
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has the potential to completely transform the healthcare industry on a global scale. It offers promising solutions to handle the increasing demands and reduce costs, particularly when resources are limited. Nevertheless, the implementation of AI in healthcare, especially in low- and middle-income countries, presents certain obstacles. The varying results and insufficient local execution highlight the intricacy of this matter. In order to fully leverage the power of enhancing healthcare capacity with AI in improving healthcare delivery, it is essential to take a holistic approach.
The Healthcare Capacity Crisis
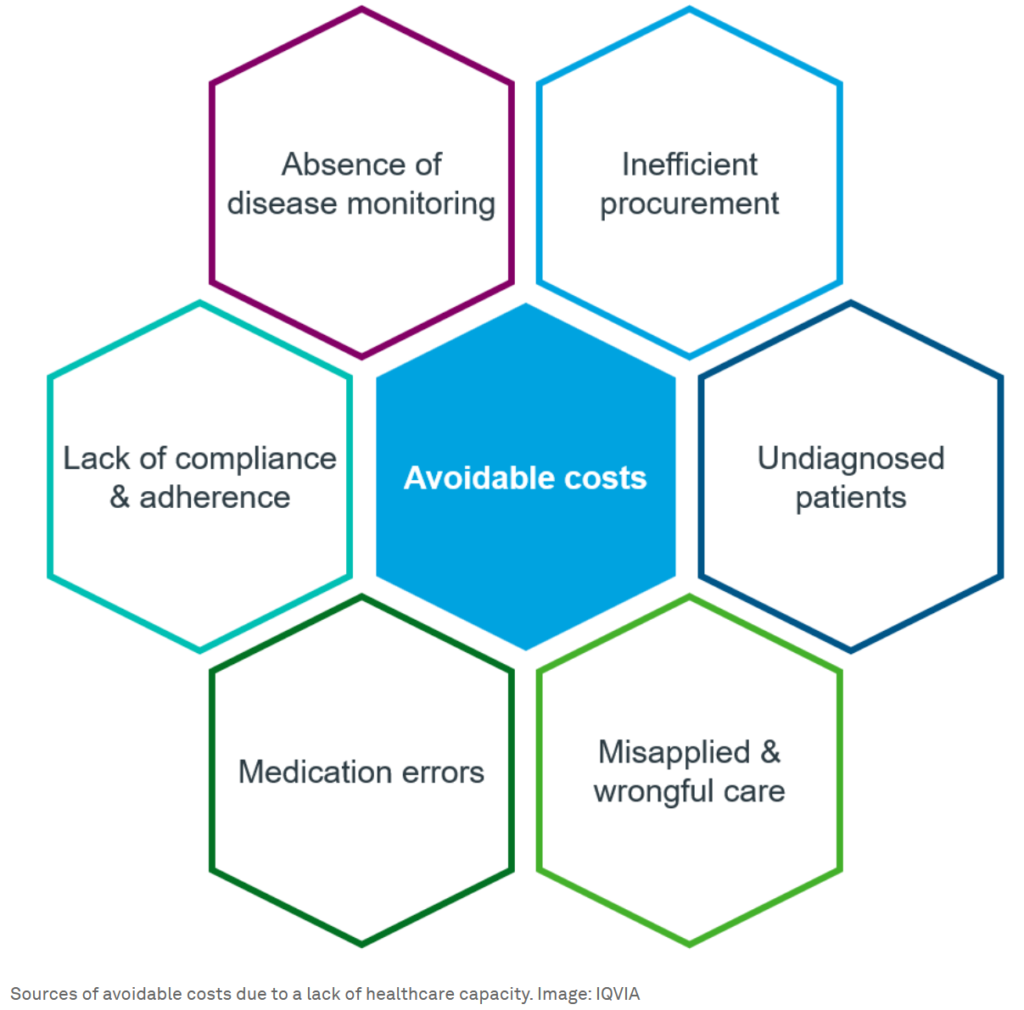
Healthcare systems globally are strained, with healthcare professionals in the United States and Europe facing burnout and resignation rates skyrocketing in early 2023. The situation is particularly dire in low- and middle-income countries, where resources to train and retain medical professionals are scarce. These capacity problems had led to a staggering $850 billion in avoidable healthcare waste in the United States alone. AI offers a powerful solution to these capacity issues, promising to streamline processes, reduce errors, and enhance patient care.
