Introduction to Anticoagulation Therapy:
There is a continuous process of development taking place within the healthcare sector, as new treatments and pharmaceuticals are introduced on a regular basis. Anticoagulation therapy is one area that receives a great amount of attention. Direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) and vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) are two kinds of anticoagulants that are commonly utilised. The Swiss Federal Office of Public Health (FOPH) has compiled a health technology assessment (HTA) report, which serves as the basis for this article’s significant review of these two areas.
Acquiring Knowledge of Anticoagulants:
Medications known as anticoagulants are used to prevent blood clots from forming. Patients who have nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (NVAF) are typically the ones who receive these medicines. The DOACs, which include apixaban, dabigatran, edoxaban, and rivaroxaban, and the VKAs, which include phenprocoumon, acenocoumarol, and warfarin, are the two primary categories of anticoagulants.
Direct Oral Anticoagulants Efficacy:
The HTA report evaluated both DOACs and VKAs for their effectiveness and safety risks. The report found that DOACs compared to warfarin had a slightly lower risk of death from any cause. They also had a lower risk of serious or life-threatening bleeding and cerebral bleeding. On the other hand, the effect of DOACs on bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract varied from one DOAC to another.
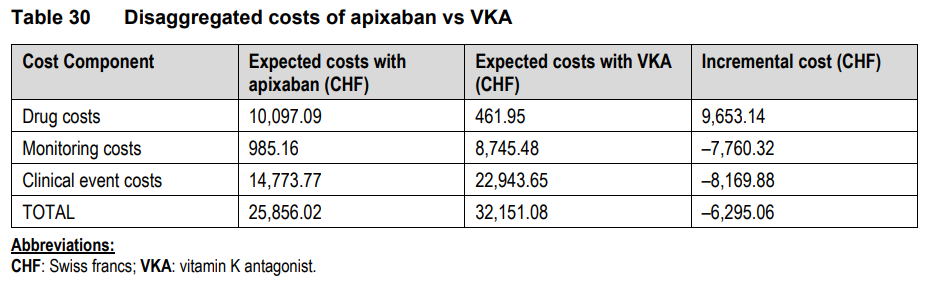
Cost-Effectiveness:
In addition to this, the paper compared the cost-effectiveness of DOACs to that of VKA devices. It was discovered that DOACs, despite the fact that they increased the costs of drugs, were cost-saving in terms of the expenses of monitoring and clinical events. The primary factors that contributed to this cost-effectiveness were the relatively minor reductions in mortality rates from all causes and the substantial costs involved with monitoring VKA.

Considerations for Healthcare:
There are a number of social, ethical, and organisational concerns that are linked with the use of DOAC, as outlined in the HTA report. Despite DOACs having a better benefit-harm profile than VKAs, they also have fewer monitoring requirements. This can impact healthcare systems and patient adherence to treatment plans.
Concluding remarks:
The HTA report findings revealed that DOACs outperformed VKAs in terms of outcomes and cost-effectiveness. However, the report also highlighted an expected rise in payer costs for oral anticoagulation in atrial fibrillation. This increase is due to the growing use of DOACs and predicted demographic changes.
