
Introduction
Nutrition research is fundamental for public health, yet its reliance on self-reported dietary data and limited food composition information poses significant challenges. The complexity of food composition data, influenced by various factors, introduces uncertainties in estimating nutrient intake, impacting the accuracy of dietary assessments. This significant bias can lead to unreliable research outcomes and misguided dietary recommendations, ultimately affecting public health policies and individual health decisions.
Bioactive Content Variability
The study examines the impact of variability in bioactives like flavan-3-ols, (–)-epicatechin, and nitrate. Comparing estimates from self-reported data and food composition tables with biomarker measurements revealed substantial discrepancies. Specifically, the study found that the estimated intake of these bioactives varied significantly. For instance, the intake of flavan-3-ols ranged from 48 mg/day (minimum) to 329 mg/day (maximum), (–)-epicatechin from 1.5 mg/day (minimum) to 33 mg/day (maximum), and nitrate from 5.5 mg/day (minimum) to 204 mg/day (maximum), demonstrating the shortcomings of traditional estimation methods.


Challenges in Relative Intake Assessment
The variability in bioactive content complicates the ranking of participants based on relative intake. Simulations demonstrated the inconsistency in relative intake assessments, showcasing the disadvantages of relying solely on dietary data. For example, the study revealed that the same diet could place a participant in either the bottom or top quintile of intake, emphasising the unreliability of current assessment approaches. In addition, only 20-30% of participants were assigned to the same quantile when comparing self-reported intake with biomarker measurements.
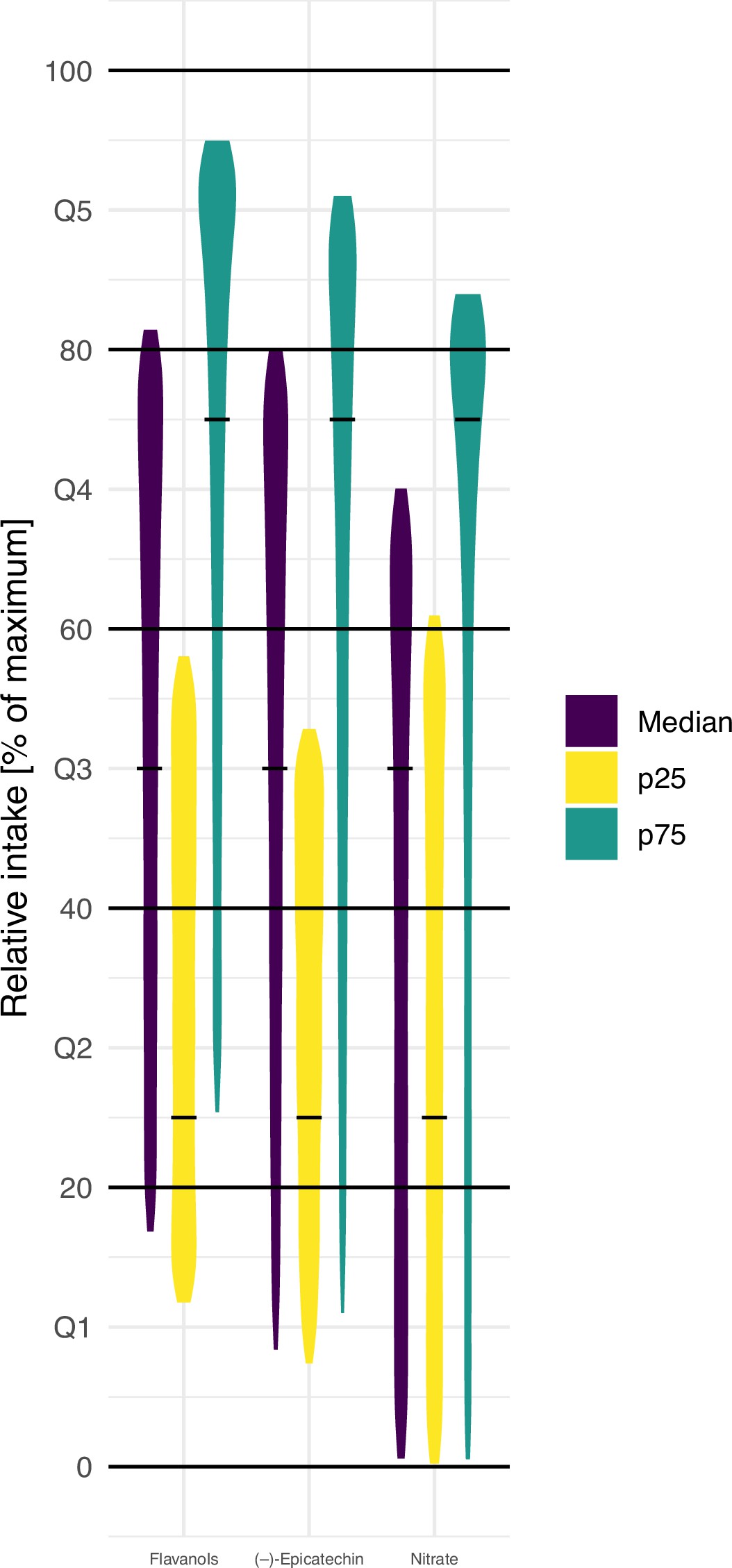
Implications for Health Endpoints
The study’s findings underscore the significant impact of food composition variability on associations between nutrient intake and health outcomes. Using food composition data alone led to conflicting results, focusing on the need for more accurate assessment methods. For instance, the study showed that relying on traditional methods could lead to diametrically opposite results in terms of health associations. Furthermore, variations in blood pressure estimates, from -1.0 mmHg to 0.8 mmHg, points out how bioactive content can skew conclusions.
Limitations
To enhance the reliability of nutrition research, the study advocates for the development and implementation of nutritional biomarkers. Biomarkers offer a more precise and unbiased assessment of nutrient intake, mitigating the uncertainties associated with food composition variability and self-reported data. By measuring biomarkers, researchers can obtain more reliable and actionable insights into dietary intake and its impact on health outcomes. For example, urinary biomarkers for flavan-3-ols and (–)-epicatechin provided more consistent and accurate estimates of intake compared to self-reported data.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the study’s outcomes shed light on the unreliability of nutrition studies reliant on conventional methods. The importance of biomarkers for dietary assessment urges a shift towards more accurate and actionable nutrition research insights. Thus, these findings underscore the necessity for enhanced nutrient intake assessment methods to bolster public health nutrition research reliability.
