Transforming Patient Outcomes in Aortic Valve Replacement
Aortic stenosis (AS) is a condition that affects around 12.4% of the global population and seen most prevalent in the elderly with an estimated 10% of individuals over the age of 80 being affected. Traditionally, surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR) was the only treatment method as there is no medicine to treat this condition. However, transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) is becoming increasingly popular among healthcare practitioners and patients due to its less invasive nature and similar clinical outcomes. This also allows for the option of valve replacement in severe AS.
Mobile Digital Health Platforms: The Future of Patient Education
With the rise of smartphones, digital health technology has become a powerful tool in patient education and monitoring. Mobile applications are now being used to collect patient data, facilitate communication between patients and providers, and most importantly, improve patient outcomes. This has been proven to be successful in the management of diseases such as diabetes and chronic heart disease. Mobile apps for Gastroenterological and orthopaedic surgery reduce follow-up visits and monitor postoperative wounds. Prostate-, and lung cancer, and C-section postoperative outcomes can also be collected via mobile apps.
The Efficacy of Digital Health Platforms: A Case Study
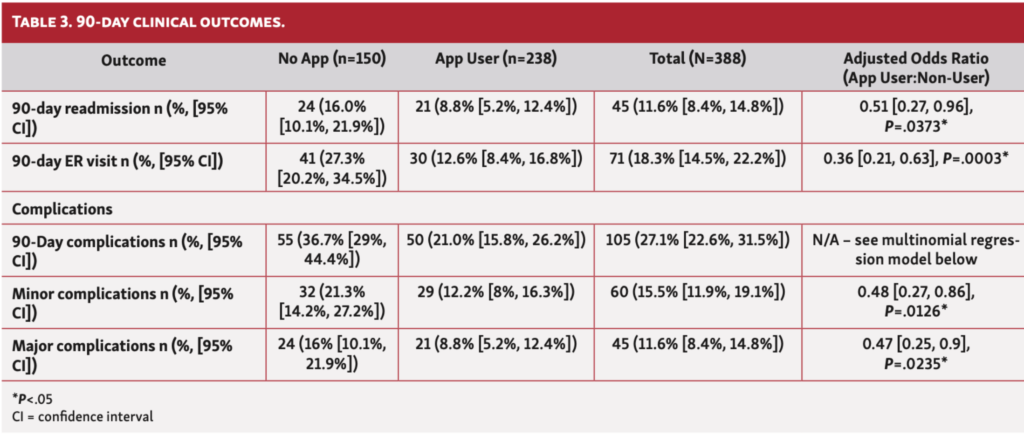
A recent study focused on the effectiveness of a mobile digital health platform, ManageMySurgery (MMS). MMS is a mobile app that supports patients during interventional procedures. This app contains links about surgery, care team communication, and duties to prepare patients for their treatments. It also serves as a reminder for checking into appointments, confirming preoperative instructions, and completing pre- and post-op surveys. The results were impressive, with significant reductions in emergency room visits, hospital readmissions, and complications among patients using the app.
Understanding the Mechanism of Benefit
This digital health application stands as one of the first for cardiac surgery shown to improve patient outcomes through objective measurements. While it’s not possible to prove direct causality, the study’s results suggest that digital health tools can significantly improve patient outcomes including reduced rehospitalisation and emergency room visits. These apps serve as partners in patients’ journeys, reminding them of actions they need to take before and after surgery. This ensures improved outcomes and a better quality of life.
Limitations and Future Directions
Despite the promising results, the study was not without limitations, including the potential for selection bias and the fact that it focused solely on TAVR patients. Future studies could expand the focus to include a wider variety of cardiothoracic procedures and explore the potential benefits of integrating the app with electronic medical records.
The Future of Digital Health in Healthcare
This study represents a significant step forward in understanding the potential of digital health platforms in improving patient outcomes. By engaging patients throughout every step of their surgical procedure, digital health tools can help improve individual patient wellbeing. Resulting in reduced the workload on healthcare providers, and assisting with alleviating the overall burden on healthcare resources.