
Introduction
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection poses a significant global health challenge, with 296 million people affected worldwide in 2019. The World Health Organization (WHO) aims to eliminate HBV as a public threat by 2030, setting ambitious targets for diagnosis and treatment coverage. Evaluating treatment eligibility is crucial for managing chronic HBV infection, yet current criteria, especially in low-income countries, present challenges. Screening tools like rapid diagnostic tests for hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) are widely available, but assessing treatment eligibility remains complex.
Simplified Testing Algorithms for HBV Treatment
Traditional criteria for treatment eligibility involve multiple tests, including nucleic acid tests and liver biopsies. However, simplified approaches like the Treatment Eligibility in Africa for the Hepatitis B Virus [TREAT-B] score, based on liver enzyme levels and hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) status, offer a more streamlined method. The Treat All strategy, advocating immediate antiviral treatment for all HBsAg-positive individuals, presents a radical but untested approach.
Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of the Treat All Approach
A study in The Gambia used a microsimulation model for an HBV-infected cohort of individuals aged 20 years. Outcomes to measure effectiveness were disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) and years of life saved (YLS). Different treatment algorithms found that TREAT-B resulted in 4877 DALYs averted and Treat All resulted in 9352 DALYs averted. While Treat All and TREAT-B showed promise in reducing disease burden, Treat All was not cost-effective in this setting. In a modelled cohort of 5000 individuals aged 20 years with chronic HBV infection, the
5-year budget impact was $1.14 million for Treat All, $0.66 million for TREAT-B. The analysis highlighted the economic challenges of lifelong treatment for all HBV patients and the importance of considering cost-effectiveness in public health interventions.
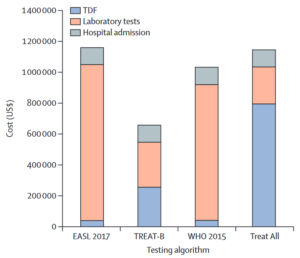
Figure 1. Five-year budget impact analysis of different testing algorithms in The Gambia Impact analysis for a cohort of 5000 individuals aged 20 years with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. TDF costs represent drug costs; laboratory tests include initial assessment and follow-up. Start-up costs are not represented because they are negligible. EASL, European Association for the Study of the Liver; TDF, tenofovir disoproxil fumarate; TREAT-B, Treatment Eligibility in Africa for the Hepatitis B Virus.
Challenges and Considerations
Implementing Treat All raises concerns about adherence, stigma, and treatment interruptions, which could impact its overall effectiveness. Operational feasibility, especially in low-resource settings, poses a significant hurdle. Comparisons with HIV treatment strategies underscore the need for tailored approaches in HBV management.
Conclusion
While the Treat All strategy may not be the optimal choice for The Gambia, the study suggests that a targeted, simplified algorithm like TREAT-B could offer a cost-effective solution to reduce HBV-related morbidity and mortality. Further research is essential to validate these findings in diverse healthcare settings.
