
Introduction:
Inflammatory rheumatic diseases (IRDs) such as Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), and axial spondyloarthritis, are prevalent chronic conditions. They pose significant burdens on patients and healthcare systems, primarily due to fatigue symptoms. Fatigue prevalence in IRDs is high, affecting the quality of life and employment of patients. However, patient experiences with fatigue management in clinical settings are often unsatisfactory.
The Burden of Fatigue in IRDs:
Fatigue is a common symptom in patients with IRDs, with up to 80% of RA patients reporting significant fatigue. This fatigue can lead to impaired quality of life and work disability. Similar fatigue prevalence rates are reported for other IRDs, ranging between 66% and 85%. The impact on patients’ quality of life and employment is equally significant.
Non-Pharmacological Interventions for Fatigue:
Growing recognition suggests that cognitive-behavioural approaches (CBAs) and programmes designed to support increased physical activity can improve fatigue and health-related quality of life. However, it is crucial to assess the cost-effectiveness of these interventions due to the scarcity of healthcare resources. Economic criteria can help determine if health gains are worth the increased health care resources needed. Only one cost-effectiveness study for fatigue in similar clinical populations was done for CBA. Thus, a recent paper from the UK presented the results of an implementation trial that examined the cost-effectiveness of adding interventions to conventional methods in IRD patients with chronic, moderate to severe fatigue.
Managing Fatigue in Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases:
A cost-effectiveness analysis was conducted alongside the Lessening the Impact of Fatigue in Inflammatory Rheumatic (LIFT) trial. This trial investigated the clinical effectiveness of adding either a CBA or a personalised exercise programme (PEP) to usual care (UC) in reducing the impact and severity of fatigue for patients with IRD over a 56-week period.
Cost-Effectiveness of PEP and CBA:
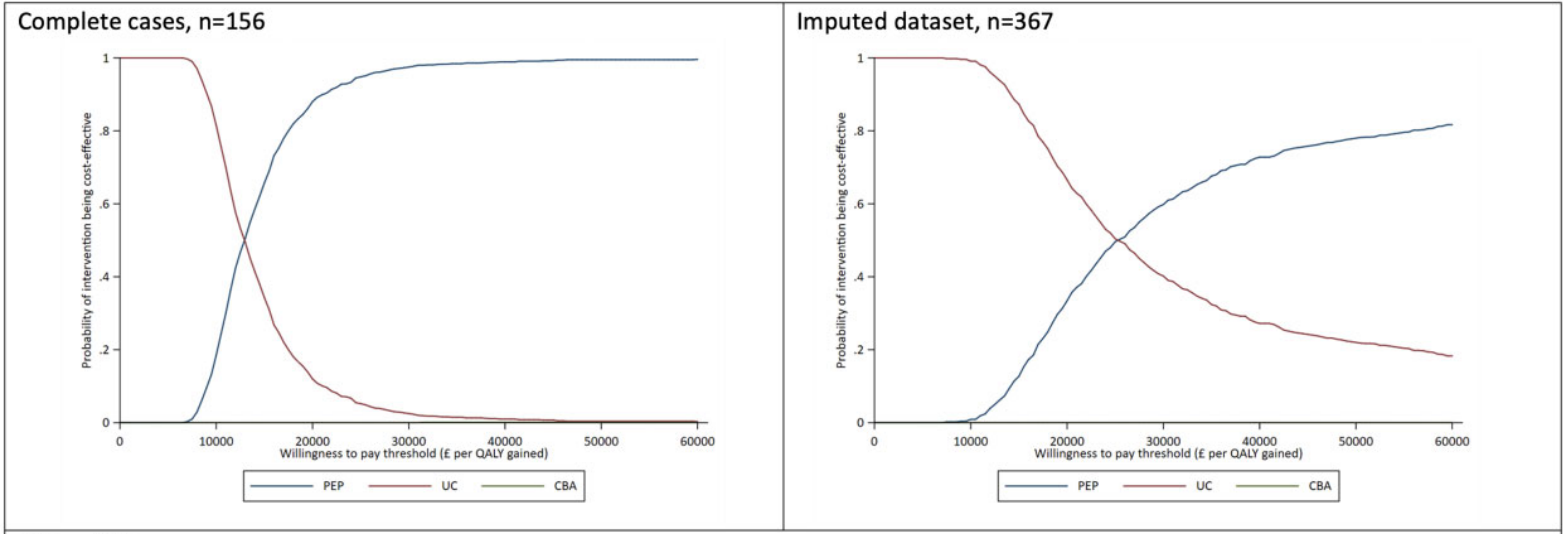
The cost-utility analysis revealed that both PEP and CBA were more expensive than UC alone. However, in the case of PEP, it was significantly more effective. And leading to an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) of £13,159 for PEP vs UC, and £793,777 for CBA vs UC. When comparing PEP against CBA, PEP was found to be dominant as it was associated with lower total mean costs and higher total mean quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) gained. The non-parametric bootstrapping results showed that, at a willingness-to-pay (WTP) threshold of £20,000 per QALY gained, PEP was found to have an 88% chance of being the preferred intervention. This economic evaluation provides valuable insights for decision-makers. Results are suggesting that PEP provides a cost-effective solution for managing fatigue in patients with IRDs.
Conclusion:
In the context of health economics and outcomes research (HEOR), a PEP offers a compelling value proposition for managing fatigue in patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases. When compared to UC alone, the integration of PEP into patient care strategies not only enhances health-related quality of life but also presents a cost-effective utilisation of healthcare resources. Therefore, from an economic perspective, PEP stands as a superior intervention to CBA and UC, underscoring its potential to optimise health outcomes and mitigate costs associated with inflammatory rheumatic diseases.
