
Introduction
With 68% of adults aged 65 and older living with multiple chronic conditions, maintaining independence in daily and social activities is vital for healthy ageing. Occupational therapy (OT) for frail older adults is crucial in this context, enhancing functional performance and social participation. Occupational therapists are healthcare professionals dedicated to enabling individuals to engage in meaningful daily activities within their living environments. Particularly, their holistic approach addresses physical, cognitive, and emotional challenges, fostering health and well-being.
The Role of Occupational Therapists
Occupational therapists help older adults manage their chronic conditions by enabling engagement in meaningful daily activities. They use evidence-based practices to optimise healthcare resource utilisation, significantly improving older adults’ functional performance, reducing fall rates, and decreasing hospital readmissions. Their goal is to foster health and well-being within the individual’s living environment. For instance, Clemson et al. discovered that home safety adaptations can reduce falls by 26% in individuals aged 60 and older, and by 38% in high-risk groups, such as those who have fallen in the past year, recently been hospitalised, or require assistance with daily activities. Hence, research shows that OT recommendations significantly improve older adults’ functional performance and reduce fall rates. A recent article from BMC Geriatrics investigated an evidence-based intervention designed to improve therapy adherence among frail older adults and their caregivers in Belgium.
Challenges in Therapy Adherence
Achieving full adherence to OT recommendations remains challenging. Factors influencing adherence include belief in the intervention’s effectiveness, involvement in goal setting, and interdisciplinary collaboration. Complex interventions for multiple chronic conditions require flexibility in delivery and consideration of various influencing factors.
Developing the ProMOTE Intervention
The ProMOTE intervention is an evidence-based occupational therapy programme aimed at improving the functional performance and social participation of frail older adults living at home. It focuses on enhancing therapy adherence among these individuals and their caregivers through cognitive, behavioural, and environmental strategies. The intervention is structured into six detailed steps, each outlining specific goals, actions, communication strategies, required resources, timeframes, involved partners, and measurable quality indicators.
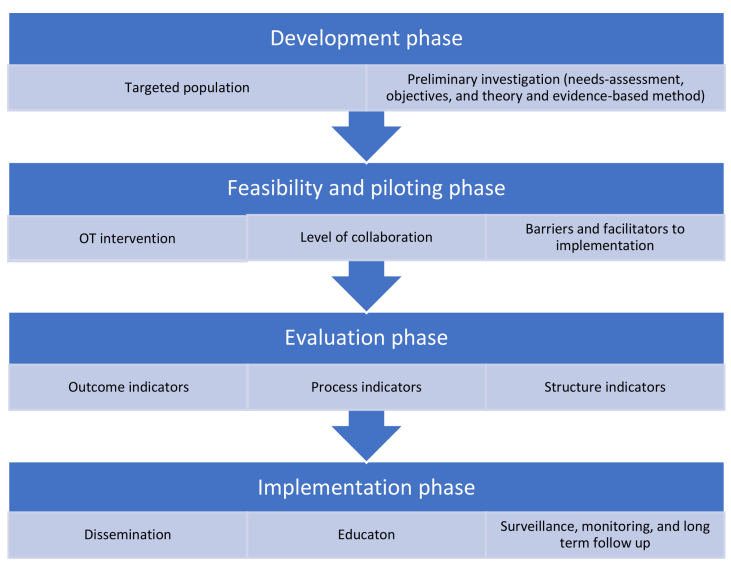
By integrating both clinical and research perspectives, ProMOTE not only specifies what needs to be done but also explains why and how to do it. This comprehensive approach supports older adults in maintaining their independence and quality of life, ultimately facilitating safe ageing in place. Therefore, the ProMOTE intervention has been piloted for feasibility, addressing barriers and facilitators to implementation. Designed to be flexible, person-centred, and integrated, it ensures comprehensive support for older adults.
Future Directions and Recommendations
To evaluate the effectiveness of the ProMOTE intervention, further rigorous studies are needed. These studies should assess the intervention’s impact on adherence, functional performance, and social participation. Furthermore, cost-effectiveness and cost-utility analyses are essential to justify increased government funding for occupational therapy in primary care. Nevertheless, a significant challenge lies in measuring the impact of occupational therapy on improved outcomes and lower costs in clinical practice, which is essential for integral quality management.
Conclusion
Occupational therapy for frail older adults is crucial for enhancing functional performance and social participation. The ProMOTE intervention, developed through evidence-based practices, aims to improve therapy adherence and promote healthy ageing. However, further research is needed to validate the intervention’s effectiveness and cost-efficiency, potentially leading to broader implementation and increased funding for occupational therapy in primary care.
