
Introduction
Lung cancer remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality worldwide. Early detection through screening can significantly improve survival rates. However, socioeconomic status (SES) plays a crucial role in both the prevalence of lung cancer and the effectiveness of screening programmes. A recent study published by The Lancet explores the relationship between SES and lung cancer outcomes, with a focus on the findings from the UK Lung Cancer Screening (UKLS) trial.
Understanding Socioeconomic Disparities in Lung Cancer
Socioeconomic deprivation is strongly linked to higher lung cancer rates. According to the Index of Multiple Deprivation (IMD) in the UK, individuals in the most deprived neighbourhoods are more likely to smoke, with 23.8% being current smokers in 2021 compared to 6.8% in the least deprived areas. This disparity in smoking prevalence contributes significantly to lung cancer risk. However, even after adjusting for smoking behaviour, lower SES remains an independent risk factor for lung cancer.
The Role of Risk Assessment in Screening
The UKLS trial utilised low-dose CT (LDCT) screening to detect lung cancer early in high-risk populations. The trial’s selection criteria included age and smoking history. Despite higher participation from individuals with higher SES, the inclusion of the Liverpool Lung Project (LLP) risk score ensured representation across all IMD quintiles. This approach highlights the importance of risk-based selection in lung cancer screening, potentially mitigating health inequalities by focusing on high-risk groups.
Long-Term Benefits of LDCT Screening
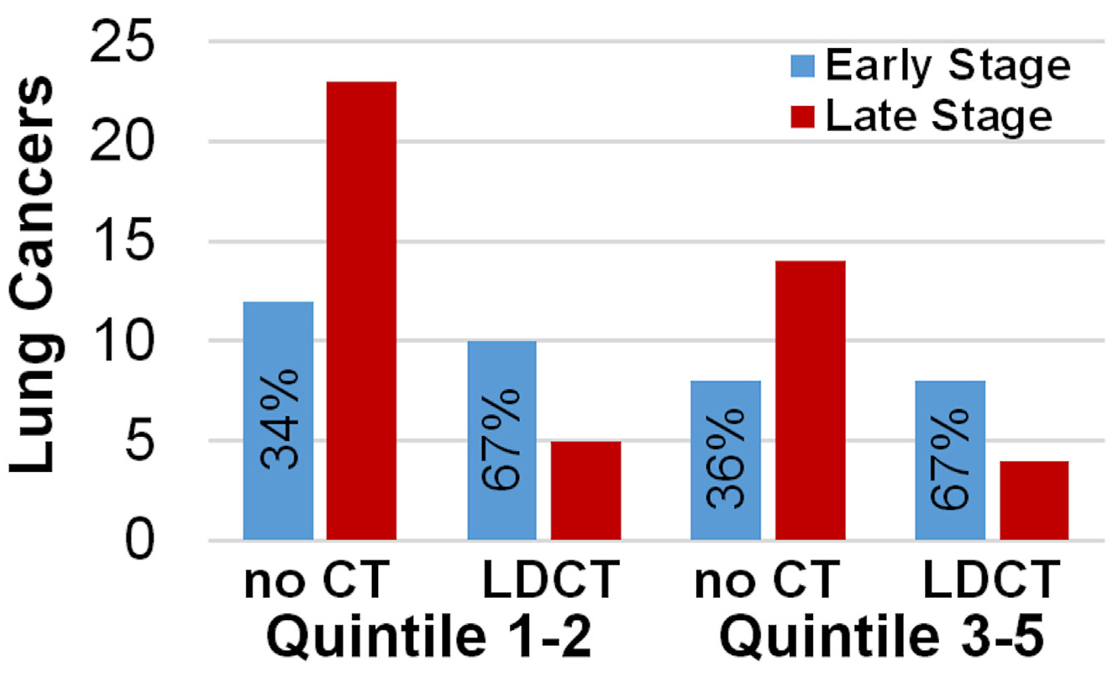
The UKLS trial demonstrated that LDCT screening offers long-term benefits in lung cancer survival, regardless of SES. Early detection allows for more effective treatments, including surgery, leading to improved outcomes. Notably, the trial found no excess incidence of lung cancer in the LDCT arm, suggesting minimal overdiagnosis. This finding highlights the effectiveness of LDCT screening in detecting lung cancer at an earlier stage, contributing to better survival rates.
Addressing Health Inequities in Screening
Despite the overall benefits of LDCT screening, the trial revealed a delayed convergence in lung cancer incidence rates between higher and lower SES groups. This delay may be attributed to greater awareness and better healthcare access among higher SES individuals. To enhance screening effectiveness for lower SES groups, more frequent awareness campaigns and improved access to LDCT facilities are essential. Engaging these populations more effectively can further amplify the benefits of lung cancer screening.
Impact of LDCT Screening on Other Health Outcomes
Interestingly, the UKLS trial also observed a reduction in deaths from other smoking-related diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and cardiovascular conditions, particularly in lower SES groups. This finding suggests that LDCT screening may have broader health benefits beyond lung cancer detection. Improved medical awareness, smoking cessation, and early diagnosis of other conditions likely contribute to these positive outcomes.
Conclusion
The UKLS trial provides valuable insights into the influence of socioeconomic status on lung cancer screening and outcomes. While LDCT screening offers significant benefits across all SES groups, targeted efforts are needed to enhance engagement and access for lower SES populations. By addressing these disparities, we can ensure that the advantages of early lung cancer detection are equitably distributed. This will ultimately lead to improving survival rates and overall health outcomes.