AI’s Transformative Potential in Healthcare
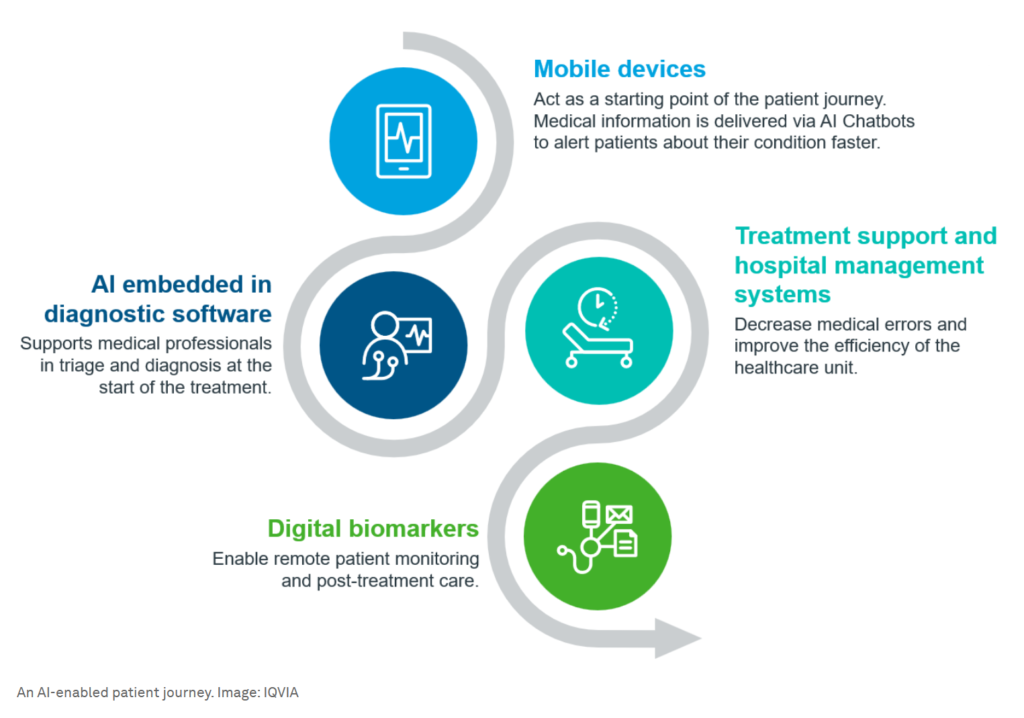
AI has already made significant strides in healthcare, particularly in digital pathology by accurately identifying lesions on medical images. It has also been valuable in research and development, particularly in modelling protein folds. However, its full potential is yet to be realised. With strategic investment and regulation, AI could dramatically increase care capacity in the medium term, supporting healthcare professionals and reducing medical errors. From diagnostics to treatment and remote patient monitoring, AI could support and enhance the level of care provided by healthcare professionals and should not be mistaken for replacing doctors in the near future. AI could be used in a future patient journey from accessing a health app to diagnostics, treatment, and remote patient monitoring. Automatic monitoring and triage have shown promise for treatment and post-discharge care.
Overcoming AI Adoption Challenges in Healthcare
Despite its potential, AI adoption in healthcare faces several hurdles, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. These include unreliable results, poor usability, and a lack of understanding of local context. To drive systematic adoption, a combination of trust, privacy, regulatory guardrails, and education is needed.
Regulating AI in Healthcare:
The pace and scope of AI development are much faster than regulators have had to address. To prevent misuse, there needs to be a consensus on guiding principles for building safe AI tools – a Hippocratic Oath for AI. Current initiatives like the EU AI Act, the US Executive Order on Safe, Trustworthy AI, and the world’s first AI Safety Summit are steps in the right direction, but more needs to be done, especially in low- and middle-income countries.
A Path Forward: Enhancing Healthcare Capacity with AI
We cannot overstate the urgent need for guiding principles for AI in healthcare. These principles must foster innovation while ensuring safety, transparency, and accountability. We can start to unlock AI’s significant potential in healthcare by connecting new technologies to low- and middle-income countries. We should also create secure environments for AI tool testing and enforce robust data protection. Strong data protection measures are crucial. We need to establish guiding principles and promote accountability. Using open-source software is beneficial. We should also strive for accessible and inclusive testing environments.
Conclusion
The indisputable capacity of AI to bring about significant changes in the healthcare sector is undeniable. By adopting an appropriate strategy, we may surmount existing obstacles and utilise the potential of artificial intelligence to address the shortfall in healthcare capacity.
