
Introduction
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) is a chronic condition affecting children and adolescents, leading to persistent joint pain and inflammation. JIA affects a significant number of children in Spain. In Catalonia, the prevalence ranges from 39.7 to 44.8 per 100,000 children. In Asturias, it stands at 51.4 per 100,000 children under 16 years. Symptoms vary depending on the type of JIA but commonly include joint pain, swelling, warmth, stiffness, uveitis, rash, fever, and fatigue. JIA can lead to permanent joint damage and long-term disability if not managed effectively. Thus, early identification and appropriate therapy are crucial for optimal healthcare resource utilisation, and patient outcomes.
Measuring Disease Activity and Quality of Life
In a recent study, the Juvenile Arthritis Disease Activity Score (JADAS-71) was used to measure disease activity. According to JADAS-71, 71.4% of children had inactive disease, 11.4% had low disease activity, 9.5% had moderate disease activity, and 7.6% had high disease activity. The mean JADAS-71 scores were 1.4 for oligoarthritis and 1.0 for polyarthritis, indicating low disease activity.
The Childhood Health Assessment Questionnaire (CHAQ) measured functional disability, with a mean score of 0.2, indicating very low disability. The Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory (PedsQL™) assessed health-related quality of life (HRQoL), with high scores reported by both children and parents.
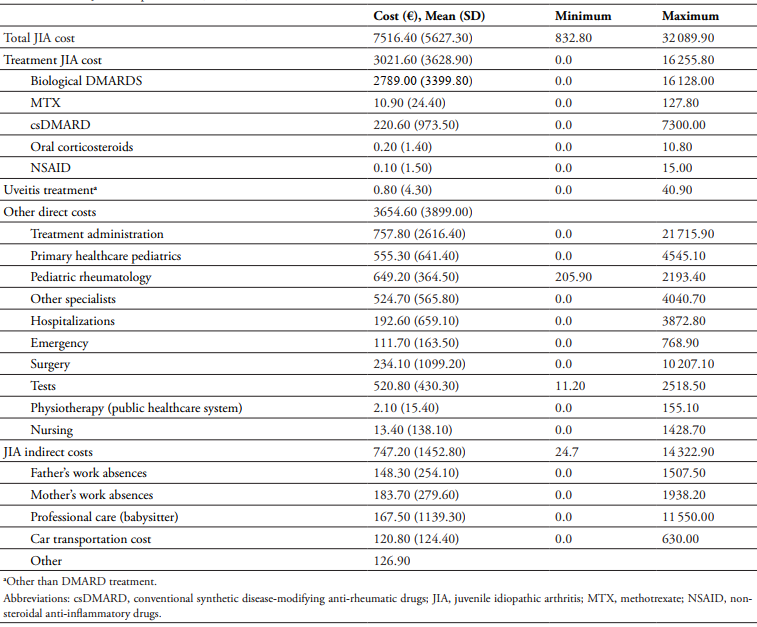
Direct Costs of JIA
Children with moderate-to-severe JIA in Spain incur significant healthcare costs, with an estimated total annual cost per child of €7516.40. The direct costs of JIA are substantial, primarily driven by medication expenses. Biologic therapies, particularly anti-TNF drugs, are significantly more expensive than conventional treatments. For instance, biologic therapies can cost ten times more than conventional synthetic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (csDMARDs). In this study, 94.4% of children received some form of JIA treatment, with 96% on one biologic DMARD (bDMARD).
Medical visits also contribute to direct costs. Children frequently visited paediatric rheumatologists, general paediatricians, ophthalmologists, and other specialists. During the study period, 15 patients required surgical treatment, with six surgeries related to JIA. Laboratory tests were another significant expense, with an average of 13.1 tests per child over 24 months. Comparisons with studies from other European countries reveal varying cost structures, with medication costs often representing a significant proportion of total healthcare expenditures.
Indirect Costs and Family Impact
JIA also imposes indirect costs on families. These indirect costs include factors such as parental work absences, caregiving responsibilities, transportation expenses, and out-of-pocket costs for supportive care. Work absences and loss of productivity due to a child’s illness are common. 64% of fathers and 68.9% of mothers missed work, with fathers missing an average of 6.9 days and mothers 8.0 days. Transportation costs are another burden, with 83.2% of parents using their own vehicles for medical visits.
Hospitalisations further strain families. Of the 14 children hospitalised, 23.4% of parents needed accommodation, averaging 3.7 nights. Moreover, 10.3% of children required assistance and mobility devices, 12.3% needed private physiotherapy, and 34.3% required private psychological support. Sixteen parents also sought private psychological support. The study found that the indirect costs per family reached €747.20, reflecting the broader financial impact beyond medical treatments.
Conclusion
JIA places a significant economic burden on affected families and the healthcare system in Spain. Direct costs are driven by expensive biologic therapies and frequent medical visits. Indirect costs include work absences, transportation, and additional care expenses. Despite these challenges, most children in the study had low disease activity and HRQoL, highlighting the importance of effective treatment and support. While biologic treatments have shown efficacy in managing JIA, the long-term cost-effectiveness and overall economic impact of these therapies remain areas of ongoing research. By understanding the financial burdens associated with JIA, stakeholders can develop targeted strategies to optimise patient care, improve outcomes, and alleviate the economic challenges faced by families affected by this chronic condition.
