
Introduction
Preventable medical errors and adverse events in US hospitals are a significant concern, with estimated costs reaching $17 billion annually. Among these, falls represent the largest category of preventable adverse events. The costs associated with falls range from $351 to $13,616 per patient. A recent study aimed to estimate the cost of falls and related injuries using electronic health record (EHR) data and to analyse the costs and benefits of implementing the Fall TIPS (Tailoring Interventions for Patient Safety) Program. The Fall TIPS Program is an evidence-based initiative that has been associated with a 15% to 25% reduction in inpatient falls and a 0% to 34% reduction in injurious falls.
The Cost of Falls
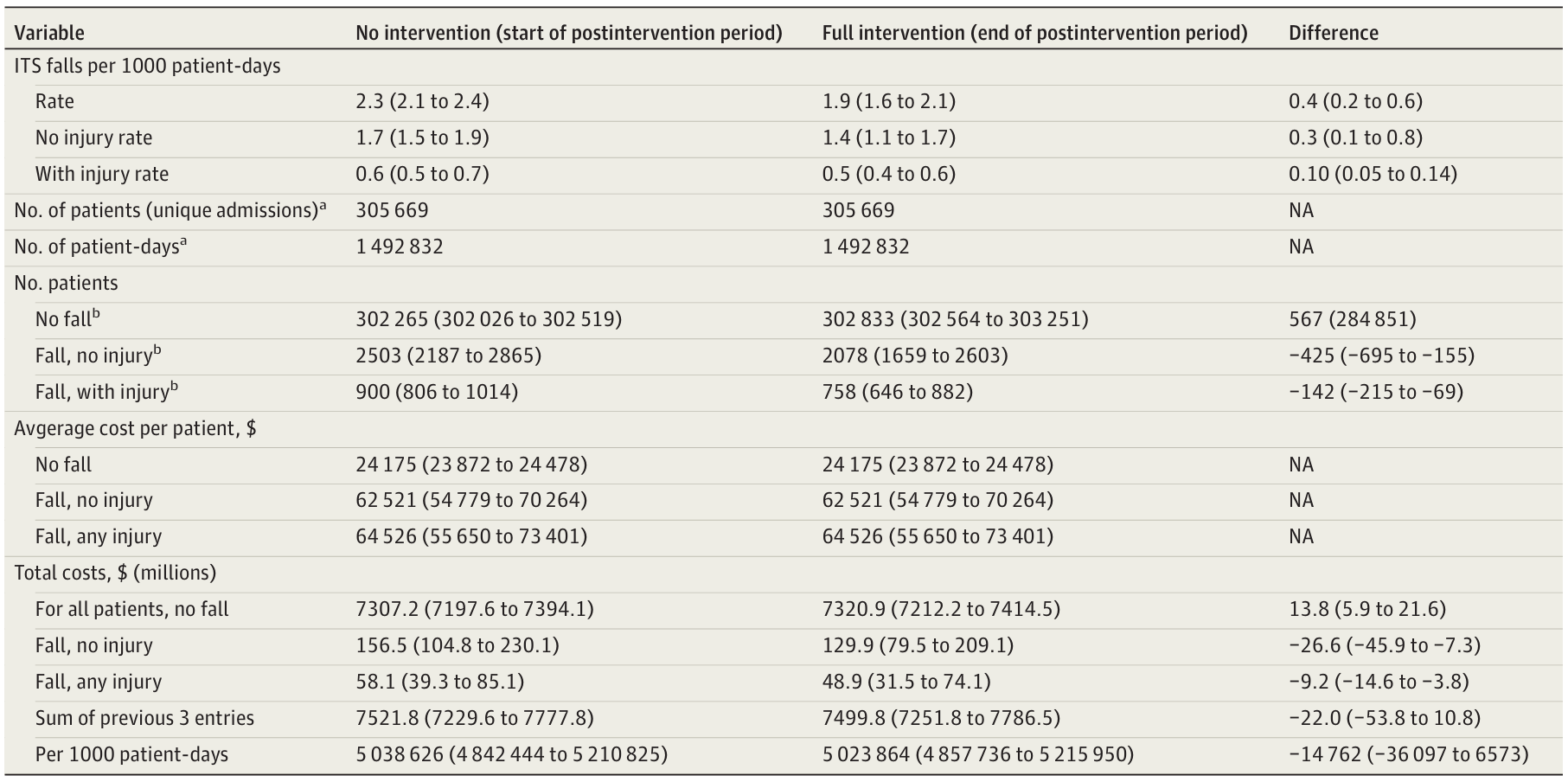
Falls in hospitals incur significant costs, both direct and indirect. The average total cost of a fall is $64,526, with direct costs amounting to $36,776. Interestingly, the severity of the injury does not significantly affect the cost. This implies that even non-injurious falls can lead to extensive evaluations and prolonged lengths of stay (LOS). The Fall TIPS Program has shown a total cost saving of $22 million over approximately five years at the intervention sites, projecting to a nationwide annual cost saving of $1.82 billion.
Benefits of the Fall TIPS Program
The Fall TIPS Program offers substantial cost benefits. The program’s implementation has prevented 50 excess deaths and saved $22 million in the post-intervention period across two healthcare systems. The costs of falls, whether with or without injury, were not appreciably different. This finding suggests that programs preventing all falls provide the greatest cost-saving opportunities. The program’s material costs averaged approximately $0.88 per 1,000 patient-days, focusing on registered nurse time. Even under conservative assumptions, the program results in net cost savings over a wide range of scenarios.
Policy Implications
In 2008, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) ended fall-related cost reimbursement, a controversial policy because some falls are not preventable. Many hospitals responded by implementing fall prevention strategies supported by little or no evidence. Today, there is wide variation in the implementation of effective fall preventive strategies. Financial incentives within the national quality payment program have been used to decrease the frequency and cost of patient falls. However, they address only fall injuries and a minority of cases. Policies that incentivize hospitals to prevent all falls may be the most cost-effective. The CMS should promote evidence-based fall prevention programs like the Fall TIPS Program.
Generalisability and Future Directions
This cost-benefit analysis is based on academic medical centres and community hospitals and should be generalisable to other organisations using the Fall TIPS Program. The level of detail to which costs can be compared depends on hospital-specific cost differences. This analysis could have accounted for true one-time development costs, but other hospitals will not incur development costs because the Fall TIPS Program already exists. Conversely, costs incurred and cost benefits depend on existing organisational structures to support patient safety. Cost benefits can be extrapolated by scaling results according to the number of patients. It may be possible to use data on patient characteristics, falls or injuries, and safety culture scores to perform a more sophisticated extrapolation to typical patient populations in other types of hospitals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the findings of this economic evaluation support that preventing falls through the use of an evidence-based program may reduce the costs associated with these adverse events. We found that the costs of falls were only marginally different by injury level. Policies that promote the reduction of all falls using evidence-based interventions may be most effective in reducing the frequency of harm and the associated costs.
