
Introduction
Type 2 diabetes impacts over 500 million individuals globally, leading to substantial healthcare costs and mortality rates. While holistic approaches are recommended, focusing on glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) levels remains crucial for long-term outcomes. Studies like the UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) and Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes (ACCORD) trial highlight the significance of HbA1c control in reducing diabetes-related complications and enhancing quality of life. The cost-effectiveness of IDegAsp, which is a fixed-ratio combination of two types of insulin; insulin degludec and insulin aspart, in diabetes management has been a topic of significant interest, especially in light of recent findings from the ARISE study. This study, conducted across six countries, provides valuable insights into the economic and clinical benefits of IDegAsp compared to prior therapies.
Understanding the ARISE Study
The ARISE study was a real-world, single-arm investigation conducted in Australia, India, Malaysia, the Philippines, Saudi Arabia, and South Africa. It aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of IDegAsp in managing type 2 diabetes. The study’s primary endpoints were the proportions of patients achieving HbA1c targets of less than 7.0% and individualised treatment targets. In Australia and India, contrasting healthcare systems, the prevalence of type 2 diabetes underscores the need for improved management strategies.
The Role of Insulin Therapy
Given the progressive nature of type 2 diabetes, insulin therapy often becomes necessary. However, patient aversion to injectables can result in therapeutic inertia, hindering glycemic control. The ARISE study demonstrated that transitioning to IDegAsp improved HbA1c levels and reduced hypoglycemia rates, showing promise in enhancing outcomes for patients.
Key Findings from the ARISE Study
- Cost of Treatment
In Australia, the annual treatment cost per patient with IDegAsp was AUD 5314, compared to AUD 2428 for prior therapies. This increase of AUD 2886 was primarily due to higher treatment and needle costs, partially offset by fewer self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) tests. In India, the annual treatment cost per patient with IDegAsp was INR 55,505, compared to INR 35,896 for prior therapies, resulting in an increase of INR 19,609.
- Number of Patients Needed to Treat (NNT)
The NNT to bring one patient to target was significantly lower with IDegAsp. In Australia, 6.9 and 4.7 patients needed to be treated to achieve HbA1c targets of less than 7.0% and individualised treatment targets, respectively, compared to 14.1 and 37.0 patients with prior therapies. In India, 11.2 and 10.5 patients needed to be treated to achieve the same targets with IDegAsp, compared to 23.3 and 31.3 patients with prior therapies.
- Cost of Control
The cost of achieving HbA1c targets was generally lower with IDegAsp. In Australia, the cost to control HbA1c levels below 7.0% was AUD 36,647 with IDegAsp, compared to AUD 34,198 with prior therapies, an increase of AUD 2449. However, for individualized treatment targets, the cost was AUD 25,065 with IDegAsp, significantly lower than the AUD 89,929 with prior therapies, resulting in a decrease of AUD 64,863.
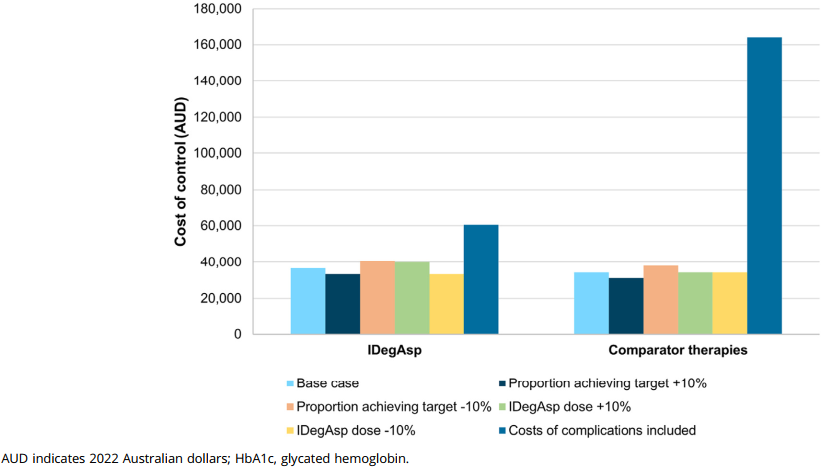
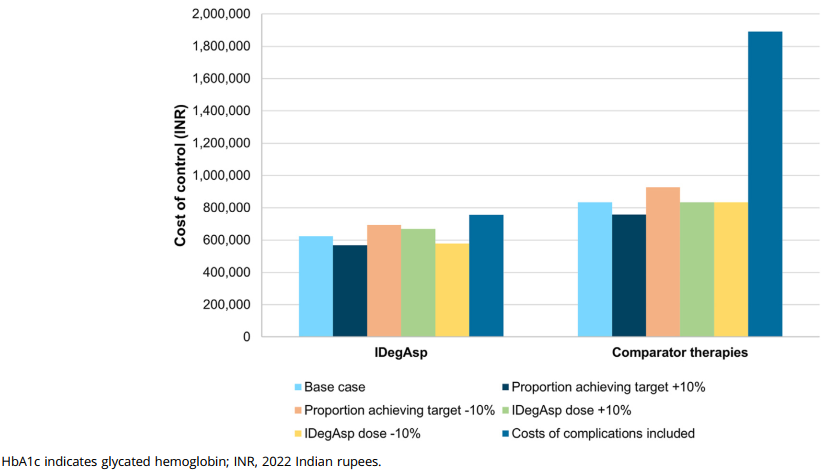
In India, the cost to control HbA1c levels below 7.0% was INR 623,648 with IDegAsp, compared to INR 834,790 with prior therapies, a reduction of INR 211,142. For individualized treatment targets, the cost was INR 584,260 with IDegAsp, much lower than the INR 1,121,749 with prior therapies, leading to a decrease of INR 537,490.
Short-term Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Analysing the short-term cost-effectiveness of IDegAsp in Australia and India revealed promising results. While initial treatment costs increased with IDegAsp, the number of patients needed to treat to achieve glycemic targets was significantly lower compared to prior therapies in both countries. IDegAsp showed cost advantages in achieving predefined individualised treatment targets, indicating its potential for improving outcomes efficiently.
Implications for Healthcare Systems
The findings from the ARISE study have significant implications for healthcare systems in both Australia and India. Despite the higher initial costs associated with IDegAsp, the lower NNT and cost of control for individualised treatment targets highlight its potential for cost-effectiveness in the long term. This is particularly relevant for healthcare payers focused on immediate clinical and cost outcomes.
Conclusion
In both countries, IDegAsp demonstrated improved cost of control for glycemic targets, particularly for individualised treatment goals. Sensitivity analyses confirmed the robustness of these findings, emphasising the potential benefits of IDegAsp in managing type 2 diabetes effectively. IDegAsp emerges as a cost-effective treatment option for achieving short-term glycemic targets in Australia and India, showcasing its potential to enhance diabetes care outcomes. The study’s simplicity and transparency offer valuable insights, complementing long-term analyses essential for comprehensive evaluations. The study underscores the importance of tailored therapies in improving patient well-being and reducing the burden of type 2 diabetes. Future research could explore additional parameters such as body weight and hypoglycemia impact to provide a more holistic understanding of IDegAsp’s benefits.
