
Introduction
Falls pose significant challenges for older Australians, impacting both individuals’ quality of life and the healthcare system. Older adults (65 years and older) are 68 times more likely to die from falls compared to those aged 15-64 years. Besides, falls are the primary cause of injury-related fatalities across all age groups, with older adults being disproportionately affected, comprising 94% of all deaths resulting from falls. The financial burden is also substantial, with falls costing the Australian healthcare system A$2.3 billion annually. Despite these alarming statistics, falls have not received adequate policy attention as a public health issue. Adopting a systems approach to falls prevention in Australia can significantly reduce the incidence of falls and alleviate the associated burdens on individuals and the healthcare system.
Goals of Falls Prevention Policies
Current policies for falls prevention in Australia aim to reduce the incidence of falls and mitigate their impact. Specific goals include decreasing the proportion of older people with fall-related insecurities, expanding falls prevention programs in regional areas, and establishing education programs targeting falls. The National Preventive Health Strategy 2021–2030, although not explicitly focused on falls, provides a framework for improving access to healthy diets and increasing physical activity, which can indirectly reduce falls.
Policies: Identifying Gaps and Needs
Falls are often linked to poor nutrition, physical inactivity, and chronic diseases. They can lead to severe injuries, increased hospital admissions, and a higher likelihood of being admitted to aged care facilities. Addressing this issue requires a comprehensive understanding of the risk factors and the implementation of targeted interventions. The current draft National Injury Prevention Strategy 2020-2030 covers factors like housing standards and exercise programs but omits others such as nutrition and public awareness. A holistic policy should address all these factors and clearly outline implementation strategies, monitoring, and governance structures.
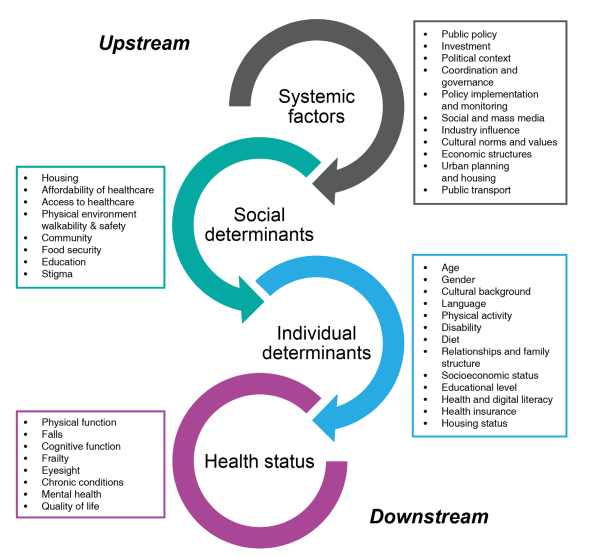
The Importance of Collaboration
Effective falls prevention requires collaboration across various sectors. Meaningful partnerships between healthcare providers, urban planners, aged care facilities, and policymakers are essential to achieve the desired outcomes. Long-term, multipurpose spaces where researchers and policy actors can share and test their understandings of policy issues are likely to be fruitful. Inclusion of diverse groups, including Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people and those with disabilities, is essential. Furthermore, there is a need for better information and data sharing across local, state, and federal governments.
Actions and Interventions
To achieve the goals of falls prevention, several actions and interventions are proposed. These include tailored programmes for different age groups, interdisciplinary partnerships, inclusive mass media campaigns, financial incentives, and funding for non-pharmacological interventions. Moreover, measures such as improving access to home environment assessments, increasing access to culturally relevant falls prevention programmes, and incorporating design features to reduce falls in public buildings and pathways are essential. It is also crucial that health service organisations have guidelines and models for falls prevention activities.
Values and Norms: Addressing Ageism and Ableism
Ageism and ableism can obscure proposed policy changes. Most Australians agree that ageism exists in society, with 64% of older people affected in the last five years. Policy documents often reflect institutional ageism, portraying older adults as a financial burden. Future policies should avoid assuming homogeneity among older people and consider the diverse contributions and needs of different cohorts of elderly.
Conclusion
Falls prevention in Australia is a pressing public health concern that requires dedicated policy resources. Adopting a systems-oriented approach can help reduce falls and their associated burdens on individuals and the healthcare system. By fostering intersectoral collaboration and targeting structural, environmental, and socioeconomic factors, falls prevention strategies can be more impactful, sustainable, and equitable.
