
Introduction
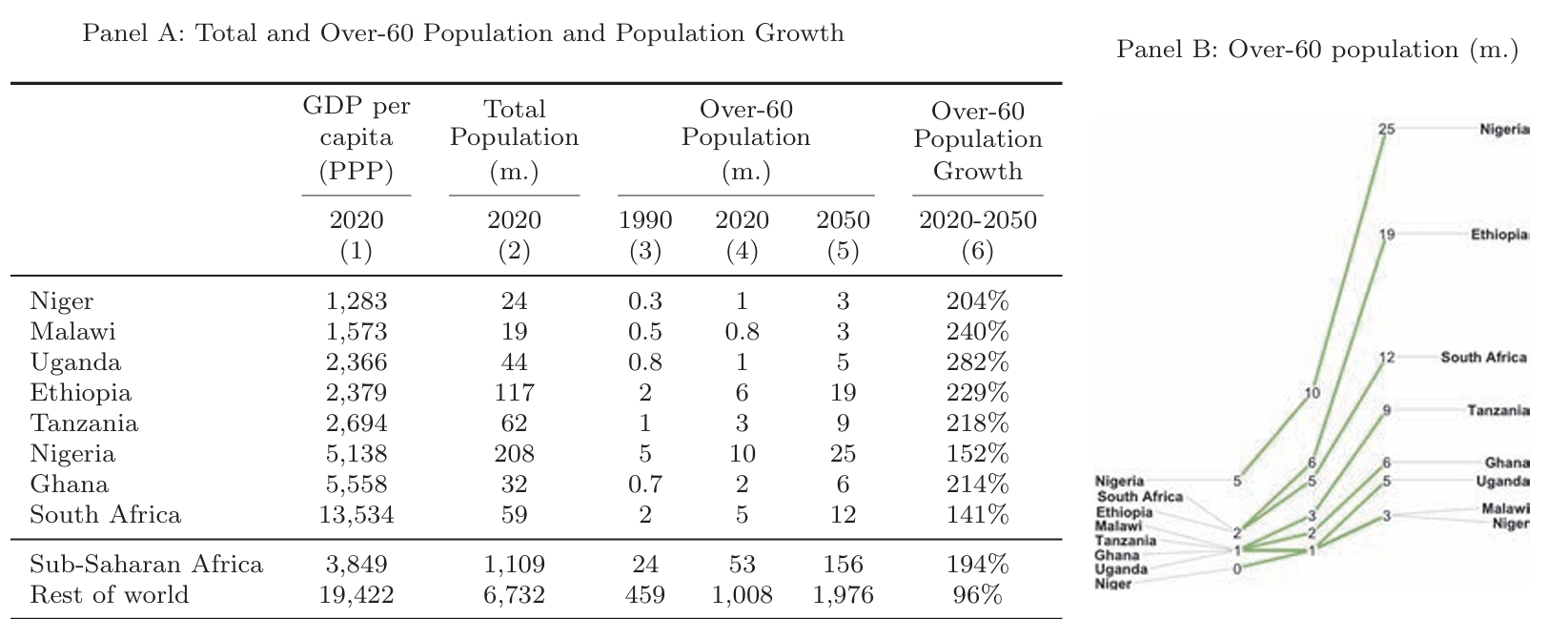
The elderly population in sub-Saharan Africa is set to experience unprecedented growth. Projections indicate a rise from 50 million in 2020 to 150 million by 2050, and over 600 million by 2100. This rapid increase necessitates urgent attention to healthcare and public support systems. Despite the current unpreparedness, Sub-Saharan Africa has the potential for innovative policy responses. The National Bureau of Economic Research explores the healthcare challenges and opportunities for sub-Saharan Africa’s Ageing Population.
Current Policy Environment
Sub-Saharan Africa’s healthcare systems lag behind other regions. For example, only 13% of countries have high service coverage, while 26% have low service coverage. Life expectancy at age 60 is 18 years, compared to 20 years in other low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) and 24 years in high income countries (HICs). The region faces a “double-burden” of disease, with rising non-communicable diseases alongside persistent infectious diseases.
Public support programs are also lacking. Social protection expenditure on older persons averages around 1% of GDP, compared to 4% in other LMICs and 8% in HICs. Less than a quarter of the elderly population has pension coverage, compared to approximately half in other LMICs and near-universal coverage in HICs.
Healthcare Challenges
The healthcare needs of the elderly in Sub-Saharan Africa are complex. Older individuals often live in rural areas with limited access to healthcare facilities. Financial and non-financial barriers further hinder access. Stigma associated with conditions like dementia exacerbates these challenges. Women, in particular, suffer worse health outcomes in old age.
The healthcare systems are unprepared for the anticipated rise in non-communicable diseases. Many systems have experience treating infectious diseases but lack the infrastructure to manage chronic conditions. This gap must be addressed to improve health outcomes for the elderly.
Financial and Social Support
Family-based care systems have traditionally supported the elderly in Sub-Saharan Africa. However, these systems are under strain due to urban migration, declining fertility, and increased female labour force participation. Women are more likely to be unmarried and live alone in old age, increasing their risk of adverse health outcomes, financial insecurity, and social isolation.
Public support programs such as pensions and health insurance are essential. Governments must develop and expand these programs to reduce reliance on family-based care. Innovative solutions that incorporate familial and community involvement can help maintain psychological well-being.
Future Directions
Despite the current unpreparedness, there is an opportunity for effective policy design and implementation. Sub-Saharan Africa could benefit from a demographic dividend, with a growing working-age population reducing dependency ratios. This could free up resources for public programs.
Research is essential to inform policy. Data collection efforts should focus on high-quality, longitudinal datasets. Harmonisation with international studies will facilitate global comparisons. Context-specific measures of health care access, health outcomes, and financial security are necessary. Researchers should also explore the impact of education, human capital, and living standards on outcomes in old age.
Policies should address socioeconomic and gender-based inequalities. Older individuals in Sub-Saharan Africa are disproportionately exposed to poverty and deprivation. Lower-income and lower-education individuals exhibit higher mortality, greater disability, and lower quality of life. Women and unmarried individuals are particularly vulnerable. Policies must target the most vulnerable among the older population.
Conclusion
The rapid growth of the elderly population in Sub-Saharan Africa presents unique challenges and opportunities. Informal care systems are under threat from social and economic changes. However, positive economic growth and a demographic dividend could provide resources for innovative policymaking. Research and policy must focus on the needs of the elderly to ensure they receive adequate healthcare and support.
