
Introduction
Pay-for-Performance (P4P) strategies have garnered attention for their potential to enhance healthcare quality and efficiency, particularly in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). Brazil’s National Programme for Improving Primary Care Access and Quality (PMAQ) serves as a prime example, with its vast reach and varied implementation across municipalities. A recent study examines PMAQ’s design features and their correlation with healthcare performance, offering insights for future P4P schemes.
Scheme Design: A Critical Factor in P4P Success
P4P initiatives are not one-size-fits-all. Their success relies on carefully considered design features, such as incentive targets, payment attributes, and safeguard mechanisms. These elements influence healthcare worker responses and the overall efficacy of the programme. An analysis of PMAQ reveals how these design features impact the quality of primary healthcare services.
Incentives and Performance: The Brazilian Experience
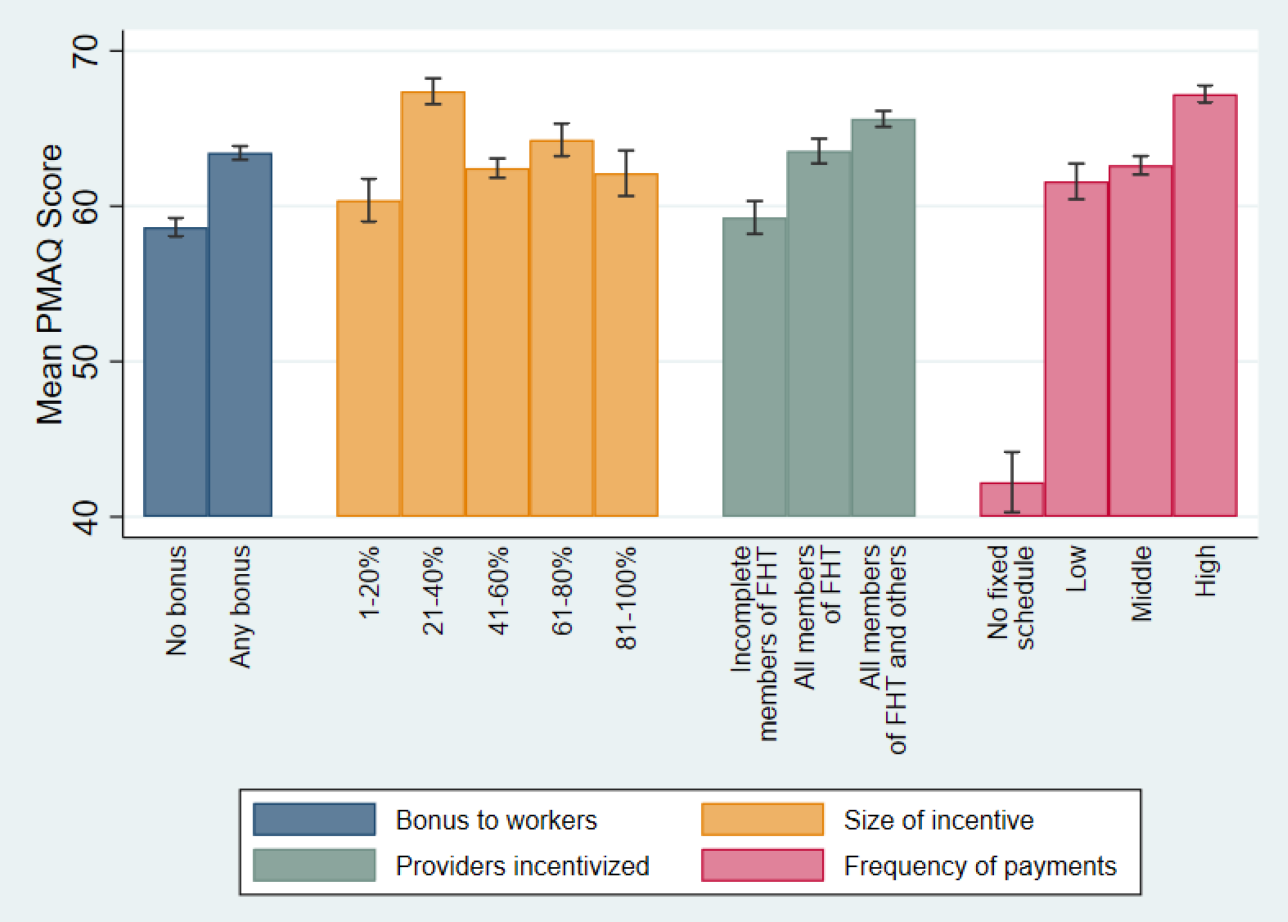
Municipal autonomy under PMAQ led to diverse approaches in disbursing funds, from direct bonuses to healthcare workers to investments in facility improvements. The study highlights the significance of bonus frequency and size, demonstrating that well-calibrated incentives can enhance team performance and, by extension, patient care quality.
Navigating the Challenges
Despite the positive findings, this study acknowledges several limitations. The reliance on self-reported data via electronic surveys introduces potential recall bias. This could affect the accuracy of the information gathered. Moreover, the sample size, representing approximately 15% of Brazilian municipalities, may not be fully reflective of the national landscape. More importantly, while the study utilises regression models, the observational nature of the data means that the associations identified cannot be conclusively deemed causal. Lastly, the study does not track the specific usage of PMAQ funds not allocated as bonuses. This is an area where further research could provide a more comprehensive understanding of the programme’s impact on healthcare delivery.
Implications of Pay-for-Performance in Brazilian Healthcare
The findings from PMAQ’s implementation shows the importance of P4P design in achieving desired healthcare outcomes. Policymakers must consider local context and healthcare system structure when crafting P4P schemes. This research suggests that a blend of frequent, appropriately sized bonuses, coupled with facility investments, can lead to substantial performance gains.
Conclusion
PMAQ’s journey offers valuable lessons for P4P programmes globally. Design features like bonus frequency and allocation size plays a very important role in driving performance. By carefully analysing these elements, we can guide the development of more effective P4P schemes that cater to the unique needs of LMICs.
