
Introduction
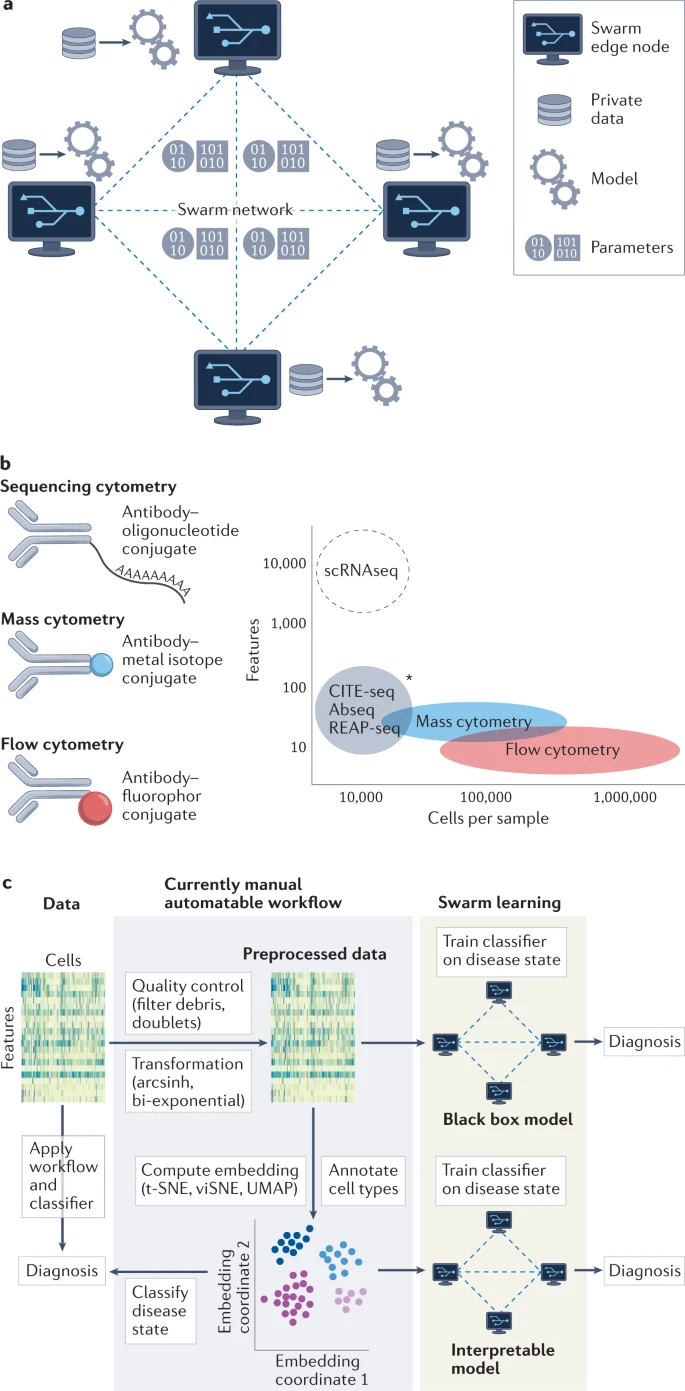
In immunological research, the translation of findings from animal models to human diseases has been challenging. Traditional methods face limitations in scalability, data sharing, and privacy concerns, hindering the progress of research in human immunology. However, recent technological advancements in genomics, artificial intelligence (AI), and novel disease modelling techniques offer promising solutions to magnify medical innovation. Among these innovations, Swarm Learning (SL) emerges as a groundbreaking approach that addresses the barriers to collaborative research while ensuring data security and privacy. Swarm Learning in Clinical AI (Figure 1a) has been gaining momentum for the advantages it brings in data accuracy and diagnostics.
Unlocking the Potential of Swarm Learning in Clinical AI
Immunological research has entered a new era with the advent of advanced technologies such as single-cell RNA sequencing and mass cytometry (Figure 1b). These tools provide unprecedented insights into cellular mechanisms but pose challenges in analysing large datasets, especially in multi centre clinical studies. Machine learning (ML), a subset of AI, plays a pivotal role in automating the analysis of complex data patterns. SL leverages ML algorithms to scale analytical approaches and uncover molecular patterns in single-cell data efficiently (Figure 1c).
SL facilitates collaborative research by allowing multiple sites to pool their data without compromising patient privacy. Each research site acts as a node in the decentralised Swarm network, participating in model training with local data. The use of private blockchain technology ensures data security and confidentiality. This enables researchers to work together on a shared ML model. By automating the process of training and improving models, SL streamlines the analysis of vast datasets, leading to more accurate disease classification and stratification.
Empowering Collaborative Research in Immunology
One of the key advantages of SL is its ability to overcome the limitations of data sharing imposed by privacy laws. While protecting individual health data is crucial, current regulations restrict the sharing of large datasets necessary for comprehensive research. SL provides a solution by enabling researchers to collaborate across multiple sites. This collaborative approach accelerates research progress, and facilitates the discovery of novel insights in human immunology.
Conclusion
SL represents a unique approach to clinical AI in immunological research. It offers a secure and decentralised platform for collaborative data analysis. It combines the power of ML, blockchain technology, and data privacy regulations. SL paves the way for innovative discoveries and advancements in human immunology. SL’s ability to scale analytical approaches, streamline data analysis, and ensure data security is exemplary. SL holds promise in the field of immunological research and improve patient outcomes worldwide.
