
Introduction
The effectiveness of current mental health planning in Australia has been repeatedly questioned. Despite increased national attention, mental health issues remain prevalent, costing AU$200 billion annually in social and productivity losses. Effective treatment and prevention strategies exist but are not fully implemented due to fragmented care, resource scarcity, and high out-of-pocket costs. Improved regional planning, using system dynamics modelling in mental health, is crucial, as centralised solutions often fail to address local variations. Economic evaluation can guide resource allocation and priority setting, yet traditional methods may not capture the complexity of mental health systems.
The Need for Improved Economic Evaluation
Economic evaluation is essential for informing resource allocation in healthcare. Traditional health technology assessments (HTAs) often use static cohort Markov models, which may not be suitable for complex public health issues. A systematic review of 65 economic evaluations of mental health interventions highlighted the need for improved methods that capture intersectoral costs and outcomes. Dynamic simulation modelling, including system dynamics, agent-based modelling, and discrete event simulation, offers a promising alternative. These methods account for the dynamic changes, feedback loops, and interactions within complex systems.
System Dynamics Modelling in Mental Health
System dynamics modelling is particularly suitable for macro health policy and long-term strategic decisions. It has been underutilised in mental health economic evaluations, despite its potential to address complex system behaviours. This study used system dynamics modelling to assess the cost-effectiveness of eight interventions aimed at improving mental health in the Australian Capital Territory (ACT). The ACT, with a population of 454,500 has experienced rapid growth and has a relatively young and educated demographic.
Findings and Implications
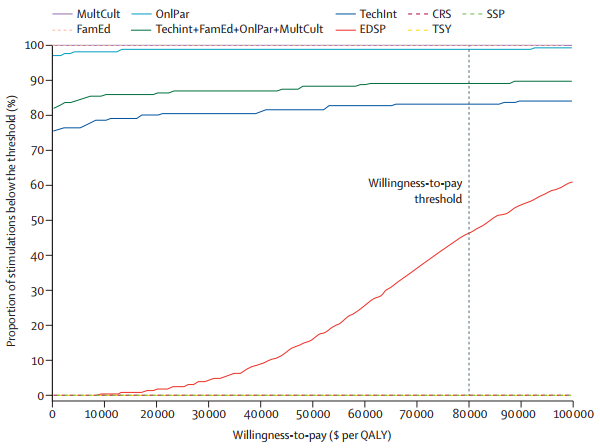
The study found that four interventions—technology-enabled integrated care, family education, online parenting programmes, and multicultural-informed care—were cost-effective. These interventions either improved health benefits while reducing costs or had incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs) below the willingness-to-pay threshold of AU$79,930 per quality-adjusted life year (QALY). Conversely, four interventions—emergency department-based suicide prevention, crisis response services, trauma services for youths, and school-based suicide prevention—were not cost-effective in the base case.
The incremental net monetary benefit (INMB) analysis revealed that technology-enabled integrated care had the highest INMB at AU$358 million, followed by the online parenting programme at AU$58 million, family education at AU$31 million, and multicultural-informed care at AU$11 million. The combination of these interventions yielded an INMB of AU$460 million. Interventions like emergency department-based suicide prevention and trauma services for youths had negative INMBs, indicating they were not cost-effective.
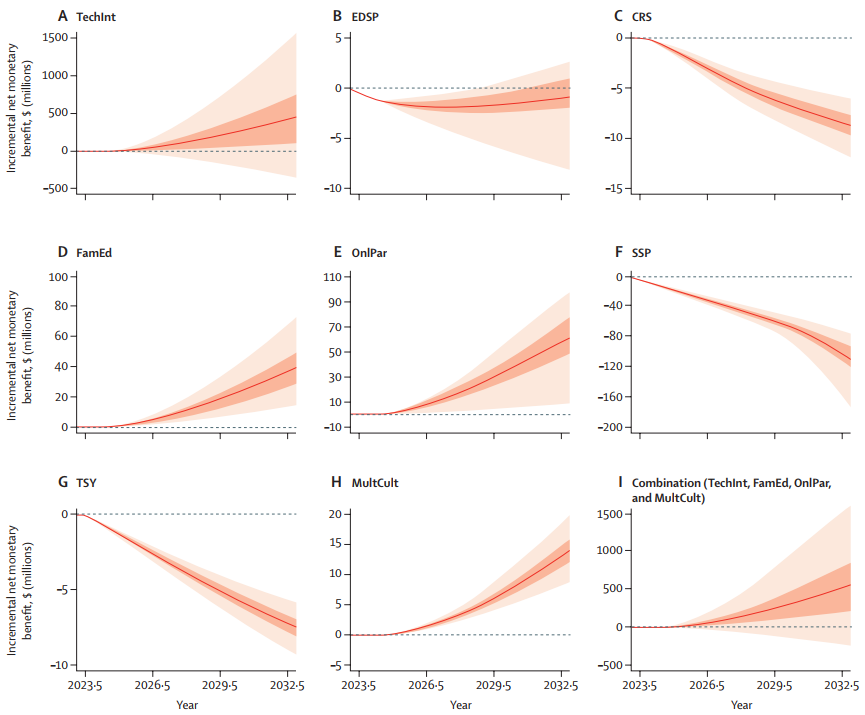
When all cost-effective interventions were combined, the results were even more favourable. The combination led to significant health improvements and cost reductions, particularly from a societal perspective. Synergistic effects were observed, with the combined interventions providing greater benefits than the sum of individual effects. The combination resulted in 5732 incremental QALYs compared to 5717 for the summation of individual interventions. Furthermore, the combination provided an additional AU$1 million in cost savings compared to the summation of individual interventions.
Advantages of System Dynamics Modelling
System dynamics modelling offers several unique advantages over conventional economic modelling. First, it can identify synergistic effects between interventions, revealing greater systemic benefits. Second, it uncovers unintended consequences, such as increased service demand due to effective interventions. Third, it allows for scenario testing of service capacity growth, providing a more realistic assessment of resource needs. Finally, it offers a user-friendly interface for stakeholders to interact with the model, enhancing transparency and accountability in decision-making.
Conclusion
Youth mental health interventions, supported by system dynamics modelling, offer a promising approach to improving mental health outcomes. The findings support the implementation of technology-enabled integrated care, family education, online parenting programmes, and multicultural-informed care. System dynamics modelling has proven useful for resource allocation in complex systems like mental health. It should become a regular tool for planners, aiming to make regional systems more efficient and equitable. By implementing effective strategies and using advanced modelling techniques, we can enhance mental health systems significantly.
