
Introduction
Quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) play a pivotal role in determining the cost-effectiveness of treatments, particularly within the National Health Service (NHS) of England and Wales. While theoretically equal, the practical application of QALYs has raised concerns, especially regarding rare diseases and unique patient populations. This article explores the impact of time horizons on QALY calculations and implicitly funding decisions for healthcare treatments.
Understanding QALYs and NICE’s Evaluation
QALYs blend clinical benefit and treatment duration, with the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) using them to assess cost-effectiveness. Treatments exceeding GBP 30,000 per QALY gained face funding challenges. However, the application of QALYs across diverse patient groups has sparked debates on fairness and transparency in decision-making processes.
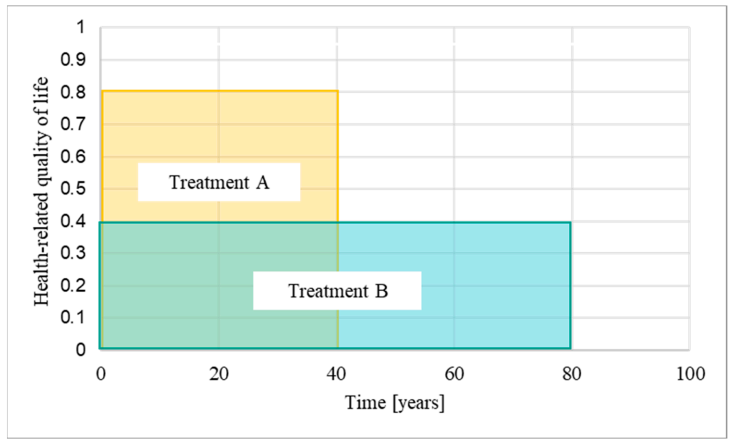
Case Studies: Afamelanotide and Givosiran
Examining evaluations of afamelanotide for erythropoietic protoporphyria and givosiran for acute hepatic porphyria reveals discrepancies in time horizons. The length of time considered for treatment impacts QALY gains and subsequent funding recommendations, highlighting the need for consistency and realism in assessments.
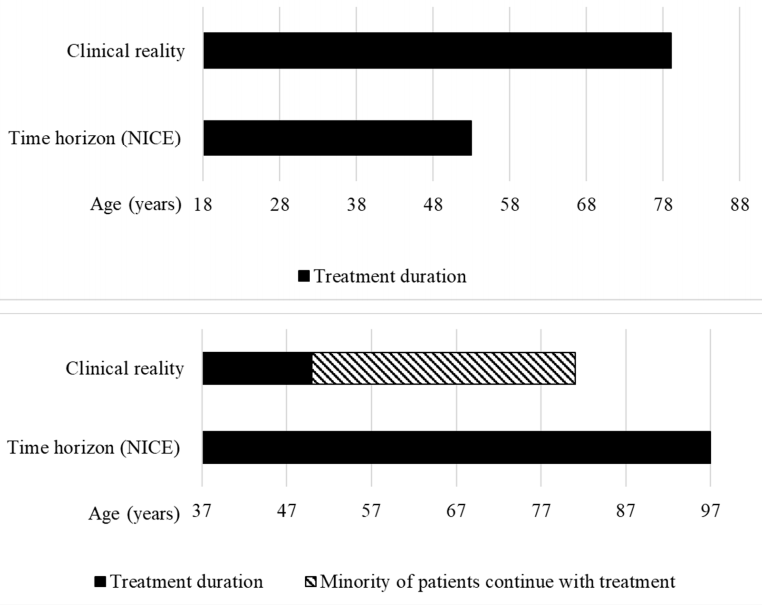
Analysis of Time Horizons in HST Programme
A comprehensive review of time horizons in Highly Specialised Technologies (HST) evaluations uncovers a trend towards extended durations, sometimes surpassing expected treatment periods or life expectancies. Extended time horizons can alter perceived treatment benefits and impact funding decisions, potentially influencing resource allocation within the healthcare system.
Implications and Recommendations
The study underscores the importance of aligning time horizons with clinical realities to ensure equitable funding decisions. Transparent reporting and methodological consistency in QALY calculations are crucial for promoting fairness and trust in healthcare funding processes. Addressing discrepancies and rationalising parameters like time horizons can enhance the integrity of decision-making frameworks.
Conclusion
The analysis calls for a re-evaluation of time horizons in QALY calculations to uphold fairness and accuracy in healthcare funding assessments. By fostering transparency, consistency, and evidence-based decision-making, organisations like NICE can better serve diverse patient populations and uphold the principles of equitable healthcare access.
