
Introduction
Mental health disorders, particularly depression and anxiety, significantly impact US children and adolescents. With an annual cost of $247 billion, these conditions affect millions and pose a substantial burden on society. Recent data highlights an increase in clinically diagnosed depression and anxiety among youths aged 5 to 22 years from 2017 to 2021. These trends are drawn from a large integrated healthcare system in Southern California. A recent analysis focuses on the incidence and prevalence of these disorders, considering factors such as age, gender, race, ethnicity, and weight status.
Rising Incidence and Prevalence
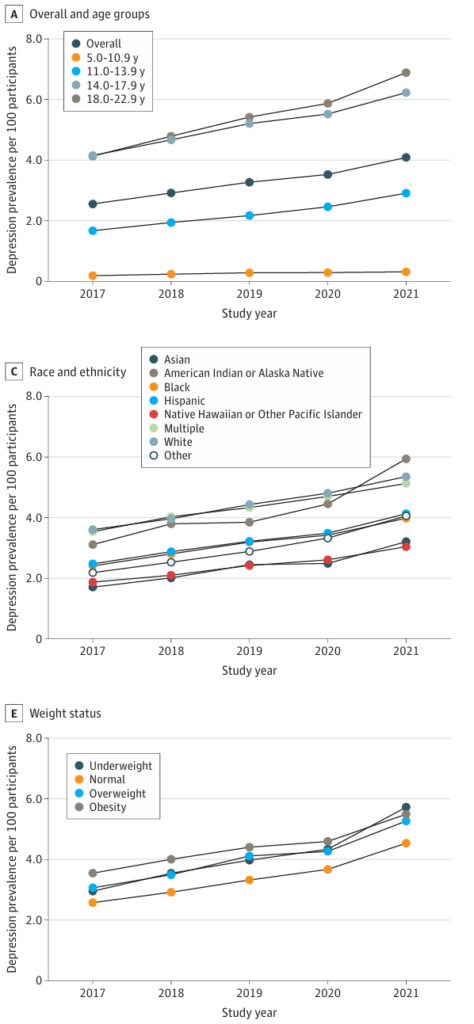
The period from 2017 to 2021 saw a marked increase in clinically diagnosed depression and anxiety among youths. Depression incidence rose by 55.6%, while prevalence increased by 60.0%. Anxiety without depression also showed significant growth, with a 31.1% rise in incidence and a 35.2% increase in prevalence. These trends were more pronounced during the COVID-19 pandemic, reflecting heightened mental health challenges during this period. Adolescents aged 14 to 17 and young adults aged 18 to 22 experienced the highest rates of depression. Anxiety without depression was notably higher among underweight individuals.
Demographic Disparities
The study reveals significant disparities in mental health diagnoses across various demographic groups. Female youths, those of American Indian, Alaska Native, or non-Hispanic White descent, and individuals from higher-income households exhibited higher rates of depression. Anxiety without depression was more prevalent among underweight individuals. These findings align with previous research indicating higher depression and anxiety rates among girls, older children, and those of White ethnicity. Interestingly, the study found higher depression and anxiety rates among youths from affluent families, contrasting with earlier survey data.
Impact of Weight Status
Weight status emerged as a critical factor influencing anxiety without depression. Underweight individuals exhibited the highest incidence and prevalence rates. Previous studies suggest that weight-related teasing may contribute to social isolation and mental health issues among underweight youths. Findings emphasise the need for early interventions to address anxiety in this group, potentially preventing the onset of depression. Obesity, a known risk factor for depression, further complicates the mental health landscape for affected youths.
COVID-19 Pandemic Influence
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly disrupted healthcare systems and exacerbated mental health challenges for adolescents. The data indicate that the pandemic contributed to the rising trends in depression and anxiety diagnoses. Despite healthcare access challenges, the rates of newly diagnosed clinical depression did not decline during 2020. Instead, the pandemic intensified existing trends, with 2021 recording the highest incidence of depression and anxiety without depression. This highlights the need for robust mental health services to support youths during and beyond the pandemic.
Conclusion
This recent study highlights the increasing incidence and prevalence of clinically diagnosed depression and anxiety without depression among US youths. These trends, observed across all demographic groups, call for enhanced mental health services. Addressing disparities in mental health diagnoses and providing early interventions for at-risk groups, such as underweight individuals, are crucial steps toward improving the well-being of our young population. As we navigate the post-pandemic landscape, strengthening mental health support systems remains imperative.
