Introduction
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection poses a substantial global challenge, impacting millions worldwide. Italy, in particular, has seen significant progress in managing HBV through vaccination and antiviral therapies, improving patient outcomes over the years. Despite these advancements, HBV infection remains a significant public health concern in Italy, with approximately 425,000 individuals were living with chronic infections in 2014. Liver transplantation (LT) emerges as a crucial therapeutic intervention for end-stage liver disease caused by HBV infection, offering hope for patients. However, the procedure comes with its own set of challenges, including post-transplant complications, immunosuppression-related issues, and considerable economic costs. The economic burden of liver transplantation for Hepatitis B in Italy is a topic that needs closer examination.
The Burden of Liver Transplantation for Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a major risk factor for liver cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and liver failure. As a result, it poses a considerable burden on the healthcare system. LT is often the best therapeutic option for patients with HBV-related end-stage liver disease. Post-transplant HBV prophylaxis, involving a combination of hepatitis B immunoglobulin (HBIG) and nucleos(t)ide analogues (NAs), is crucial for long-term success. However, the cost of HBIG and the availability of high-barrier NAs have led to reduced use and duration of immunoglobulin in recent years. Despite these advancements, information on the overall economic burden of LT in Europe remains scarce.
A recent article published in Frontiers in Public Health investigated 233 patients who had LT in Italy due to HBV in 2022. They reported the average lifetime direct healthcare cost for an HBV patient as €395,986. Moreover, the discounted lifetime financial impact of HBV patients on the Italian National Health System was calculated as €92.3 million. These costs are influenced by various factors, with end-stage renal failure, immunosuppression, and the transplant procedure itself being major cost drivers. The expenses associated with HBV prophylaxis and antiviral drugs also contribute significantly to the overall economic burden.
Patient Flow and Complications
Marzano et al. conceptualised a model based on the information retrieved from the pragmatic literature review. The patient flow for LT is divided into three phases: pre-transplant, post-transplant acute phase, and post-transplant chronic phase. Patients start the model by entering the waiting list for LT. After an average waiting time, they undergo transplantation, which can be successful or complicated by acute issues. In the chronic phase, patients may experience routine follow-ups or chronic complications. At any point, patients might need re-transplantation or could die due to transplant-related or non-transplant-related causes.

Cost Analysis
Taking into account the incidence estimates from the literature and the values of cost elements utilised in the model, the primary cost influencer was post-transplant end-stage renal failure, making up 31.9% (around €126 k) of the overall expenditure. This was followed by the expenses linked to immunosuppression (20.6%, approximately €81 k) and the cost of LT (15.8%, roughly €63 k). HBV prophylaxis involving HBIG and antivirals contributed to 12.4% (about €49 k) and 6.4% (approximately €25 k) of the total cost, respectively. Lastly, the cost of the waiting list represented 3.8% (approximately €15 k) of the total expenses, while follow-up, complications, and other conditions apart from renal failure were minimal.
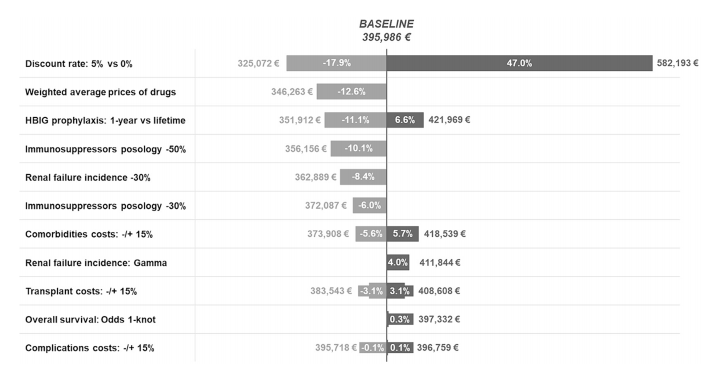
Sensitivity analyses reveal the impact of different scenarios on the cost of LT, highlighting the importance of factors such as discount rates, drug prices, and treatment durations. These analyses provide valuable insights into how variations in these factors can affect the total cost of care for HBV patients undergoing LT.
Conclusion
The economic burden of liver transplantation for Hepatitis B in Italy is significant. Effective management strategies, including tailored HBV prophylaxis and careful monitoring of post-transplant complications, are essential to improve patient outcomes and reduce costs. While this study sheds light on the economic implications of LT for HBV patients in Italy, it also underscores the need for ongoing research and evaluation in this field. By further exploring the cost dynamics and outcomes associated with LT, healthcare professionals can better understand the challenges and opportunities in managing HBV-related liver disease and develop cost-effective healthcare strategies.
