
Introduction:
There have been major shifts in healthcare delivery due to the recent pandemic, with telehealth being one area that has seen the most impact. In the United States, the use of telehealth services for mental health care has seen a remarkable increase, fuelled by changes in federal and state policies related to financial reimbursement of these services.
The Rise of Telehealth in Mental Health Care:
Particularly in the midst of the epidemic, telehealth has emerged as an indispensable instrument for the delivery of mental health treatments. According to studies, the overall volume of services for mental health issues has remained consistent, despite constraints on in-person care. This can be partly due to the rise in the number of telehealth appointments. On the other hand, the availability of these telehealth services and the makeup of these services are still substantially unexplored.
The Secret Shopper Approach:
A ‘Secret Shopper’ strategy was utilised in a recent study in order to gain an understanding of the present landscape of telehealth services for mental health care professionals. In this approach, researchers make contact with establishments while posing as potential customers in order to inquire about the availability of services. By taking this method, a clear and up-to-date image of the layout of services across the United States is provided.
Findings and Discussions:
The survey revealed that approximately one in five facilities did not respond despite multiple attempts. Among those successfully contacted, most were accepting new clients and offering telehealth services. However, the availability of telehealth services varied across states, and there was heterogeneity in the types of clinical services offered via telehealth.
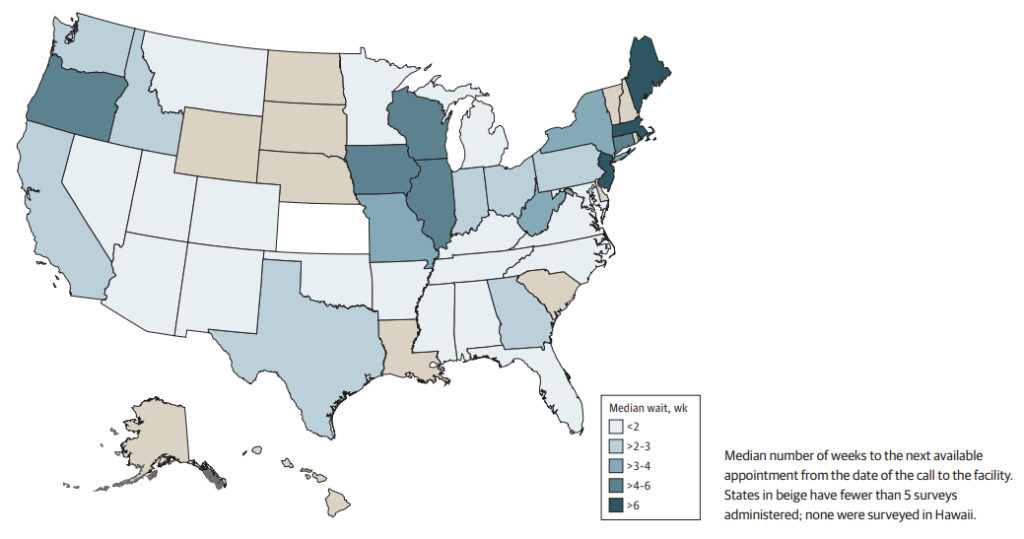
at Surveyed Mental Health Treatment Facilities
The survey also found that the median wait time for a telehealth appointment was over two weeks, with significant geographic variation. Interestingly, private facilities were nearly twice as likely to offer telehealth services compared with public facilities.
Implications and Future Directions:
These findings underscore potential heterogeneity in the availability of treatment from specialty practitioners in the US. More work is needed to investigate the possible reasons for these differences. Policymakers should consider broadening policies allowing facilities to offer telehealth across state lines to improve telehealth wait times.
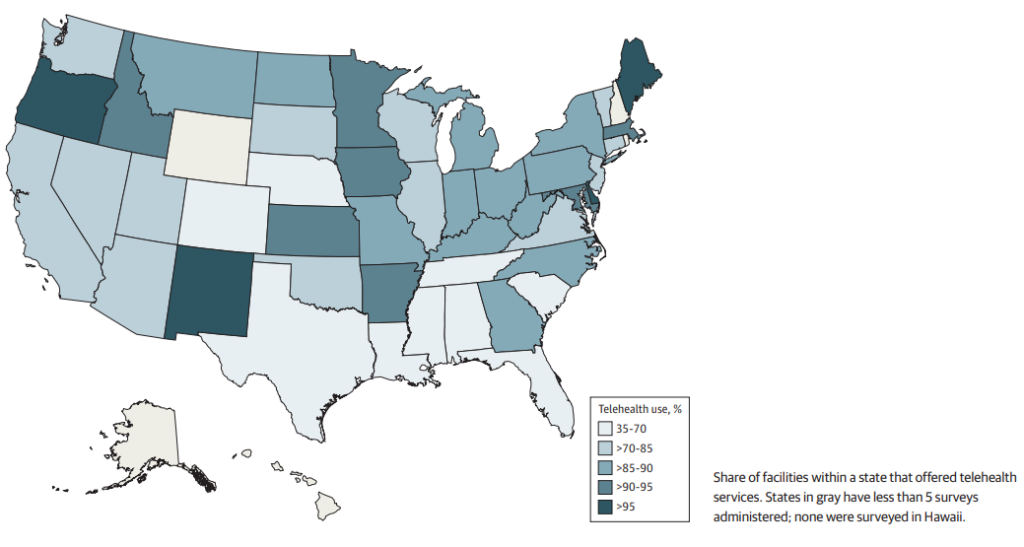
With Reported Telehealth Services
Conclusion:
The COVID-19 pandemic has undeniably accelerated the shift towards telehealth in mental health care. However, prospective clients may face several hurdles in finding a facility that offers comprehensive telehealth services. Therefore, it is paramount to continue exploring ways to optimise the availability and accessibility of these services.
