A recent study conducted in Malaysia has shed light on the significant impact of pharmacist interventions on glycemic control in diabetic patients. The study, which focused on the Diabetes Medication Therapy Adherence Clinic (DMTAC) program, revealed a substantial reduction in HbA1c levels among patients after their visits to the clinic.
The findings of this study were consistent with previous smaller-scale studies conducted in a health clinic and a tertiary hospital in Malaysia. These studies also demonstrated a significant reduction in HbA1c levels among diabetic patients. Additionally, the study found that patients who did not default from follow-up visits achieved significantly lower HbA1c levels compared to those who did default.
Several factors were identified as independent predictors of HbA1c levels, including the frequency of DMTAC visits, duration of diabetes, number of dosage adjustments, and the use of antidiabetic agents. The study also highlighted the overall improvement in HbA1c levels among all subjects, including the defaulters, from baseline until post-2 (up to a year).
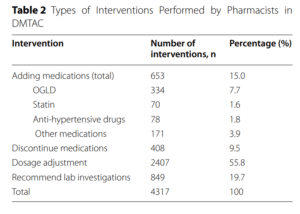
The study emphasized the need for adherence to follow-up schedules in diabetes clinics, as patients who adhered to DMTAC follow-up experienced a greater reduction in HbA1c levels. It also highlighted the potential benefits of a more holistic and multidisciplinary approach to treating diabetic patients, such as combining different clinics and reducing the number of follow-ups.
While there was no significant difference in glycemic control between patients who visited DMTAC in hospitals and primary health clinics, a higher default rate was observed in hospital patients. This suggests the need to strengthen primary health care and optimize its utilization among diabetes patients.
The study also analyzed the predictors that led to HbA1c reduction and found that more frequent DMTAC visits during the initial phase had a positive impact on glycemic control. However, this impact was not observed in the second phase of follow-up. Optimization of diabetic treatment, particularly through pharmacist-led interventions such as dosage adjustment and the addition of antidiabetic agents, significantly improved glycemic control in the longer term.
This real-world study provides valuable insights into the factors and interventions associated with improved glycemic control in diabetes patients. It highlights the crucial role of pharmacists in diabetes care and offers guidance to policymakers in determining key performance indicators in DMTAC.