
Introduction:
Long QT Syndrome (LQTS) is a cardiac disorder associated with sudden arrhythmic death. Traditional methods of detection, such as resting electrocardiography (ECG), are often inadequate as they fail to identify 30% to 50% of patients with concealed LQTS. However, recent developments in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) show promise in improving LQTS diagnosis accuracy.
Genetic Testing in LQTS Diagnosis:
Genetic testing plays a crucial role in diagnosing LQTS. A positive result is present in 80% of patients with a definite diagnosis of LQTS. Most cases that are genotype-positive (90%-95%) have culprit variants in the KCNQ1 or KCNH2 genes. The identification of a positive genotype in a patient has significant implications for their risk of arrhythmias, lifestyle recommendations, genetic counselling, and pharmacologic therapy. However, it’s important to note that genetic testing alone is not sufficient for diagnosing LQTS, especially in cases of concealed LQTS.
Machine Learning and LQTS Diagnosis:
ML, particularly convolutional neural networks (CNNs), is increasingly being applied to detect LQTS on ECGs. It can complement genetic testing, providing a more comprehensive and accurate diagnostic approach. These advanced AI methodologies offer a more accurate and efficient approach to identifying LQTS, even in patients with concealed or mild symptoms.
CNN Model Development and Testing:
A recent study tested a CNN model that identifies LQTS on baseline ECGs. The researchers developed this model for a diverse group of patients suspected of having LQTS. Furthermore, the model can differentiate between the most common LQTS genetic types. These types specifically involve variants in KCNQ1 or KCNH2.
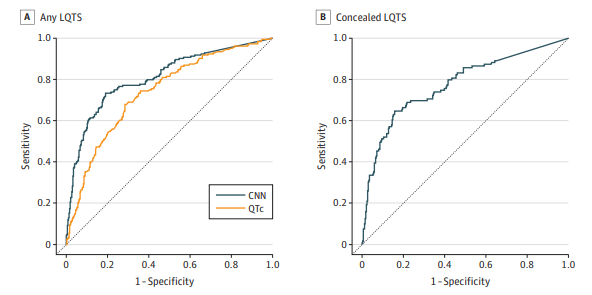
and Concealed LQTS Detection
Model Validation and Performance:
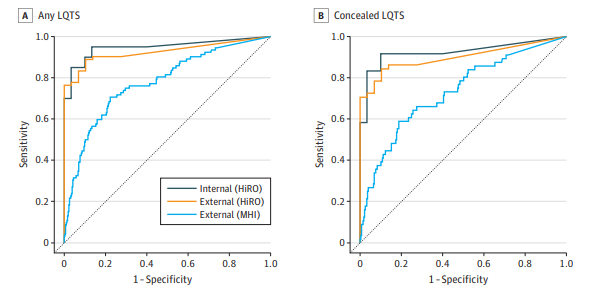
The CNN model demonstrated high accuracy and sensitivity in detecting LQTS and distinguishing between KCNQ1 and KCNH2 variants. The model’s performance was robust across different centres, ages, sexes, and ethnicities. It outperformed QTc intervals measured by arrhythmia experts, particularly in identifying LQTS in ECGs with normal or borderline QTc intervals.
Clinical Applications of CNNs in ECG Interpretation:
The use of CNNs in ECG interpretation could revolutionise LQTS diagnosis. ML can detect hidden features on ECGs, even in cases of concealed LQTS. This technology could be crucial for screening, helping to identify patients who may need further testing or are at risk of QT-mediated arrhythmias when exposed to QT-prolonging drugs. ML approaches are characterised by their lower requirement for knowledge, reduced time and labour intensity, and independence from other clinical information, unlike human readers. These methods can be used in small, underserved communities, where LQTS may be more common.
Conclusion:
CNNs are effective in detecting LQTS and differentiating between the two most common genotypes. Broader validation over an unselected general population may support the broad application of this model to stratify torsade de pointes risk in patients with suspected LQTS.
