
Robot-Assisted Surgery (RAS) is a technologically advanced form of minimally invasive surgery, offering a higher degree of precision compared to traditional laparoscopic methods. RAS allows surgeons to control the instruments of the robotic system remotely, providing a further minimally invasive surgical option for patients.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), there are currently 19 known manufacturers of robotic systems designed to aid in surgical procedures. The most widely used among these is the da Vinci® Surgical System.
The Austrian Institute for Health Technology Assessment (AIHTA) report focused on the use of RAS in thoracic and visceral surgery. Thoracic surgery primarily treats conditions of the lungs, chest wall, and diaphragm, while visceral surgery focuses on diseases of abdominal organs, the gastrointestinal tract, endocrine organs, the abdominal wall, and the peritoneum.
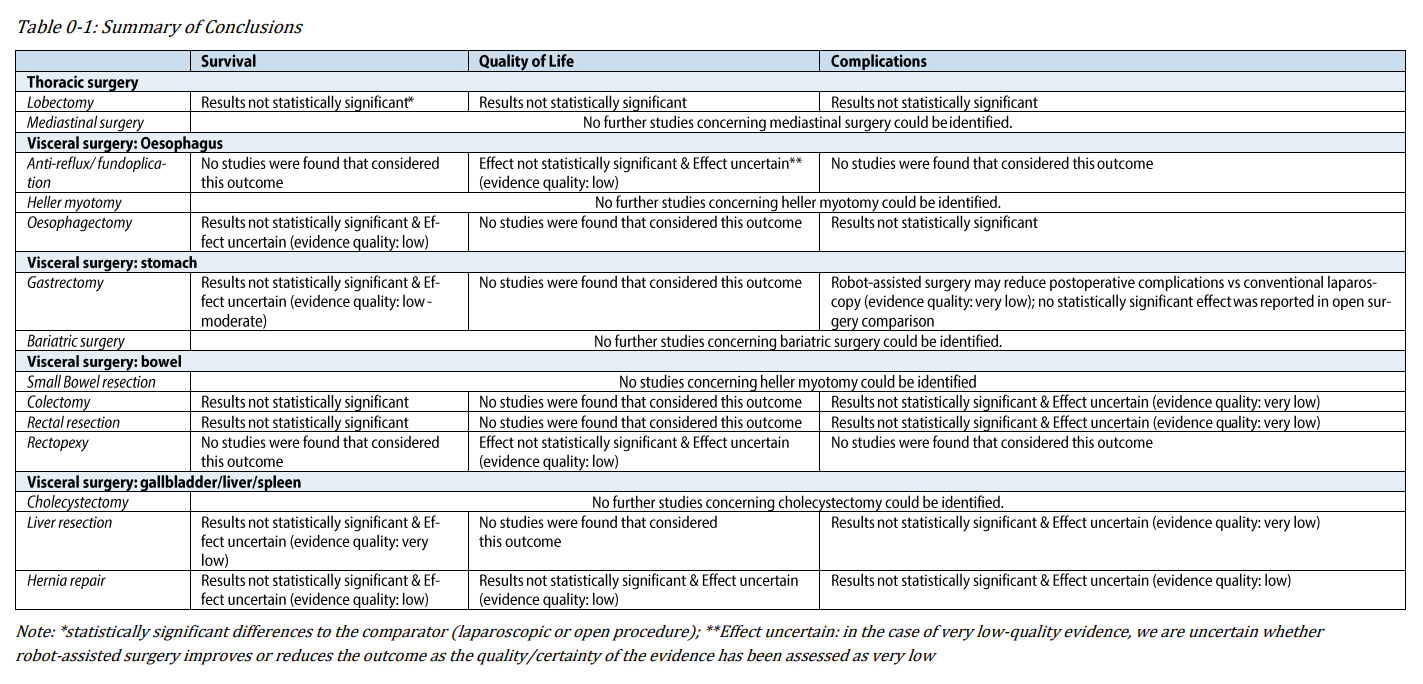 However, the report revealed mixed results regarding the effectiveness and safety of RAS. While RAS claims to reduce readmissions and shorten hospital stays, no statistically significant differences were detected compared to laparoscopic or open procedures.
However, the report revealed mixed results regarding the effectiveness and safety of RAS. While RAS claims to reduce readmissions and shorten hospital stays, no statistically significant differences were detected compared to laparoscopic or open procedures.
On the positive side, RAS resulted in decreased blood loss in certain procedures and fewer postoperative complications in others. However, it also tends to have a higher mean cost per procedure than conventional surgical methods.
The report concluded that while RAS might present potential advantages for certain indications and outcomes, most of the claimed benefits could not be materialised. Moreover, the financial and environmental implications must be considered in purchasing decisions.
In conclusion, while RAS is a promising tool in the field of surgery, more comprehensive studies with larger sample sizes and longer follow-up times are needed to conclusively determine its superiority over traditional surgical methods.