
Introduction
Diabetes mellitus (DM), a chronic metabolic disorder marked by hyperglycaemia, poses significant global health challenges. The International Diabetes Federation (IDF) reported 537 million people living with diabetes in 2021, a number projected to exceed 600 million by 2030. In the Middle East and North Africa (MENA), 73 million individuals were affected in 2021, with an expected 87% increase by 2045. Type 2 diabetes (DM-2) accounts for nearly 90% of these cases. Early detection is vital to manage diabetes effectively and prevent complications. Yet, the IDF noted that around 50% of diabetes cases were undiagnosed in 2021.
Traditional diagnostic methods, such as fasting plasma glucose (FPG), oral glucose tolerance tests (OGTT), random plasma glucose (RPG), and haemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), have limitations. For instance, FPG misses 30% of diabetes cases and requires fasting, which can be inconvenient. OGTT is labour-intensive and often misclassifies 12% of individuals. RPG, though convenient, shows high variability. HbA1c, while a gold standard, can be costly and affected by haemoglobin variants. Given these challenges, novel, accessible, and accurate diagnostic methods are needed, especially in middle- and low-income countries.
The Promise of Retinal Imaging
Retinal imaging has emerged as a promising tool for diabetes diagnosis. Recent studies have explored its use in detecting cardiovascular diseases and diabetic retinopathy (DR). Building on this, Al-Absi et al. presented the development and evaluation of DiaNet v2, a deep learning-based model focused on diagnosing diabetes mellitus (DM) through retinal images. The primary objective was to enhance the accuracy and accessibility of diabetes diagnosis, particularly in regions with high prevalence, such as the MENA.
DiaNet v2: Enhanced Accuracy and Validation
DiaNet v2 utilises over 5,000 retinal images, achieving over 92% accuracy in identifying diabetes. This improvement highlights the importance of large datasets and refined model architecture. DiaNet v2 was validated using Hamad Medical Corporation’s (HMC) dataset, confirming retinal images as a robust diagnostic source. The Qatar Biobank (QBB) dataset lacked ophthalmologist annotations, which we supplemented with HMC’s curated data. This enhanced dataset included various pathologies, such as vitreous haemorrhage and microaneurysms, aiding in accurate diabetes detection. Advanced deep learning techniques were applied to analyse these retinal images effectively.
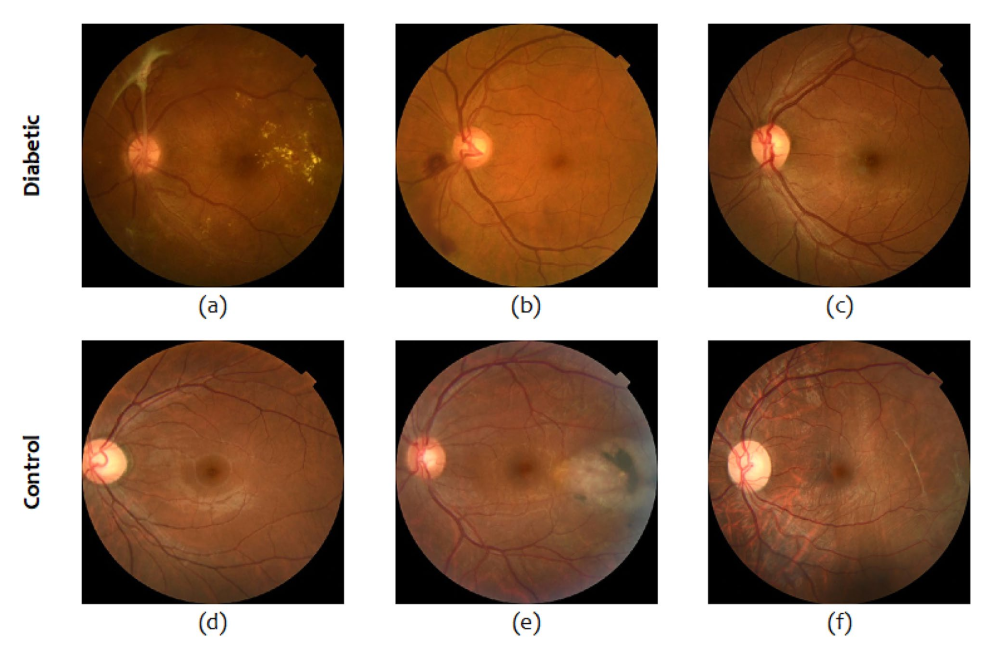
microaneurysm (b), mild NPDR (c), glaucoma (d), laser caused trauma (e) and retinal detachment (f).
Significance and Implications
Current diagnostic methods for diabetes, including FPG, OGTT, RPG, and HbA1c, have notable limitations such as potential misclassifications and patient discomfort. The DiaNet v2 model presents a non-invasive, accurate, and accessible method for early diabetes detection and treatment planning.
The DiaNet v2 model demonstrated impressive performance in distinguishing diabetic patients from the control group, achieving an overall accuracy of over 92%, with a sensitivity of 93% and a specificity of 91%. This approach has the potential to revolutionise diabetes diagnosis, especially in regions where traditional diagnostic methods may be less effective or accessible.
Conclusion
This study, focused on a predominantly Middle Eastern population, demonstrates the potential of retinal imaging for early diabetes detection. The DiaNet v2 model signifies a substantial advancement in utilising retinal imaging and deep learning for diabetes diagnosis. Its high accuracy and non-invasive nature position it as a promising tool to enhance diabetes detection and management, particularly in areas where conventional methods fall short. However, the findings may not generalise to other populations. Future research should compare AI model performance with human expertise in diabetes screening. This will involve ophthalmologists of varying experience levels to benchmark AI models against human intelligence.
