Introduction
In today’s digital world, the internet plays a crucial role in how young people connect, learn, and develop. In 2022, 75% of 15–24-year-olds globally accessed the internet, a figure significantly higher than other age groups. This trend highlights the internet’s growing influence on young minds. However, as internet usage becomes widespread, concerns about its impact on mental health increase. Therefore, it is important to assess how internet use affects adolescent mental health, focusing on the mediating roles of parental support and self-education expectations.
Internet Use and Adolescent Mental Health
Research on internet use and adolescent mental health explores three main perspectives: negative, positive, and neutral impacts. The “Negative Impact Theory” links excessive internet use to mental health issues like anxiety and depression, while the “Positive Impact Theory” highlights benefits such as enhanced knowledge and social connections. The “No Effect Theory” argues that internet use does not significantly affect mental health. Theoretical explanations include the displacement hypothesis, which suggests internet use reduces time for beneficial real-world activities; social compensation theory, which posits that technology can help adolescents with social skill deficits; and the “Downward Spiral” concept, where avoidance behaviours and poor mental health reinforce each other.
The Dual Impact of Internet Use
Internet use among adolescents presents both opportunities and challenges. On one hand, it offers substantial educational and social benefits. On the other, it poses risks to mental health. In high-income countries, 86% of school-age children have internet access at home, compared to just 6% in low-income nations. This disparity shows how economic factors influence internet access. While internet access can enhance learning and social interactions, excessive use can lead to psychological issues. A study across 11 European countries found that 4.4% of adolescents exhibited “Pathological Internet Use.” This condition is linked to a lack of emotional and psychological support. Understanding the types of internet activities adolescents engage in is crucial. Positive behaviours like reading news or participating in forums can be beneficial. In contrast, activities like online gambling can be detrimental.
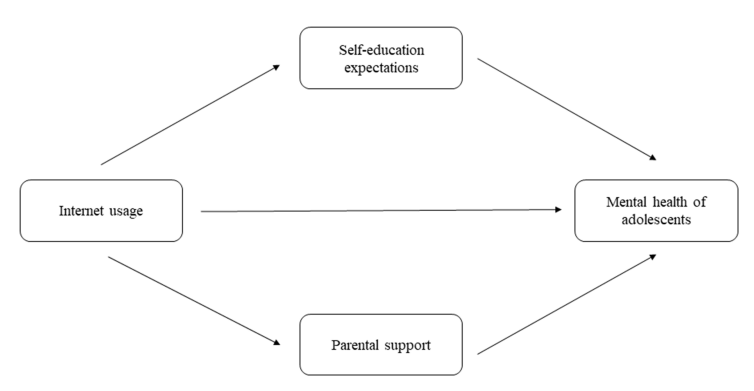
Self-Education Expectations as a Mediator
Self-education expectations significantly influence adolescent mental health. Adolescents who use the internet for learning and information gathering tend to have higher educational aspirations. This finding challenges the notion that internet overuse leads to academic burnout. Instead, it suggests that the nature of internet use is what matters. When adolescents use the internet constructively, they gain valuable knowledge and skills. This, in turn, boosts their self-esteem and mental well-being.
The Critical Role of Parental Support
Parental support plays an important role in shaping adolescents’ internet use and mental health. Supportive parenting mitigates the negative effects of internet overuse. Parents can guide their children by setting boundaries and encouraging healthy online habits. Parental mediation theory suggests that parents should employ communication strategies to reduce media’s adverse impacts. Creating a supportive home environment is essential. It encourages open communication and self-regulation, preventing internet-related issues like Internet Gaming Disorder (IGD).
Bridging Theory and Practice
Family Systems Theory suggests that a family functions as an interconnected system where interactions among members influence individual behaviours and mental health. Self-Discrepancy Theory posits that differences between one’s ideal self and actual self can lead to negative mental health outcomes. This study supports both theories and highlights the mediating roles of parental support and self-education expectations in internet use and adolescent mental health.
The findings emphasises the need for policies that promote healthy internet use among adolescents. Educating parents about internet risks and setting criteria for problematic use are crucial steps. Internet companies should develop tools to guide adolescents towards positive online experiences. For instance, cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT)-based games like SPARX can be as effective as therapist-led programs in treating depression.
Conclusion
Internet use is an inescapable aspect of modern adolescence. Its impact on mental health is complex, influenced by factors like parental support and self-education expectations. When examining the relationship between adolescents’ mental health and internet use, it’s crucial to differentiate between healthy activities like reading emails and news, which can be beneficial, and problematic behaviours like online gambling, while also assessing the intensity and content of internet use for both positive and negative impacts. By fostering positive internet habits and supportive environments, we can enhance adolescent well-being. Future research should continue to explore these relationships, considering long-term trends and diverse age groups. Addressing these challenges will help us realise the internet’s potential while safeguarding mental health.
