
Introduction
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) testing is a critical step in achieving the United Nations’ 90-90-90 goals, which aim to end acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) by 2030. The World Health Organization (WHO) and UNAIDS have emphasised the importance of accessible HIV testing services (HTS). In Nigeria, a country with one of the highest HIV infection rates globally, community pharmacies have been identified as a key player in expanding these services. Researchers looked into the implementation strategies and outcomes of HIV testing in community pharmacies in Oyo State, Nigeria.
Community Pharmacists: The Frontline Healthcare Providers
Community pharmacies are uniquely positioned to provide healthcare services due to their accessibility and the trust they have built within their communities. These pharmacies offer a range of services, including health promotion, point-of-care testing, and medication management. In Nigeria, community pharmacists have demonstrated their ability to deliver primary healthcare services, including HIV testing. Community pharmacists underwent training to equip them with the necessary skills to conduct HIV tests and provide pre- and post-test counselling. Continuous supervision and support were provided to ensure adherence to the testing protocols. Ensuring the availability of testing materials and resources was crucial for the smooth operation of the services.
Implementation Strategies for HIV Testing Services
Effective implementation strategies are crucial for the success of any healthcare intervention. These strategies enhance the adoption, implementation, and sustainability of services. In this context, implementation outcomes such as penetration, adoption, acceptability, feasibility, fidelity, and appropriateness are essential. Measuring penetration evaluates the integration level of a service within a community. When stakeholders decide to use an innovation for the first time, we call it adoption. Acceptability is a measure of stakeholders’ reception of the service. Feasibility examines the service’s practicality. Fidelity ensures the service delivery aligns with the original intention. Appropriateness evaluates the relevance of the service for the community.
Measuring Implementation Outcomes
In Oyo State, Nigeria, a study was conducted to measure the implementation outcomes of HIV testing services in community pharmacies. The study observed a high participation rate, with 90% of trained pharmacists providing HIV testing services. This high penetration rate is similar to other studies conducted globally. Factors like adequate training, pharmacist commitment, and supportive supervision influenced the service’s adoption. Clients showed high acceptability, with 77% willing to join the HIV screening. The implementation affirmed feasibility, as it encountered no major challenges. The measure of fidelity was the pharmacists’ ability to deliver the service as intended, although not all strictly adhered to the protocol.
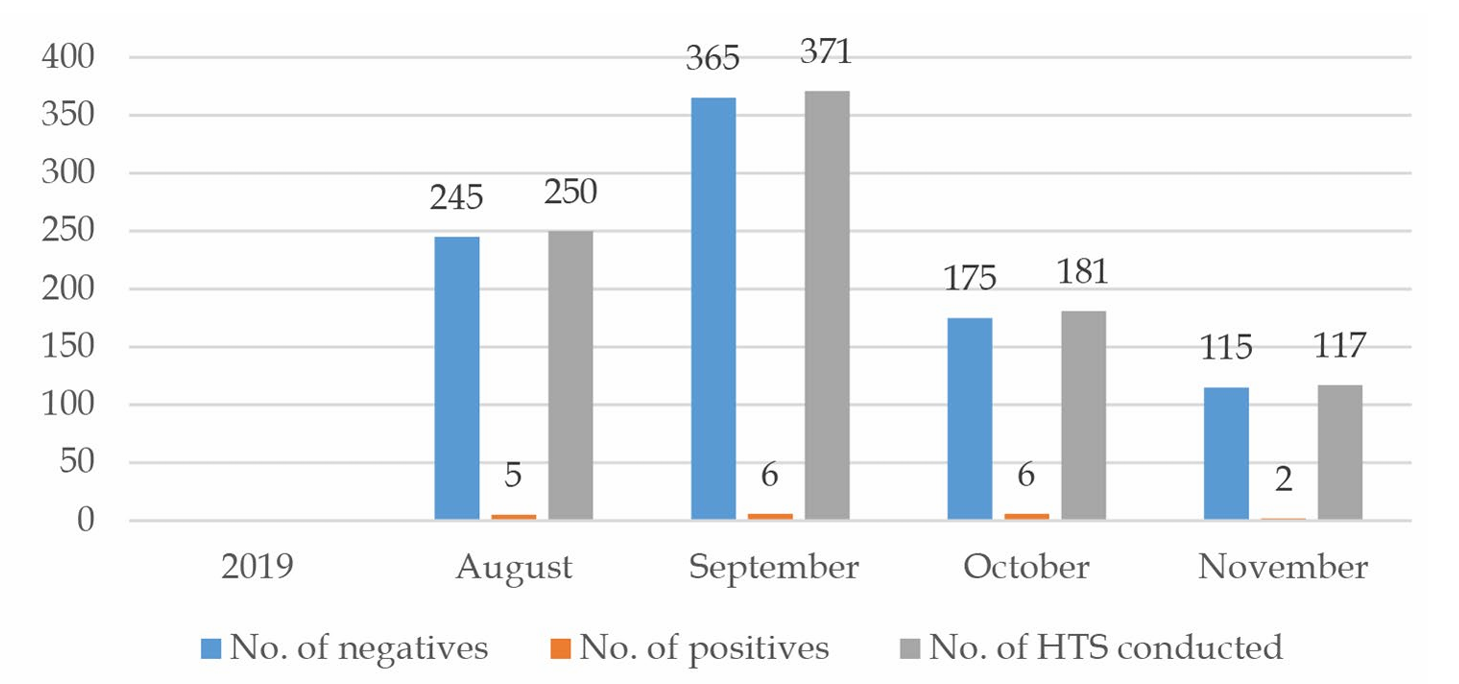
The Impact of Community Pharmacists on HIV Testing
Community pharmacists play a crucial role in providing accessible and confidential HIV testing services. Therefore, their involvement reduces the stigma associated with HIV testing and improves healthcare accessibility. The study found that pharmacists felt fulfilled and satisfied with offering HIV testing services. Clients appreciated the convenience and confidentiality of pharmacy-based testing. Previous studies confirm the ideal position of community pharmacists for providing HIV testing and other primary healthcare services.
Conclusion
Community pharmacies in Nigeria have shown great potential in delivering HIV testing services. The high penetration and adoption rates indicate that pharmacists are willing and capable of providing these services. The study’s findings highlight the importance of effective implementation strategies and support the integration of HIV testing into community pharmacy practice. However, challenges such as resource availability and pharmacist remuneration need to be addressed to ensure the sustainability of the service. Policymakers should consider including HIV testing in the community pharmacy curriculum and providing the necessary support to pharmacists. By leveraging the accessibility and trust of community pharmacies, Nigeria can make significant strides towards achieving the UN’s goal of ending AIDS by 2030.
