
Introduction
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a significant public health concern in the United States. Nearly one in two people aged 15 to 59 years are infected with at least one type of HPV. HPV is linked to almost all cervical cancers, 90% of anal cancers, and a significant percentage of other cancers. Vaccination against HPV is the primary prevention strategy, with the potential to prevent over 90% of these cancers. However, vaccination rates remain below the Healthy People 2030 goal of 80% completion among adolescents aged 13 to 15 years.
HPV Vaccination Rates and Recommendations
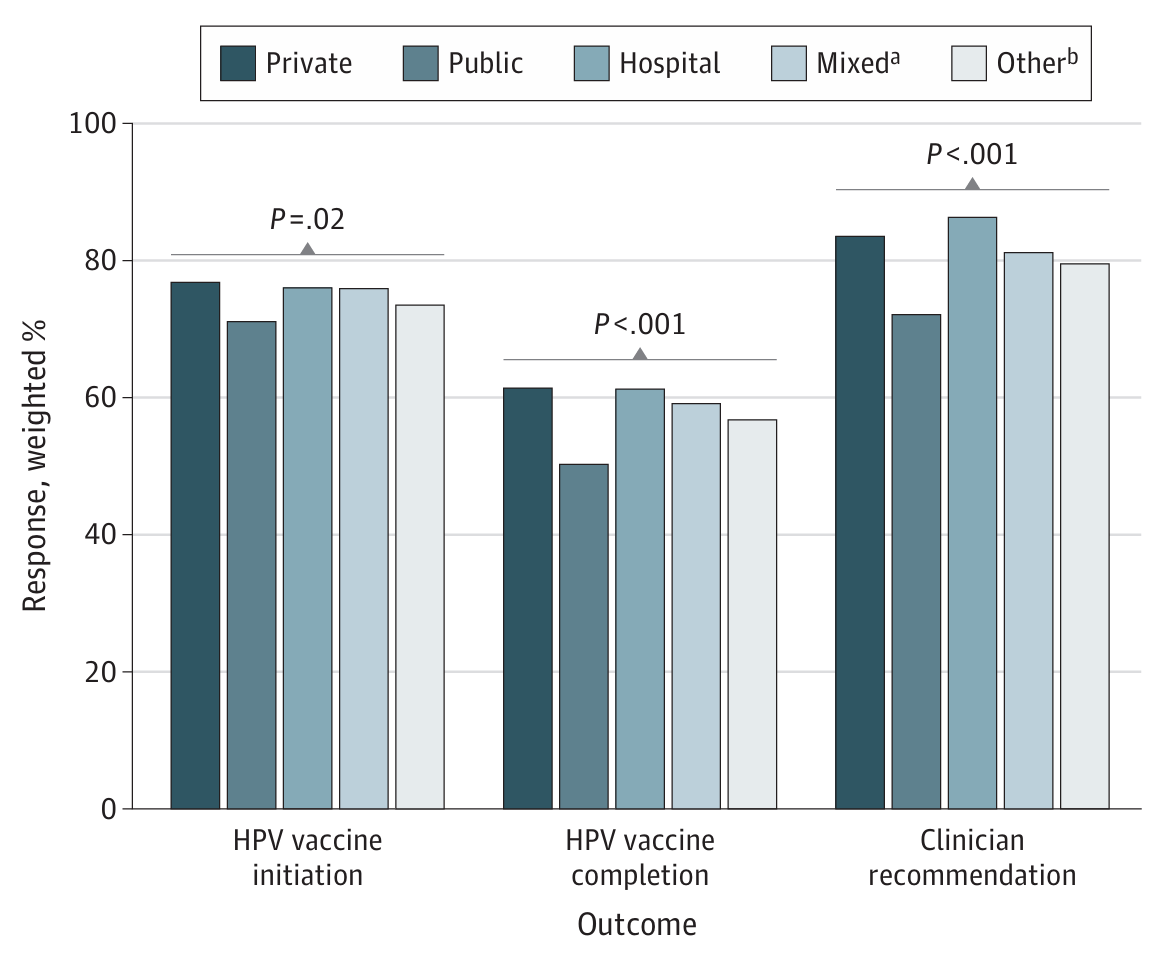
Despite the proven efficacy and safety of the HPV vaccine, immunisation rates are lower than other routine vaccinations. As of 2021, 76.9% of adolescents aged 13 to 17 years received at least one dose, but only 61.7% completed the series. Clinician recommendation is the strongest factor in HPV vaccine uptake. However, differences exist in vaccination rates and clinician recommendations based on healthcare settings.
The Role of Healthcare Facilities
HPV vaccines are administered at various healthcare facilities, including public health centres, hospitals, and private facilities. Public health centres serve racially and ethnically diverse populations, often with a higher prevalence of minority patients. These centres play a crucial role in addressing healthcare disparities. However, adolescents receiving vaccinations at public facilities have lower odds of initiating and completing the HPV vaccine series compared to those at private facilities. This difference may be partly explained by the geographic distribution of facilities, with private facilities more common in urban areas and public facilities in rural areas.
Geographic and Socioeconomic Factors
Rural areas often face a shortage of healthcare practitioners, who may prioritise urgent care over preventive services. Moreover, rural residents may encounter specific challenges, such as travel distance and transportation problems, which hinder access to preventive healthcare. Adolescents in rural areas have lower HPV vaccination rates compared to urban counterparts. Efforts to ensure rural healthcare practitioners have the time, resources, and training to educate parents about HPV vaccination could increase uptake.
Insurance and Healthcare Coverage
Another factor influencing HPV vaccination rates is the type of healthcare coverage. Parents of adolescents with private insurance may seek care in private clinics, while those with public insurance or no insurance may rely on public facilities. Vaccination coverage is significantly lower among uninsured adolescents compared to those with private insurance. The Vaccines for Children (VFC) program offers free vaccines to eligible adolescents, but lack of awareness and misconceptions about the program can be barriers. Increasing parental awareness and screening patients for vaccine eligibility could improve vaccination coverage among uninsured adolescents.
Conclusion
This study highlights the disparities in HPV vaccination rates based on healthcare facility type. Adolescents receiving vaccinations at private facilities have higher rates of vaccine initiation and completion compared to those at public facilities. Efforts to reduce these disparities should focus on increasing clinician participation in promoting HPV vaccination, especially in public facilities. Enhancing awareness about HPV, its associated cancer risks, and the benefits of vaccination is crucial. By addressing these disparities, we can improve HPV vaccination rates and protect more adolescents from HPV-related cancers
