
Introduction
Vision impairment poses a significant global health challenge, affecting around 2.2 billion individuals worldwide. In Spain, 13.4% of the population over 15 years old experiences visual limitations, with conditions like glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy (DR), and macular degeneration being key contributors. Ageing and chronic conditions like diabetes mellitus (DM) play a critical role in vision loss, with diseases like glaucoma, DR, diabetic macular edema (DME), age-associated macular degeneration (AMD), and high myopia (HM) being prominent in Spain. Individuals with visual impairment often face challenges in daily life, leading to lower quality of life scores, increased risks of accidents, and higher rates of depression and anxiety. However, these eye diseases not only impact quality of life but also contribute to the substantial economic impact of vision loss on both healthcare systems and society.
Economic Burden Analysis
In a recent study from Spain, Pablo et al. analysed the costs related with five major eye diseases: glaucoma, DR, DME, AMD, and HM. A ten-year time horizon from 2021 to 2030 was used. The perspective was that of Spanish society, incorporating direct healthcare costs, non-healthcare costs, and productivity loss.
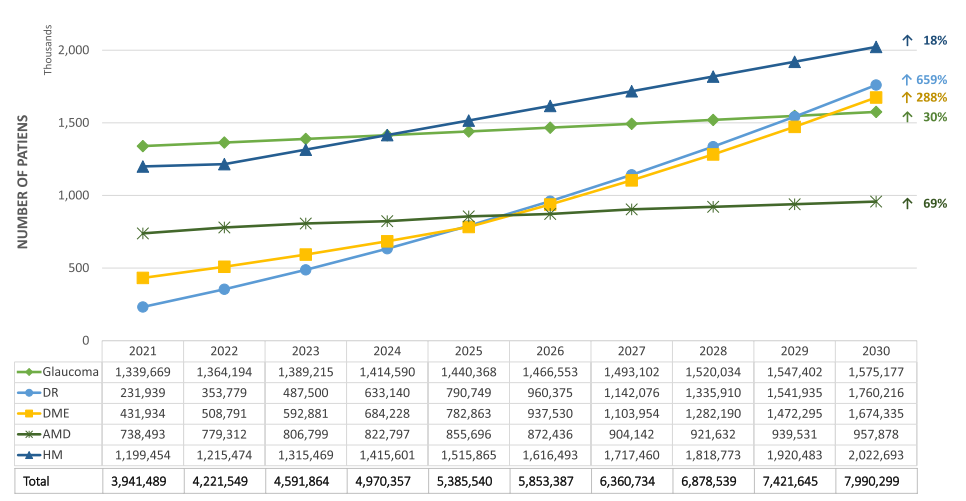
The analysis projected a significant increase in patients with vision loss and blindness in Spain, reaching 7.99 million by 2030, with an estimated total cost of €99.8 billion from 2021 to 2030. Direct non-healthcare costs accounted for the largest proportion of the total cost, emphasising the substantial impact on society. Moreover, researchers identified diseases like glaucoma and diabetic macular edema as major contributors to the economic burden.
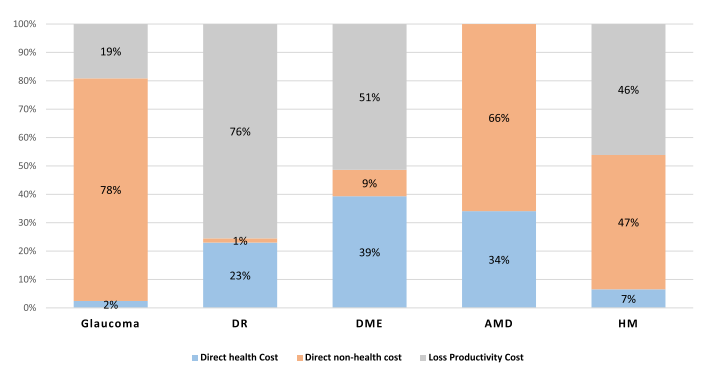
Proportion of Costs and Resources
Direct healthcare costs encompassed expenses related to disease management within healthcare settings. Specifically, these included consultations, diagnostic tests, interventions, hospital stays, and disease-specific medications. On the other hand, direct non-healthcare costs involved expenses arising from patients’ adaptations to mitigate the effects of visual impairment. Examples are informal care, transportation, visual improvement devices, and housing adaptations.
Productivity loss was calculated using the human capital method, considering only patients of working age (under 65 years). However, this cost was relevant for glaucoma, DR, DME, and HM, but not for AMD, as the affected population was typically older.
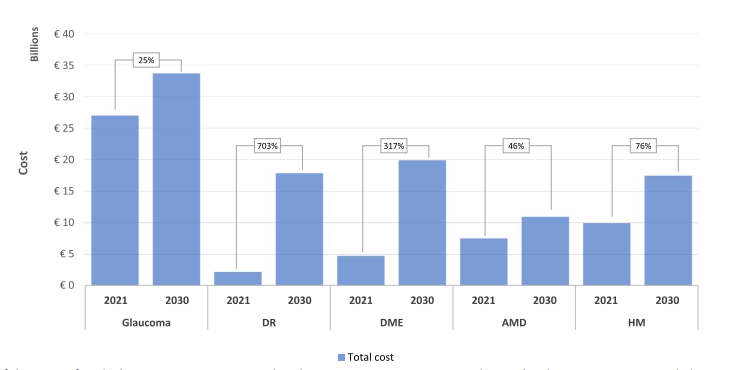
Estimating the Costs for the Next 10 years
In comparing costs from 2021 to estimated costs in 2030, pathologies like DM, specifically DR and DME, show significant cost increases of 703% and 317%, respectively. Whereas conditions like glaucoma, AMD, and HM exhibit smaller increases of 25%, 46%, and 76%, respectively, by 2030.
The cost estimates were updated to 2021 euros using the Consumer Price Index (CPI). For costs from other countries, adjustments were made using the Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) factor to convert the costs to Spanish euros. The annual CPI variation in Spain over the last decade was applied to project costs from 2022 to 2030.
Discussion and Recommendations
The prevalence of AMD and DR is expected to rise, increasing associated costs. But then, it is estimated that 50% of visual impairment cases could have been prevented. Therefore, preventive strategies, early detection programmes, and investment in new treatments are crucial to mitigate the impact of these ophthalmological diseases. The study also highlights the need for coordinated efforts to address the growing economic burden of vision loss. Initiatives focusing on vision rehabilitation and blindness prevention, including the use of AI-based tools for early diagnosis, are essential for reducing the societal and economic costs associated with these conditions.
Conclusion
Understanding the economic implications of vision loss and blindness is vital for developing effective strategies to alleviate the burden on healthcare systems and society. Collaborative efforts between administrations and patient associations are essential to implement preventive measures. There is a high possibility of asymptomatic patients, especially in the early stages of glaucoma. Therefore, enhancing public awareness regarding the importance of timely eye care and effective detection programmes can reduce the risk of irreversible blindness. Furthermore, increased investments in public health initiatives can lead to long-term benefits, improving both patient outcomes and economic relief for society.
