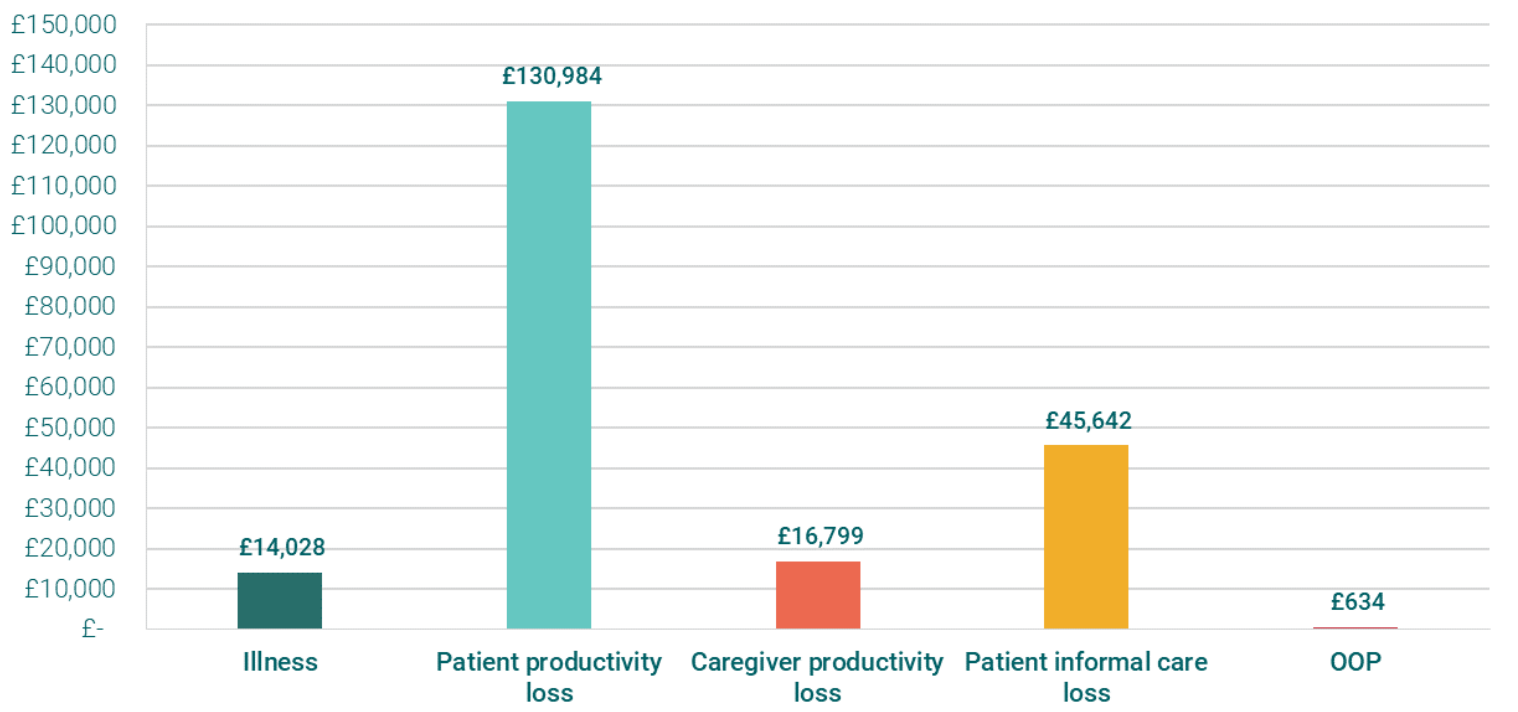
OOP= Out of pocket
The Socioeconomic Impact of Cervical Cancer in the UK
The total socioeconomic burden of new cervical cancer cases in the UK, at the current incidence rate of 9.7 cases per 100,000, is approximately £691 million. To put this into perspective, this burden equates to about 40% of the UK’s combined spending on immunisation and early detection programmes pre-COVID-19 (£1.7 billion in 2019) or about 8% of the total UK pre-COVID-19 spending on preventative care (£8.3 billion in 2019).
