
Introduction
In recent years, the healthcare industry has witnessed a surge in the use of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies to improve patient care and outcomes. As the field of health economics and outcomes research (HEOR) continues to evolve, it is crucial to understand the economic evaluations of AI-based health interventions. A recent study conducted by Voets et al. provides valuable insights into the current landscape of AI in healthcare. This article aims to summarize the key findings of the study and shed light on the merged perspectives of HEOR, AI, and health outcomes. The application of Health Economics in AI allows us to analyse a balanced view of how intrinsic digital innovation is in the healthcare landscape. This article authored by Vithlani et al., builds on the progressive work of Voets et al.
Relevance of Economic Evaluations
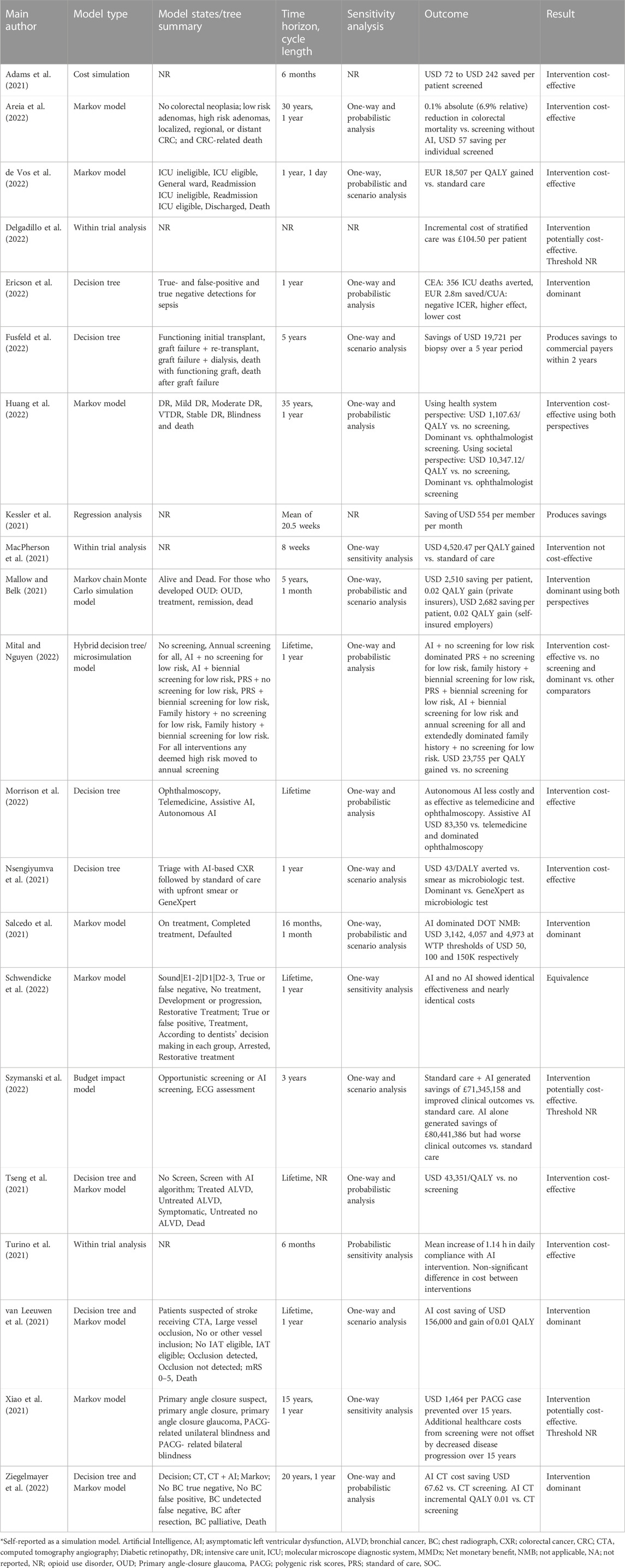
Economic evaluations play a crucial role in assessing the value of AI-based health interventions. The original review by Voets et al. found that cost minimization was the prevailing type of health economic evaluation (HEE). However, the updated review reveals a shift towards cost-utility analysis (CUA) as the most common study type. This change suggests a growing emphasis on assessing the broader economic and health outcomes of AI interventions. The application of Health Economics into AI brings about numerous debates on how evaluative methodologies are efficient.
Model-Based Evaluations
The updated review also highlights a significant difference in the use of model-based evaluations compared to the original review. The study found that 45% of the HEEs were model-based, the updated review indicates that the large majority of HEEs now employ this approach. Model-based evaluations allow for estimating future costs and benefits of AI technologies.
Limitations and Reporting Standards
Despite the increase in the use of sophisticated economic evaluation techniques, the evidence supporting these methods remains limited. The quality assessment conducted in the study revealed potentially serious limitations in the sources and assumptions regarding input data. The reporting of HEEs also lacked clarity, making it challenging to determine fundamental aspects such as cost application, integration with clinical care, and anticipated users of AI interventions.
Conclusion
The intersection of health economics, AI, and health outcomes is a rapidly evolving field with significant implications for the healthcare industry. The study conducted by Voets et al. provides valuable insights into the current landscape of AI in healthcare. It highlights the need for economic evaluations of AI-based health interventions. It found that AI health technologies are on the rise, with automated image analysis being the most commonly evaluated purpose of AI interventions. The shift towards cost-utility analysis suggests a growing emphasis on assessing the broader economic and health outcomes of AI interventions.
