
Introduction
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) affects 5%–10% of the global population, with a higher incidence in China. Duodenal ulcer (DU) and gastric ulcer are common types of PUD, with DU prevalent in males aged 20-50. DU symptoms range from abdominal pain to severe complications like bleeding. Surgical treatment for peptic ulcers is considered when patients are unresponsive to medical therapy, noncompliant, or at high risk of complications, with options including vagotomy or partial gastrectomy for refractory ulcers that do not heal despite addressing underlying risk factors. The development of new proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) with improved efficacy, such as anaprazole or ilaprazole, is crucial, as they can significantly reduce the need for surgical intervention, which carries inherent risks and complications. This study demonstrates the pharmacoeconomic comparison of anaprazole to ilaprazole, which was selected as a reference drug due to its extensive clinical use in DU treatment.
Gastric Acid Suppression and Anaprazole
Gastric acid suppression is pivotal in DU treatment, with PPIs like Anaprazole playing a crucial role. Anaprazole sodium enteric-coated tablet (anaprazole) is a domestically developed PPI in China, holding an international patent. Approved in June 2023 as a class 1 innovative drug for treating duodenal ulcers, it has been included in the National Reimbursement Drug List (NRDL). Anaprazole inhibits gastric acid secretion, utilises a unique co-metabolism involving multiple enzymes and non-enzyme pathways, and reduces the drug’s retention time in the body due to its dual-channel excretion mechanism through the intestines and kidneys, which potentially decreases its side effects. Additionally, it reduces the impact of CYP enzyme gene polymorphisms. These better outcomes make it a potentially safer option for elderly patients and those on multiple medications.
Clinical Efficacy and Safety
Clinical efficacy is measured by the ulcer healing rate, assessed using endoscopic images after four weeks of treatment. The primary outcome indicator is the transition of ulcer status from the active phase to the scar phase. Safety is evaluated using the incidence rate of adverse drug reactions (ADRs). The study found that anaprazole has a higher ulcer healing rate compared to ilaprazole.
Health State Utilities and QALYs
Quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) are used to measure the effects in this model. QALYs are calculated by multiplying life expectancy with health preference utility. The health utility values for the active, healing, and scar stages are 0.7030, 0.7790, and 0.8420, respectively. The study did not apply discounting due to its short duration.
Pharmacoeconomic Comparison of Anaprazole and Ilaprazole
Assessing the economic impact of anaprazole is essential in a landscape of escalating healthcare costs. The study employs a Markov model to simulate patient health status transitions. This model includes four disease states: active, healing, scar, and recovery. Patients start in the active phase and transition through treatment phases until recovery. The model assumes that patients must progress from the active phase to the healing phase before advancing to the scar phase.
- Cost-Utility Analysis (CUA)
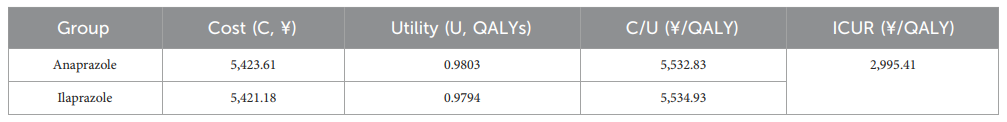
The study conducted a cost-utility analysis (CUA) to evaluate the economic impact of the treatments. The incremental cost-utility ratio (ICUR) is the principal outcome measure. The willingness-to-pay (WTP) threshold is set at the per capita Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of China for 2022. CUA results indicate that anaprazole has a higher composition and utility value than ilaprazole with an ICUR of 2,995.41¥/QALY, making it a cost-effective intervention below the WTP threshold of 85,698¥/QALY.
- Budget Impact Analysis (BIA)
The study assessed the potential impact of anaprazole on the health insurance fund from the perspective of health insurance. The total cost was calculated based on the frequency and dosage described in the medication guidelines and the actual circumstances of the clinical trials. Charges for registration and testing were derived from the price list of public medical services available on the hospital’s official website.
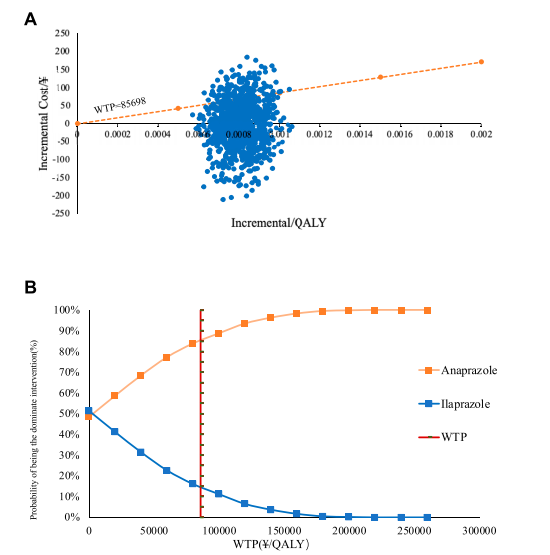
economical compared to ilaprazole at that WTP. (B) depicts the cost-effectiveness acceptability curve (CEAC).
Discussion and Future Implications
Anaprazole’s dual-channel excretion mechanism and reduced drug interaction risks position it as a favourable choice for DU treatment. Pharmacoeconomic evaluations comparing anaprazole to ilaprazole reveal promising cost-effectiveness and safety profiles, especially in the context of China’s healthcare system. Its economic viability and clinical benefits underscore the need for informed healthcare decision-making. While study limitations exist, ongoing research and long-term trials will provide more comprehensive insights into the efficacy and safety of new-generation PPIs.
