
Introduction
The correlation between poverty and higher rates of mortality and morbidity has been well-established in both academic and policy discourse. The poor, both at individual and national levels, bear a disproportionate burden of ill health. This is often due to factors such as inadequate housing, sanitation, and nutrition. It’s no surprise, then, that access to quality healthcare is seen as a crucial pathway to better economic development and reduced health and income inequalities. Therefore, the impact of Universal Health Coverage (UHC) on poverty reduction is explored in this article.
Universal Health Coverage and Poverty Reduction
UHC is a key component in the fight against poverty. UHC aims to provide health services to all people in need, ensuring no one suffers financial hardship or health deterioration due to necessary health care expenditure. The Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 3, adopted by all United Nations Member States in 2015, enshrines UHC as a key factor in achieving equity and prosperity goals.
The service coverage dimensions of UHC could impact poverty, independently, or in the absence, of any reduction in catastrophic health expenditure. A recent study sought to understand the relationship between increased health service coverage and poverty in low and middle-income countries (LMICs).
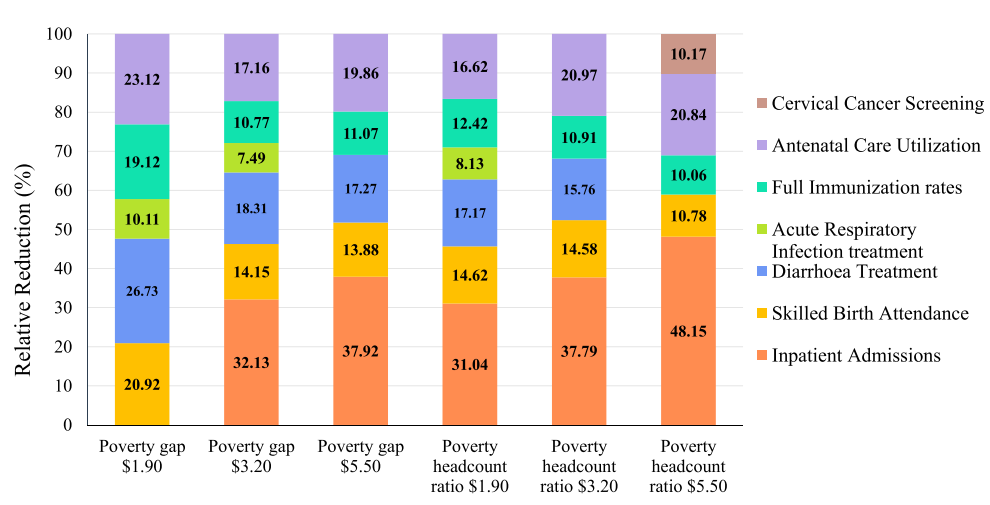
Key Findings
Recent research has discovered a link between higher coverage rates of inpatient, maternal, and child health services and smaller poverty gaps. Fewer people live below the poverty lines where these services have more coverage. These relationships hold true in most sensitivity analyses. The study also found that reductions in poverty are associated with increased coverage rates of maternal and child health services. This is particularly relevant for the poorest families in LMICs who often have less access to these services.
Impact of Universal Health Coverage on Poverty Reduction
Research findings show a correlation between increased coverage of essential health services and reduced poverty levels in low- and middle-income countries. Inpatient, maternal, and child health services stand out in this correlation. These services have a stronger association with poverty reduction, especially among people below lower poverty thresholds. This fact highlights the critical role of targeted healthcare interventions in improving the lives of the most vulnerable communities. The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of strengthening healthcare systems and increasing access to key services. Disruptions in healthcare are leading to rising poverty rates. This situation makes it crucial to prioritise UHC measures. These measures protect vulnerable people and help in achieving sustainable development goals.
Conclusion
Increasing coverage of maternal, child and inpatient services is associated with reduced poverty in LMICs. Recent findings support pro-poor approaches towards UHC and suggest that providing health services known to affect the poor may help to prevent and reduce poverty.
