
Introduction
The impact of atrial fibrillation (AF), as the most common cardiac arrhythmia, is substantial, affecting 60 million people globally, including 14 million in Europe. This condition significantly increases the risk of severe health issues. AF patients face a five-fold increase in stroke risk, a three-fold increase in heart failure (HF) risk, and a two-fold increase in myocardial infarction (MI) risk. Approximately 75% of AF patients experience clinical symptoms, contributing to an annual management cost in Europe ranging from €450 to €3000, depending on co-morbidities.
Recent advancements in AF treatment, such as non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants and more effective ablation techniques, have potentially improved patient quality of life (QoL) and reduced healthcare costs. However, previous studies may not reflect the current clinical landscape due to changes in guideline recommendations emphasising stroke prevention and symptom management.
With an ageing population, improved diagnostic methods, and increasing cardiovascular risk factors like hypertension and obesity, AF prevalence is expected to rise. Despite this, a comprehensive assessment of the association between AF symptoms, cardiovascular disease (CVD) events, health-related quality of life (HRQOL), healthcare resource use, healthcare costs, and patient outcomes is lacking. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for improving patient care and managing healthcare expenses effectively.
Patient Characteristics and Study Design
To address this issue, a recent study analysed data from a patient population across 27 countries in Europe and Central Asia. The study enrolled patients from 250 centres, following them for two years. The average age was 70 years, with 40% being female. Patients were classified based on the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) symptom score, with 36% experiencing mild symptoms and 19% severe or disabling symptoms.
The primary outcomes were HRQOL and healthcare costs. Secondary outcomes included the number of emergency room (ER) admissions, cardiology visits, and general practitioner (GP) visits. HRQOL was measured using the EQ-5D-5L questionnaire, which assesses mobility, self-care, usual activities, pain or discomfort, and anxiety or depression.
Impact of AF on HRQOL
The study revealed that AF symptoms and CVD events significantly decrease HRQOL. Severe symptoms and events like ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), thromboembolic incidents, and worsening HF were linked to notable HRQOL reductions. These findings align with earlier studies that reported negative associations between symptom severity and HRQOL. For example, the Swiss-AF study found severe symptoms led to a 0.069 reduction in EQ-5D scores.
Impact of AF on Healthcare Costs
CVD events and, to a lesser extent, symptoms were associated with increased healthcare costs, primarily driven by inpatient care. The study found that severe or disabling symptoms increased healthcare costs by €544, while mild symptoms had a marginal effect. Cardiovascular events had a substantial impact on costs, with angina/non-STEMI (NSTEMI) adding €5823, STEMI €11,718, new-onset/worsening HF €3689, thromboembolic events €3182, and bleeding events €3792 annually. These findings highlight the significant financial burden of cardiovascular events on healthcare systems.
Previous studies also highlighted significant cost contributions from coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular disease, and HF. For instance, a Danish study reported an average total cost of €49,576 over three years for ischaemic stroke patients with AF.
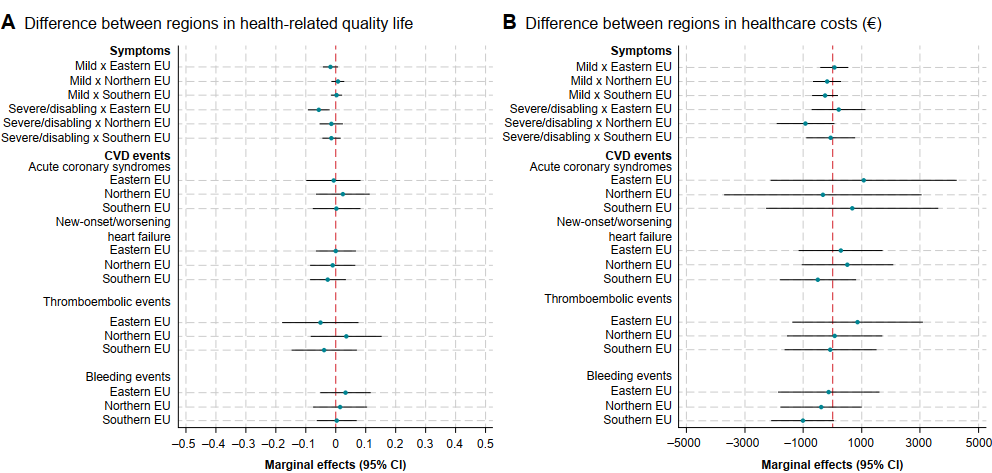
Regional and Gender Differences
There were no significant differences in HRQOL or healthcare costs between European regions (Figure 1) or by sex. This finding contrasts with some studies suggesting higher care home costs for women. However, the study did not include care home costs, and further research is needed to confirm these results.
Conclusion
Cardiovascular events and severe symptoms in AF patients lead to increased healthcare costs and reduced QoL. Effective management strategies are essential to mitigate these impacts and improve patient outcomes. These findings highlight the need for continued innovation in AF management to improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs. Furthermore, by understanding the cost drivers and patient needs, healthcare providers can better allocate resources and enhance care delivery.
