
Introduction
Skin cancer remains a significant health concern in worldwide, with nearly 5 million individuals treated annually in the United States alone. The incidence of skin cancer, particularly melanoma, is on the rise. Researchers recently developed a national study examining the effectiveness of digital interventions in reducing skin cancer risk among young adults. Their primary focus was on how these digital interventions influence sun protection behaviours and UV radiation (UVR) exposure among the youth.
Skin Cancer Risk Factors
Skin cancer, including melanoma and keratinocyte carcinomas, poses severe health risks. These cancers can be deadly, cause significant tissue damage, and lead to disfigurement. Risk factors include a personal or family history of skin cancer, fair skin, numerous moles, and excessive UVR exposure from the sun or tanning devices. Despite being largely preventable, skin cancer continues to affect millions.
The Role of Digital Interventions
Digital interventions have shown promise in modifying health behaviours. Almost all young adults in the 18-25 age group use the internet, with 96% owning a smartphone. Furthermore, around 70% of young adults are using social media platforms like Facebook and Instagram. These platforms provide an efficient means for recruitment and dissemination of behavioural interventions.
Study Design and Methods
The study utilised a hybrid type II effectiveness-implementation trial to evaluate the impact of a web-based intervention. Participants were recruited online and included 964 young adults at moderate to high risk of developing skin cancer. The intervention was grounded in the Integrative Model of Behavioral Prediction (IM) and included interactive features, incentives, goal-oriented components, and ongoing email and instant message updates. The study compared three groups: the enhanced intervention, the basic intervention, and an electronic pamphlet (e-pamphlet) control group.
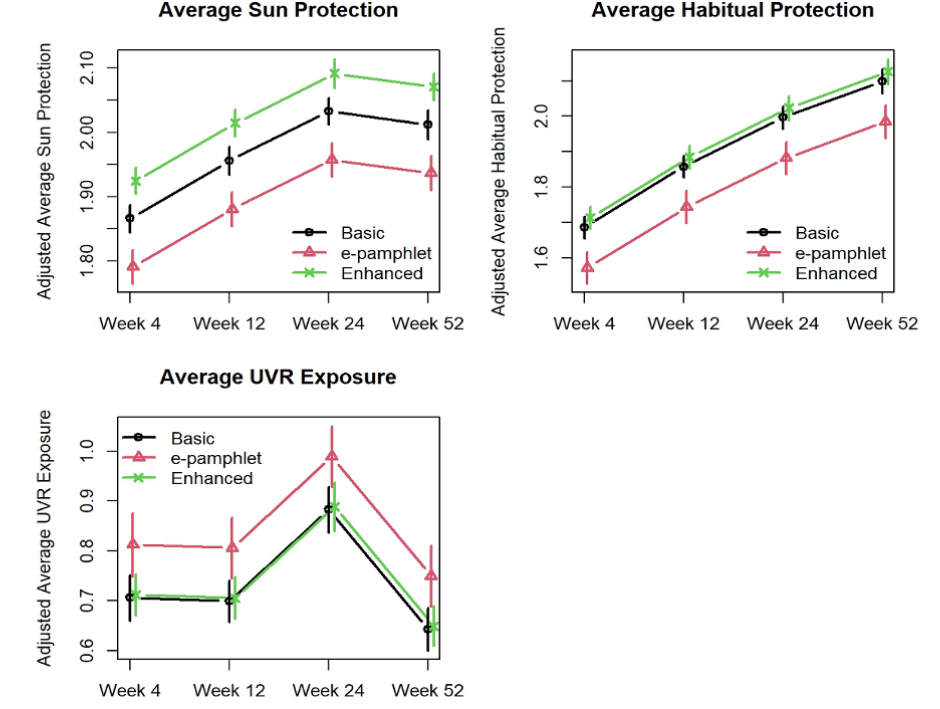
Results and Discussion
The study found that both the basic and enhanced digital interventions significantly improved sun protection behaviours and reduced UVR exposure compared to the e-pamphlet group. The enhanced intervention showed a greater impact on overall sun protection, although it did not significantly outperform the basic intervention in other areas. Sunburns were reduced, and skin self-examinations increased, indicating positive behavioural changes.
Conclusion
This national study highlights the potential of digital interventions in reducing skin cancer risk among young adults. The findings suggest that even simple digital tools can lead to behavioural changes, although more engaging and cost-effective strategies may enhance long-term impact. Future research should focus on refining these interventions and exploring their scalability for broader public health benefits.