The Potential Savings
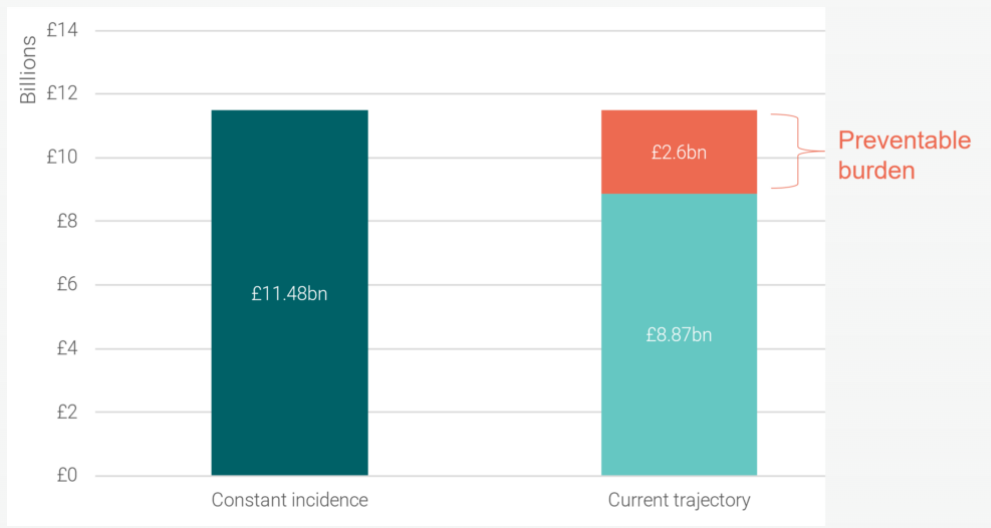
If the WHO elimination target were achieved today, there would be an instant 59% reduction in the socioeconomic burden, equivalent to about £406 million. The UK could save around £2.6 billion (Figure 2) compared to taking no action on cervical cancer elimination by achieving the WHO elimination threshold by 2046. This means that the socioeconomic burden of cervical cancer is preventable. However, these savings do not consider the cost required to achieve elimination, such as spending on prevention and control measures like vaccination and screening.
The Path to Elimination
Achieving elimination requires a comprehensive action plan from the National Health Service (NHS) to overcome barriers to access, education, and awareness while maintaining adequate funding and resources. NHS England’s recent commitment to eliminate cervical cancer by 2040 provides the impetus to improve vaccination and screening coverage and implement a clear strategy to accelerate elimination.
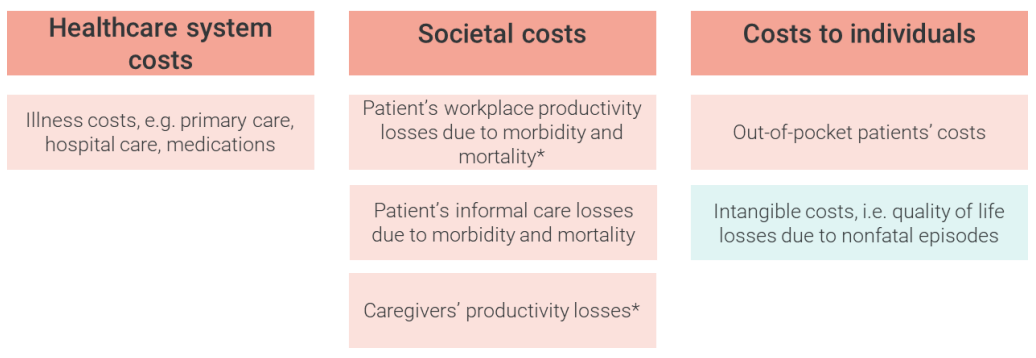
* Productivity loss quantifications already include tax returns due to workplace absenteeism.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the socioeconomic burden of cervical cancer in the UK, emphasises the urgency for effective intervention strategies to achieve the WHO elimination target by 2046, compared to taking no action. However, these savings must be weighed against the costs of implementing such strategies, including vaccination and screening programs. Therefore, it is crucial for health economists and policymakers to conduct further cost-effectiveness analyses to determine the optimal allocation of resources.
