
Introduction
The Australian Institute of Health and Welfare reported a significant rise in cancer cases, with glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) accounting for 62% of all central nervous system cancers. GBM poses challenges due to its poor median survival rate of 14-16 months. The standard treatment protocol involves a multidisciplinary approach, emphasising the need for seamless coordination among various medical departments. Despite the existing protocols, the lack of a recognised standard regimen post-progression remains a concern.
Cancer care coordination plays a significant role in enhancing healthcare quality for patients, caregivers, and clinicians. Studies have highlighted the positive impact of patient navigators or cancer care coordinators on access to care, therapy adherence, and overall patient satisfaction. In a recent study, the impact of brain cancer care coordinators (BCCCs) on quantitative outcomes such as health service resource utilisation and survival rates of GBM patients was explored.
Role of Brain Cancer Care Coordinators
BCCCs are specialised nurses who support all patients diagnosed with primary brain cancers. They assist with navigation, symptom management, and emotional support for both patients and carers, providing help both in-person at hospitals and via phone calls. Their primary goal is to ensure that patients receive timely and appropriate care, reducing unnecessary hospital visits and improving overall outcomes.
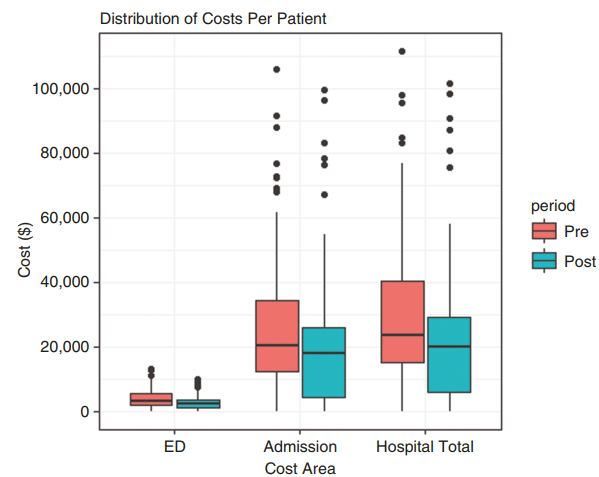
An analysis was conducted on 187 patients diagnosed with glioblastoma within the Hunter New England Local Health District between 2013 and 2019. Healthcare utilisation and outcomes before and after the implementation of BCCCs were compared. The introduction of BCCCs in 2016 marked a significant change in patient management in terms of emergency department (ED) presentations, hospital admissions and the quality of patients’ lives.
ED Presentations and Hospital Admissions
One of the key findings of the study was the impact of BCCCs on ED presentations and hospital admissions. A noticeable reduction in ED visits, from 401 to 300, was observed after the introduction of BCCCs to the healthcare system. Consequently, the total length of stay in the hospital decreased by 25%. These reductions in healthcare resource utilisation underscore the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of BCCCs in managing GBM patients.
Overall Survival Rates
Hong et al. also examined overall survival rates among patients. Before the introduction of BCCCs, the median overall survival was 12.0 months. After the implementation of BCCCs, the median survival slightly decreased to 11.16 months. Although the difference in survival rates was not statistically significant, the reduction in time spent by patients in hospital and ED can be considered as an improvement in the patients’ quality of life.
Cost-Offset Analysis
The cost-offset analysis compared the investment in BCCCs against the valuation of healthcare resource use differences between the pre and post cohorts. The study found that the introduction of BCCCs led to a reduction in emergency presentations by AUD$1200 and hospital admissions by AUD$5500 per patient, which in turn result in an annual saving of AUD$167 634 in healthcare expenditures. When the cost of hiring the care coordinator was taken into account, the program demonstrates an annual net saving of AUD$4410. This finding supports the economic viability of investing in BCCCs as a means to improve patient care and reduce overall healthcare expenditure.
Conclusion
Analysing the data of glioblastoma patients allowed a comprehensive evaluation of the impact of cancer care coordinators as it is a disease with a well-established treatment protocol. BCCCs showed an important role in managing healthcare utilisation and outcomes for patients with glioblastoma. It was demonstrated that the introduction of BCCCs led to a reduction in ED presentations and hospital admissions. Although the impact on overall survival rates was not significant, the cost-offset analysis highlighted the economic benefits of investing in BCCCs.
As healthcare systems continue to evolve, the role of specialised care coordinators will become increasingly important. By providing targeted support and improving care coordination, BCCCs can enhance patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs. Future research should focus on identifying the factors that influence survival rates and exploring ways to optimise the role of BCCCs in patient care.
